Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Rezaee A, Silverstone L, Walizai T, et al. Bithalamic lesions. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 22 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-36603
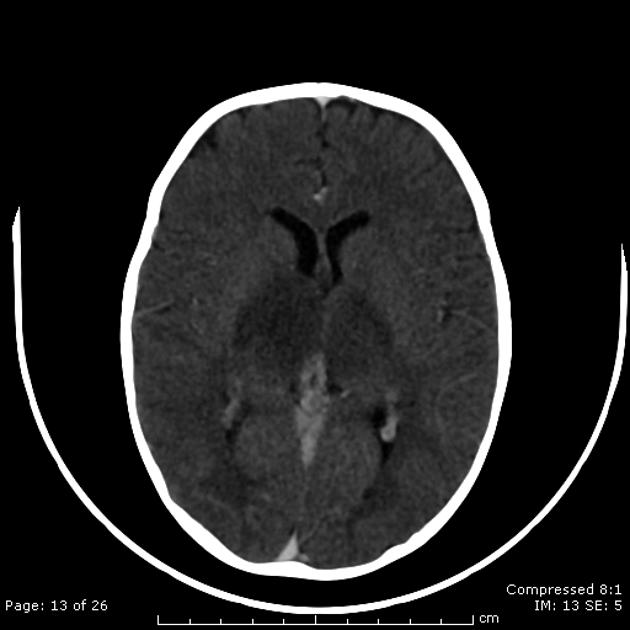
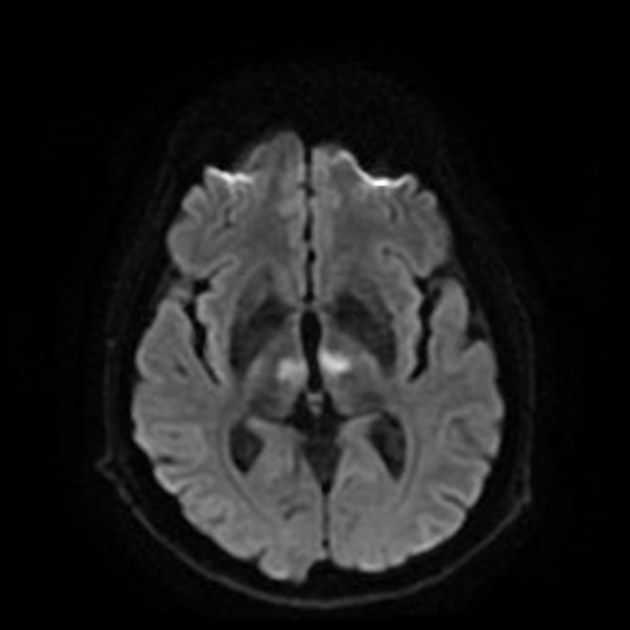
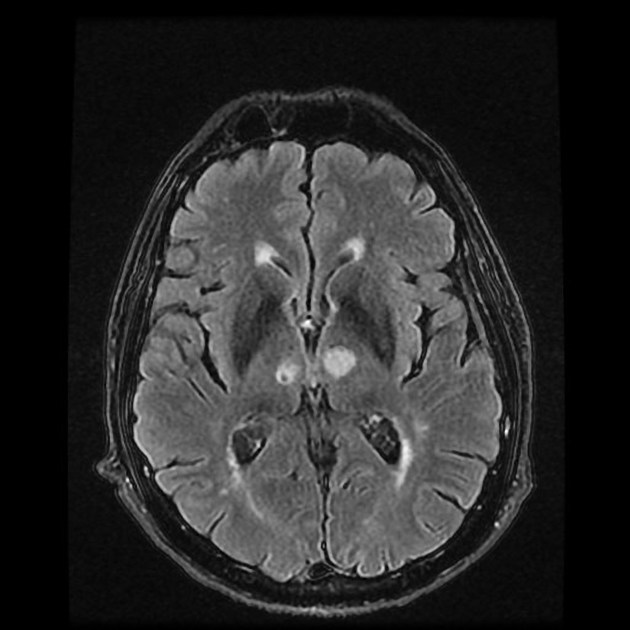
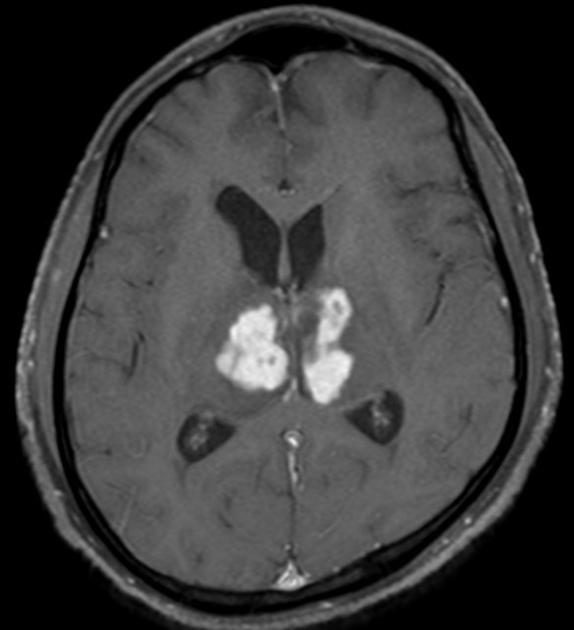
Bilateral thalamic lesions are usually seen in combination with basal ganglia, white matter and sometimes cortical lesions.
The assessment and differential approach can utilize radiological markers such as MR signal characteristics, calcifications, precise position within the thalamus, symmetry/asymmetry, the presence of concurrent extra-thalamic lesions, and the existence of expansion 6. It is essential to consistently seek a correlation between clinical and laboratory findings while further follow-up imaging often provides helpful insights, particularly when the baseline imaging method is equivocal 6.
Bilateral involvement of the thalami has a broad differential diagnosis:
-
vascular
-
infectious
-
autoimmune
-
metabolic/toxic
-
neoplasms
-
congenital disorders
status epilepticus
-
1. Menon G, Nair S, Sudhir J et-al. Bilateral thalamic lesions. Br J Neurosurg. 2010;24 (5): 566-71. doi:10.3109/02688691003777915 - Pubmed citation
-
2. Linn J, Hoffmann LA, Danek A et-al. Differential diagnosis of bilateral thalamic lesions. Rofo. 2007;179 (3): 234-45. doi:10.1055/s-2007-962857 - Pubmed citation
-
3. Khanna PC, Iyer RS, Chaturvedi A et-al. Imaging bithalamic pathology in the pediatric brain: demystifying a diagnostic conundrum. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197 (6): 1449-59. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.6702 - Pubmed citation
-
4. Osborn AG. Osborn's Brain. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN:1931884218. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
-
5. Smith AB, Smirniotopoulos JG, Rushing EJ, Goldstein SJ. Bilateral thalamic lesions. (2009) AJR. American journal of roentgenology. 192 (2): W53-62. doi:10.2214/AJR.08.1585 - Pubmed
-
6. Arkoudis NA, Filippiadis DK, Toulas P, Velonakis G. Bilateral Thalamic Lesions: A Pictorial Essay. Hellenic Journal οf Radiology. 6(3). doi:10.36162/hjr.v6i3.434
-
7. Lazzaro N, Wright B, Castillo M et al. Artery of Percheron Infarction: Imaging Patterns and Clinical Spectrum. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(7):1283-9. doi:10.3174/ajnr.a2044 - Pubmed
-
8. Ahn S, Kim B, Kim Y, Kang D, Kwon S, Kim J. Patterns and Outcomes of the Top of the Basilar Artery Syndrome: The Role of the Posterior Communicating Artery. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018;46(3-4):106-15. doi:10.1159/000492059 - Pubmed
-
9. Fragoso D, Gonçalves Filho A, Pacheco F et al. Imaging of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease: Imaging Patterns and Their Differential Diagnosis. Radiographics. 2017;37(1):234-57. doi:10.1148/rg.2017160075 - Pubmed
-
10. Poon C, Chang J, Swarnkar A, Johnson M, Wasenko J. Radiologic Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: Pictorial Review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189(6 Suppl):S64-75. doi:10.2214/AJR.07.7015 - Pubmed
Promoted articles (advertising)






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.