Cardiomyopathy classification separates the various cardiomyopathies into several subtypes. Cardiomyopathy is defined as a "disease of the myocardium with associated cardiac dysfunction".
It was initially classified according to the 1995 World Health Organizatiοn / International Society and Federation of Cardiology (WHO/ISFC) system as follows:
- dilated cardiomyopathy
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- restrictive cardiomyopathy
- arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
- specific cardiomyopathy
- non-classified cardiomyopathies which include
This has since been revised in 2006 by the American Heart Association (AHA) as follows 2:
-
primary cardiomyopathies predominantly involving the heart
- genetic
-
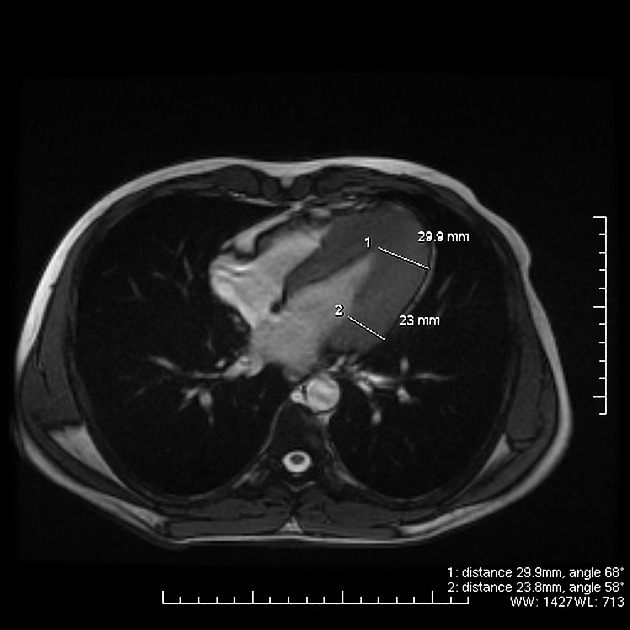
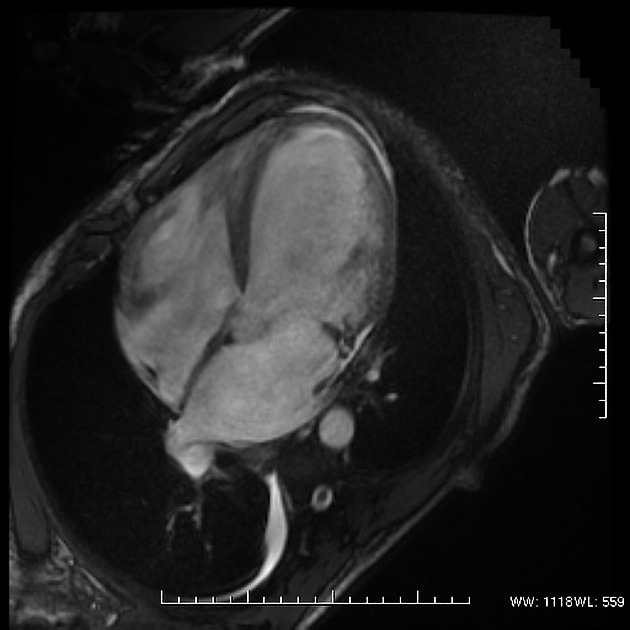
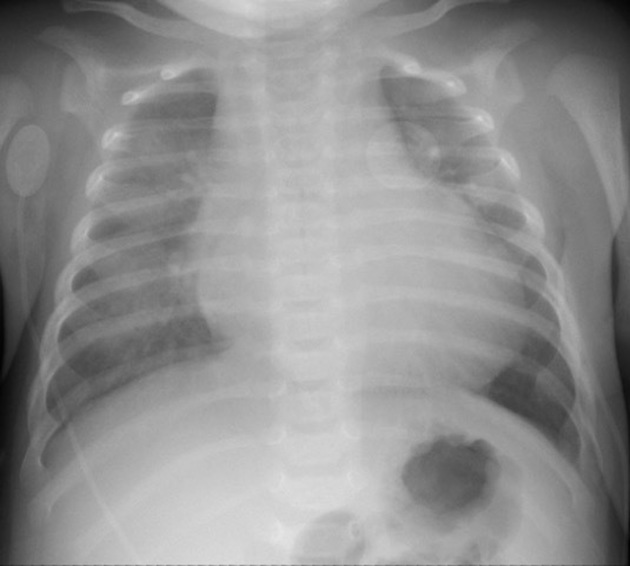
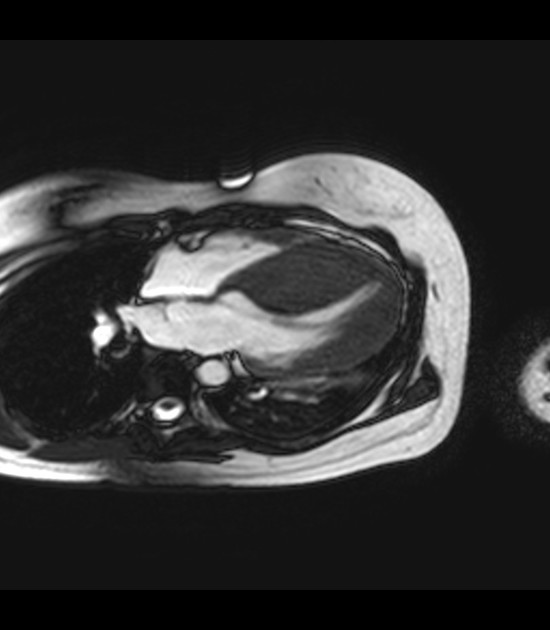
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- cardiomyopathy from primary cardiac glycogen storage diseases (PRKAG2 cardiac syndrome, Danon disease)
- arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
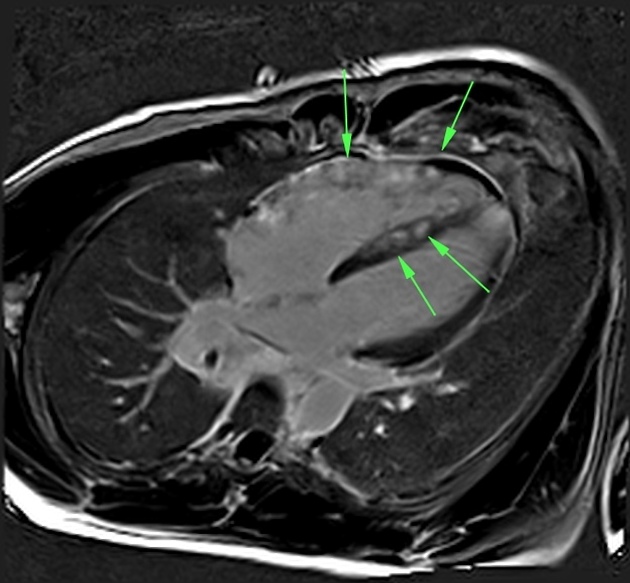
- left ventricular non-compaction
- cardiomyopathy from conduction defects
- cardiomyopathies from ion channelopathies (e.g. long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome, catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, short QT syndrome)
- cardiomyopathies from mitochondrial myopathies
-
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- mixed
- acquired
- inflammatory cardiomyopathy (i.e. myocarditis)
- stress-induced cardiomyopathy (i.e. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy)
- cardiomyopathy in peripartum and postpartum cardiomyopathy
- tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy
- cardiomyopathy in infants of diabetic mothers
- genetic
-
secondary cardiomyopathies (these conditions can have multi-organ involvement)
- infiltrative conditions - cardiomyopathy from
- cardiomyopathy from storage conditions
- cardiomyopathy from toxic agents
- drugs, heavy metals, chemicals which include
- cardiomyopathy from endomyocardial causes
- cardiomyopathy from systemic inflammatory conditions
- cardiomyopathy from underlying systemic autoimmune conditions
- cardiomyopathy from endocrine conditions
- cardiomyopathy from neuromuscular conditions
- cardiomyopathy from underlying nutritional conditions
- cardiomyopathy from underlying electrolyte imbalances
- potassium
- magnesium
- phosphate
- cardiomyopathy related to cancer treatment




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.