Artery of Percheron
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Magdi Mahsoub had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Magdi Mahsoub's current disclosures- Percheron artery
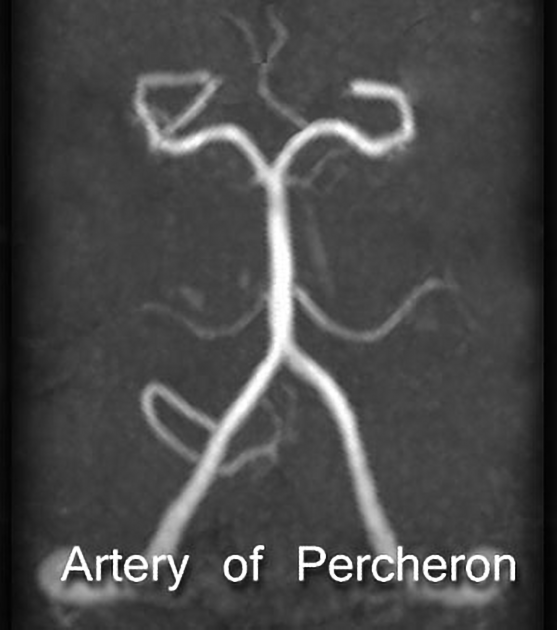
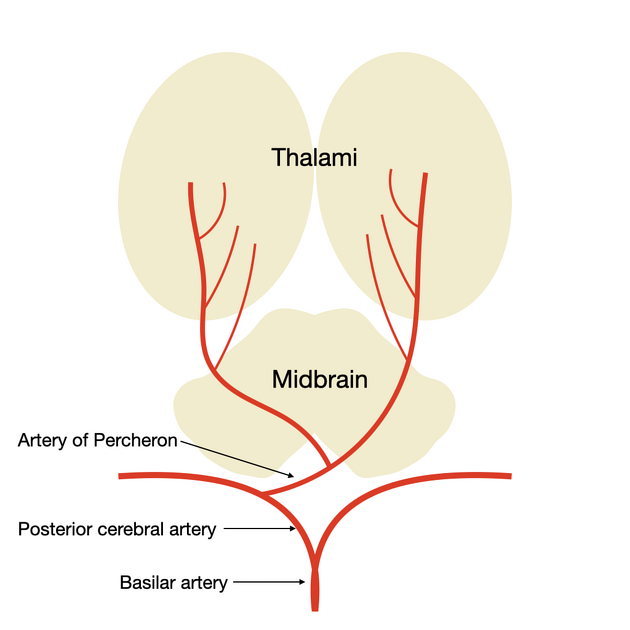
The artery of Percheron is a variant of the posterior cerebral circulation characterized by a solitary arterial trunk that supplies blood to the paramedian thalami and the rostral midbrain bilaterally. From the original classification of arterial patterns at the origin of the paramedian arteries for the thalamus 1, this variant is described as type II. Type I refers to the standard bilateral independent vascularization from the proximal segment of both posterior cerebral arteries, while type III regards the existence of a communicating artery between these two independent origins, with either thalamus receiving bilateral arterial supply.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The artery of Percheron is estimated to occur in 4-12% of the population 2,6-8. The term is used to refer to a solitary arterial trunk that branches from one of the proximal segments of either posterior cerebral artery (PCA). It supplies blood to the paramedian thalami and, most often, the rostral midbrain bilaterally 4. Occasionally it supplies the anterior thalamus, particularly when the thalamotuberal (or polar) arteries are absent (30-60% of cases) 1,3.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
History and etymology
The artery is named after the French neurologist Gérard Percheron, who described it in 1973 5.
Related pathology
artery of Percheron infarct: bilateral thalamic and mesencephalic infarctions; clinically patients are often obtunded, comatose, or agitated, with associated supranuclear vertical gaze palsy and memory deficits 9
References
- 1. Castaigne P, Lhermitte F, Buge A, Escourolle R, Hauw JJ, Lyon-Caen O. Paramedian thalamic and midbrain infarct: clinical and neuropathological study. (1981) Annals of neurology. 10 (2): 127-48. doi:10.1002/ana.410100204 - Pubmed
- 2. Uz A. Variations in the origin of the thalamoperforating arteries. (2007) Journal of clinical neuroscience : official journal of the Neurosurgical Society of Australasia. 14 (2): 134-7. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2006.01.047 - Pubmed
- 3. Lazzaro NA, Wright B, Castillo M, Fischbein NJ, Glastonbury CM, Hildenbrand PG, Wiggins RH, Quigley EP, Osborn AG. Artery of percheron infarction: imaging patterns and clinical spectrum. (2010) AJNR. American journal of neuroradiology. 31 (7): 1283-9. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2044 - Pubmed
- 4. Matheus MG, Castillo M. Imaging of acute bilateral paramedian thalamic and mesencephalic infarcts. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 24 (10): 2005-8. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 5. Percheron G. The anatomy of the arterial supply of the human thalamus and its use for the interpretation of the thalamic vascular pathology. Z Neurol. 1973; 205: 1–13. Pubmed citation
- 6. Arauz A, Patiño-Rodríguez H, Vargas-González J et al. Clinical Spectrum of Artery of Percheron Infarct: Clinical–Radiological Correlations. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014;23(5):1083-8. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2013.09.011 - Pubmed
- 7. Park S, Bae H, Yoon S, Shim J, Yun I, Choi S. Morphological Characteristics of the Thalamoperforating Arteries. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010;47(1):36. doi:10.3340/jkns.2010.47.1.36 - Pubmed
- 8. Kocaeli H, Yılmazlar S, Kuytu T, Korfalı E. The Artery of Percheron Revisited: A Cadaveric Anatomical Study. Acta Neurochir. 2012;155(3):533-9. doi:10.1007/s00701-012-1548-1 - Pubmed
- 9. Ikramuddin S, Coburn J, Ramezani S, Streib C. Artery of Percheron Infarction: Clinical Presentation and Outcomes. Neurol Clin Pract. 2024;14(2):e200266. doi:10.1212/CPJ.0000000000200266 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Artery of Percheron
- Artery of Percheron territory old infarction
- Primary CNS vasculitis with artery of Percheron and posterior circulation infarctions
- Artery of Percheron territory infarct
- Artery of Percheron infarct
- Artery of Percheron infarction
- Artery of Percheron infarction
- Percheron artery infarct
- Artery of Percheron territory infarct
- Artery of Percheron infarct
- Percheron artery territory infarct
- Artery of Percheron infarction
- Artery of Percheron infarct
- Variations of medial thalamomesencephalic blood supply (illustration)
- Bilateral thalamic infarcts
- Artery of Percheron infarction
- Artery of Percheron infarction
- Percheron artery infarct
- Artery of Percheron infarct
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.