Described below is one approach to systematic assessment and associated pathology of the cardiomediastinal contours on chest x-ray.
Mediastinum
size: widened mediastinum can be seen in aortic dissection, traumatic aortic injury, vascular ectasia, mediastinal lipomatosis (low attenuation)
abnormal contour, e.g. lymphadenopathy, anterior mediastinal mass
abnormal gas pattern, e.g. pneumomediastinum, hiatus hernia
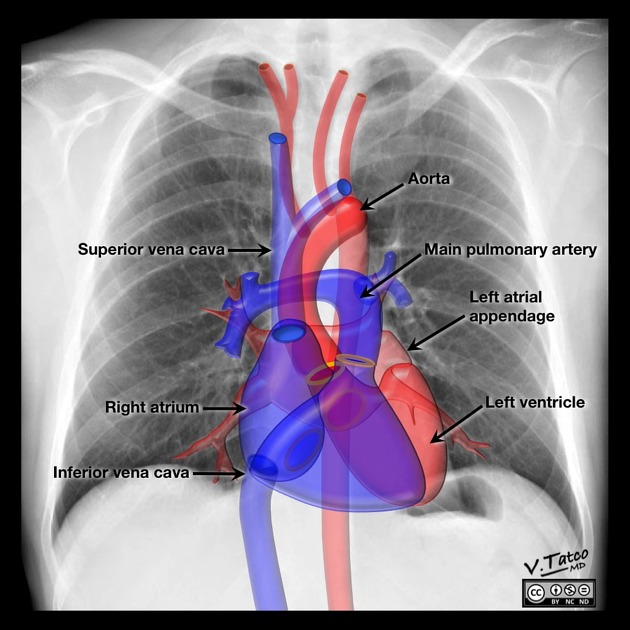
Heart (cardiac silhouette)
assess position (frontal view): normally one-third right of midline and two-thirds left of midline
assess borders and both frontal and lateral for silhouette sign and abnormal appearance
pericardial fat pad (frontal view): normally in the cardiophrenic angle(s)
-
assess overall size
normally the cardiothoracic ratio is <0.50 on a PA chest x-ray obtained in full inspiration
can be enlarged, most commonly in cardiomegaly and pericardial effusion
See also
Systematic chest radiograph assessment:
cardiomediastinal contours





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.