Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Gaillard F, Campos A, Sharma R, et al. Cerebral microhaemorrhage. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 31 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-4560
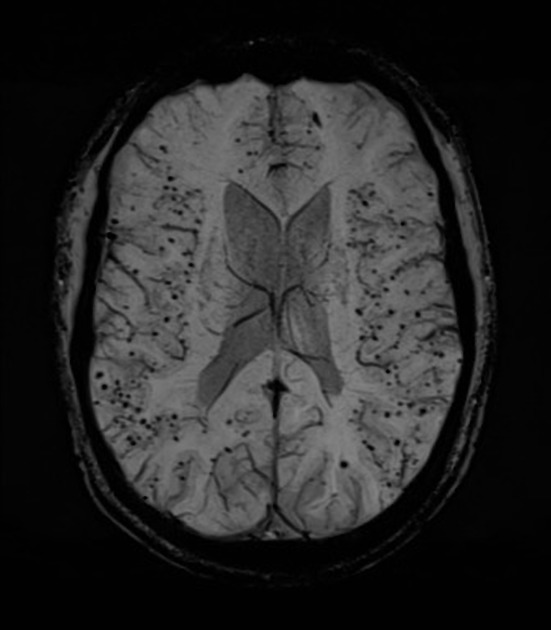
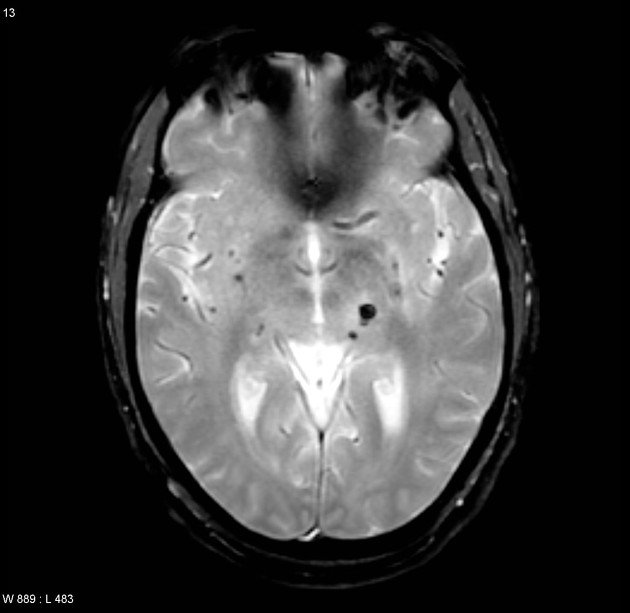
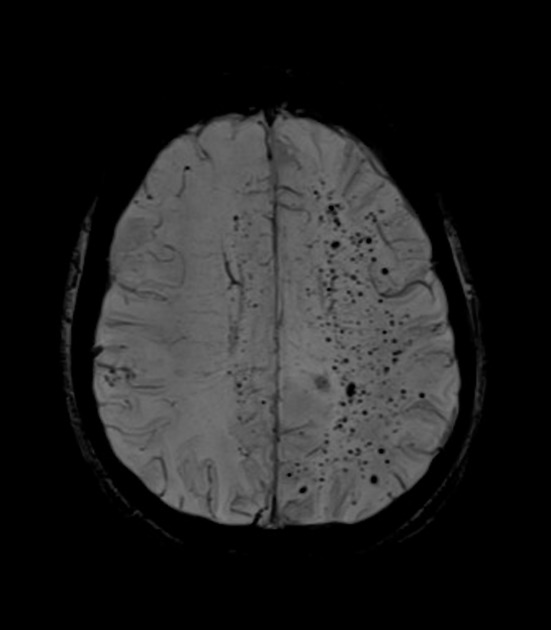
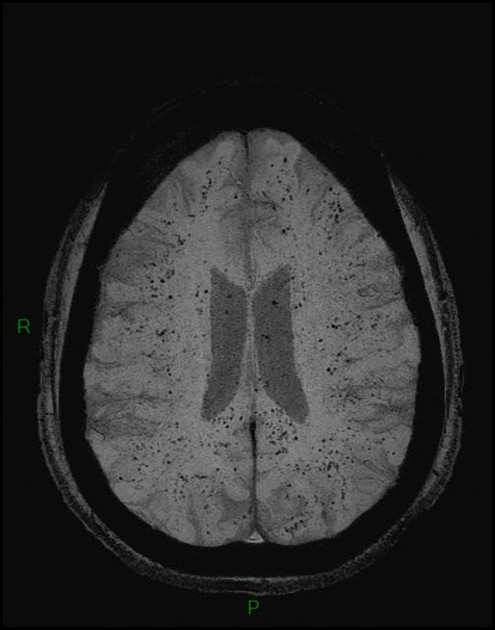
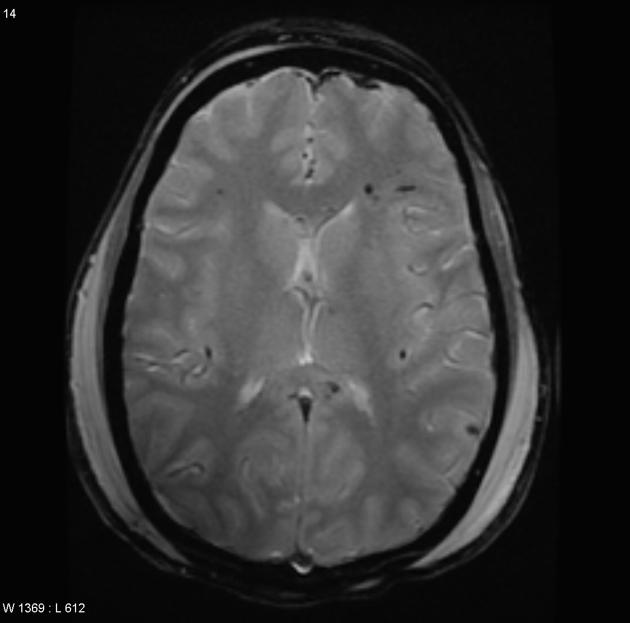
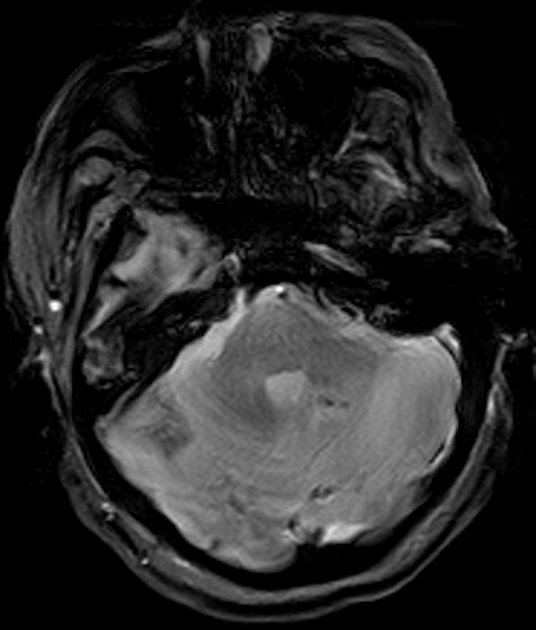
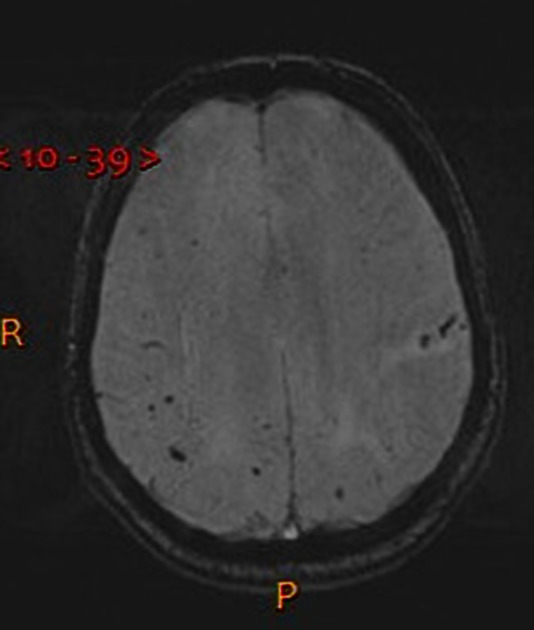
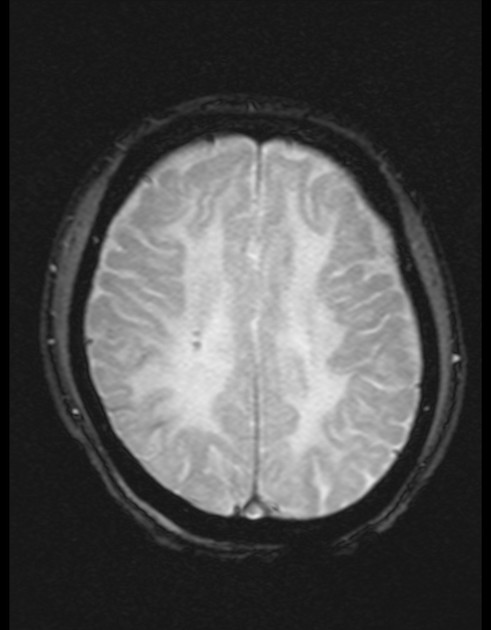
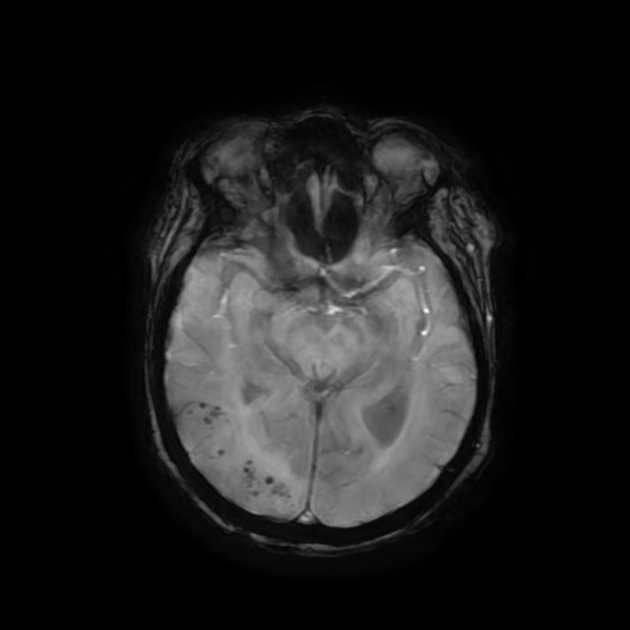
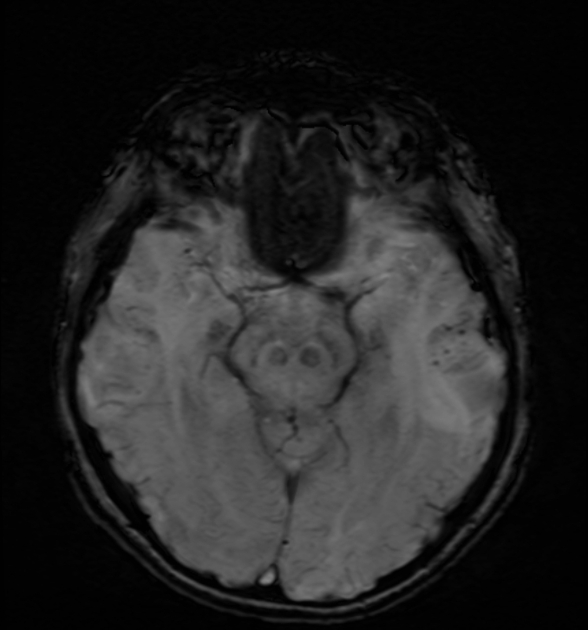
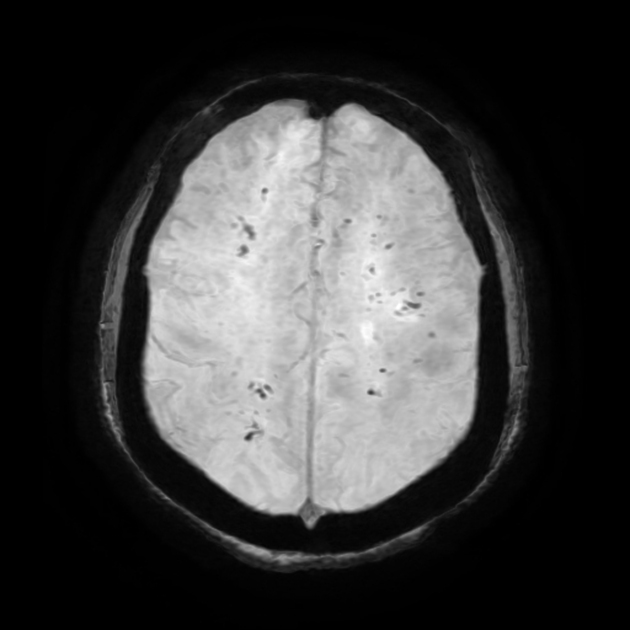
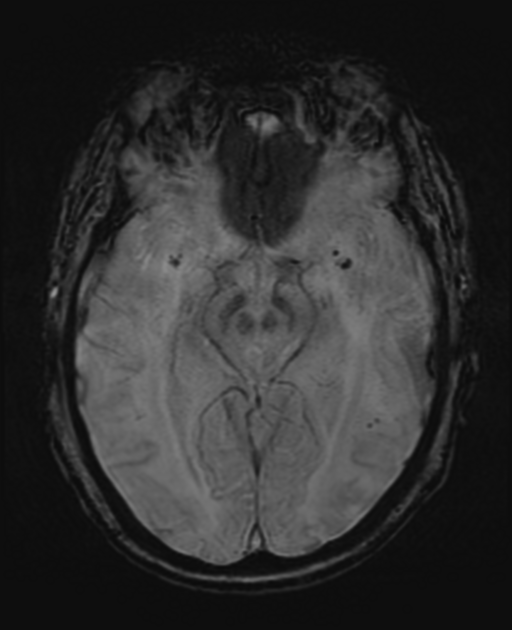
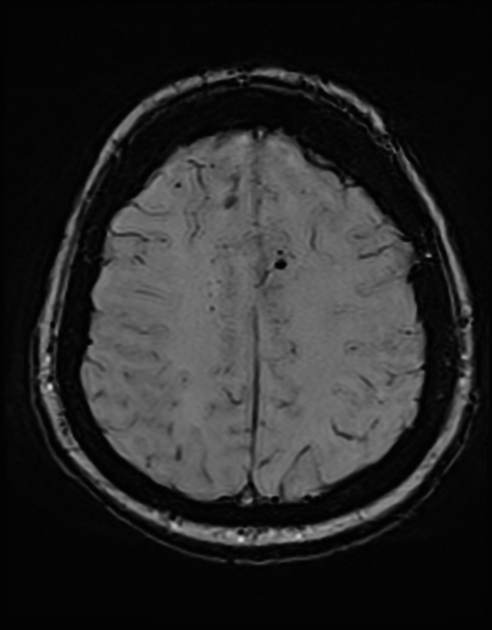
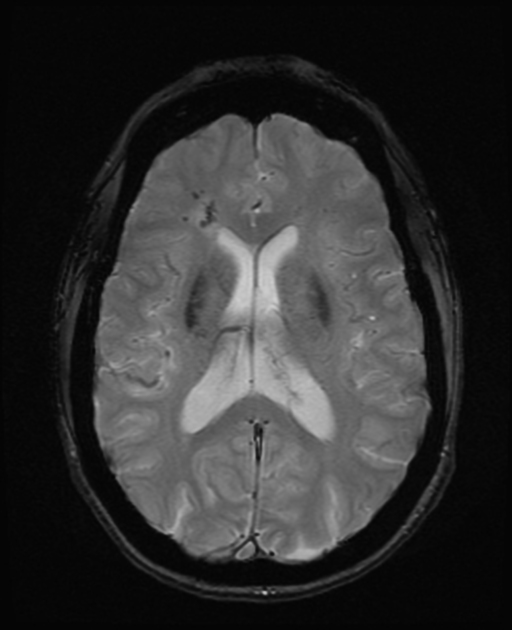
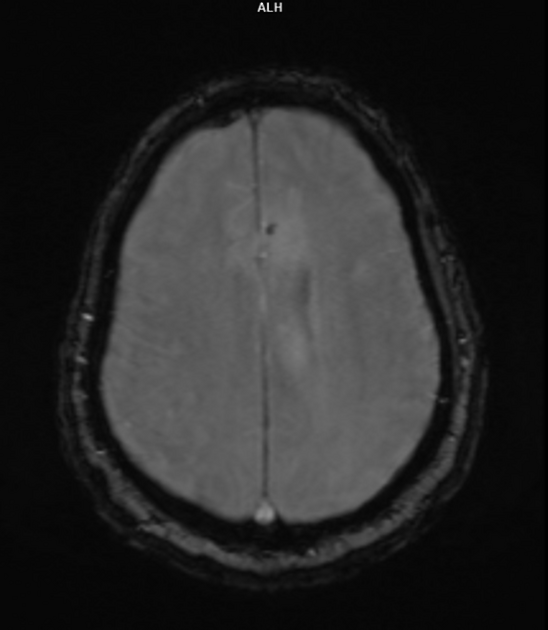
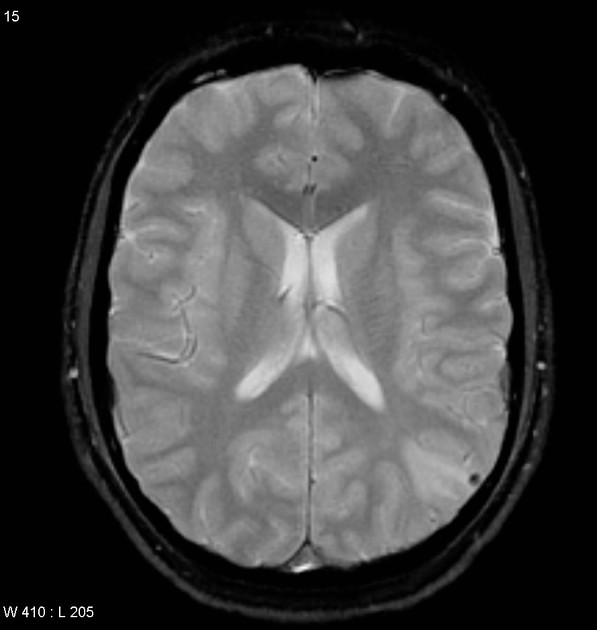
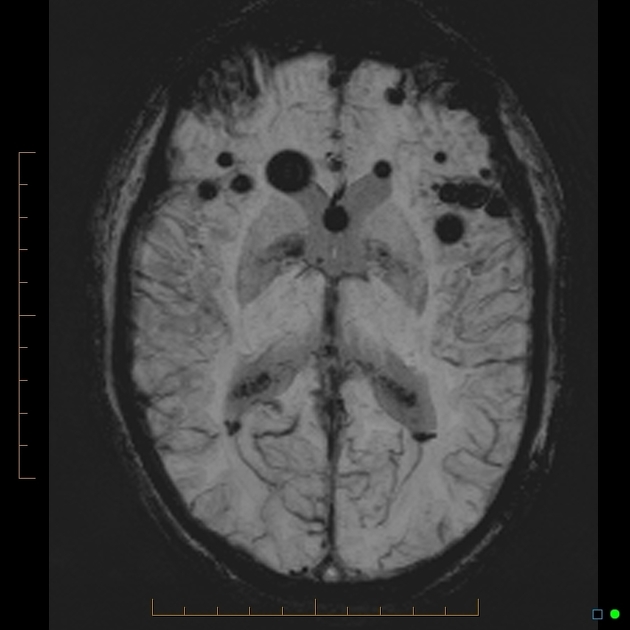
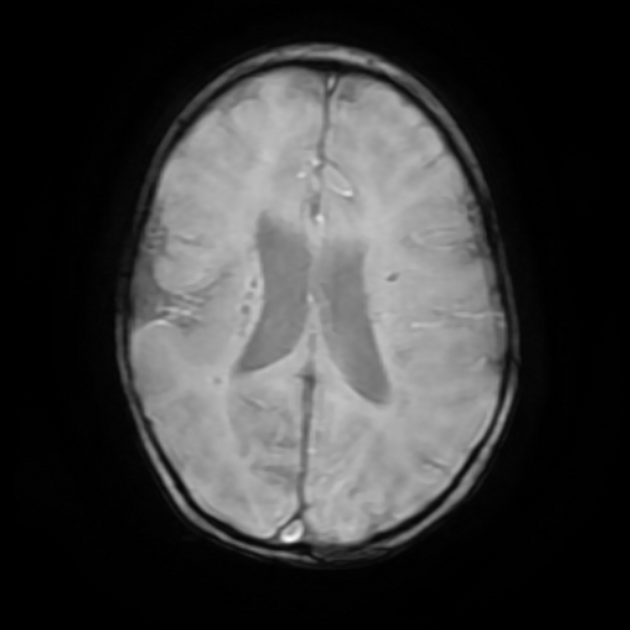
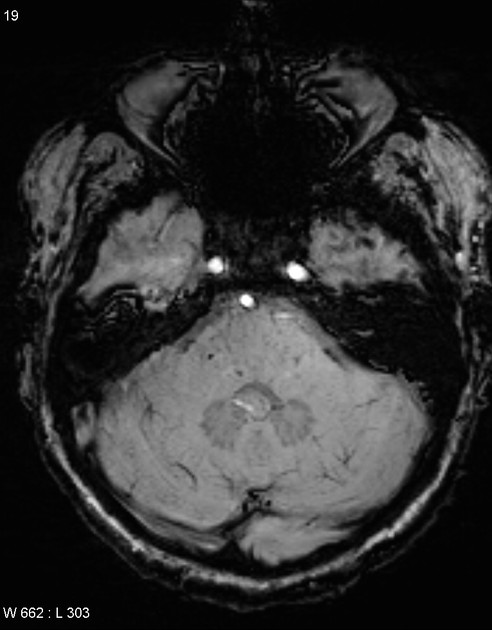
Cerebral microhaemorrhages, or cerebral microbleeds, are small focal intracerebral haemorrhages, often only visible on susceptibility-sensitive MRI sequences.
Common aetiologies
Less common aetiologies
acute haemorrhagic leukoencephalitis (AHLE) 8
acute hepatic encephalopathy 41
amyloid related imaging abnormalities (ARIA-H) 16
cathepsin A-related arteriopathy with strokes and leukoencephalopathy (CARASAL) 29,30
-
cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) 1,8
cerebral autosomal recessive arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CARASIL) 20,21
cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome 11
-
cerebral vasculitis (primary or secondary) 1,8
-
COL4A1 brain small-vessel disease 5,8
microhaemorrhages have been reported in up to 53% of cases, characteristically in the centrum semiovale, deep grey matter, or brainstem 5,8
Fabry disease 35,36
-
haemorrhagic micrometastases 1,8
heterozygous HTRA1-related cerebral small vessel disease 40
hypoxia and/or being critically ill (e.g. acute respiratory distress syndrome, high-altitude cerebral oedema, COVID-19) 8-10,39
immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) 32
-
intracranial embolism
intracranial infection (e.g. cerebral malaria, mycotic aneurysm, dengue encephalitis, HSV encephalitis) 8,37,38
intravascular lymphoma 8,17
linear scleroderma 25
moyamoya disease and moyamoya syndrome 22,23
neurosarcoidosis 12,13
pontine autosomal dominant microangiopathy with leukoencephalopathy (PADMAL) 27,28
posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) 8
progressive facial hemiatrophy (PFHA) 1,8
radiation-induced cerebral vasculopathy 1,8
retinal vasculopathy with cerebral leukoencephalopathy and systemic manifestations (RVCL-S) 33,34
Sneddon syndrome 18,19
thrombotic microangiopathies (e.g. haemolytic uraemic syndrome (HUS) and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)) 8
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
MRI
Cerebral microhaemorrhages are only seen on MRI and are only seen on susceptibility weighted T2* sequences such as gradient-recalled echo (GRE) and susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) 24.
They appear as conspicuous 2-10 mm punctate regions of signal drop out with blooming artifact 24. This blooming grossly overestimates the size of the lesions, thus they are usually inapparent on other MRI sequences and CT 24.
-
1. Blitstein MK, Tung GA. MRI of cerebral microhemorrhages. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189 (3): 720-5. doi:10.2214/AJR.07.2249 - Pubmed citation
-
2. Palma JA, Zubieta JL, Dominguez PD et-al. Pneumocephalus mimicking cerebral cavernous malformations in MR susceptibility-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30 (6): e83. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1549 - Pubmed citation
-
3. Tisdell J, Smith TW, Muehlschlegel S. Multiple septic brain emboli in infectious endocarditis. Arch. Neurol. 01;69 (9): 1206-7. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2011.3563 - Pubmed citation
-
4. Zaitsu Y, Terae S, Kudo K et-al. Susceptibility-weighted imaging of cerebral fat embolism. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2010;34 (1): 107-12. doi:10.1097/RCT.0b013e3181a962c1 - Pubmed citation
-
5. Lanfranconi S, Markus HS. COL4A1 Mutations as a Monogenic Cause of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Stroke. 41 (8): e513. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.581918 - Pubmed
-
6. Jeon SB, Kang DW. Neurological picture. Cerebral air emboli on T2-weighted gradient-echo magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry. 78 (8): 871. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2006.102954 - Pubmed
-
7. Liebeskind DS, Sanossian N, Sapo ML, Saver JL. Cerebral microbleeds after use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in children. Journal of neuroimaging : official journal of the American Society of Neuroimaging. 23 (1): 75-8. doi:10.1111/j.1552-6569.2012.00723.x - Pubmed
-
8. Sharma R, Dearaugo S, Infeld B, O'Sullivan R, Gerraty RP. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: Review of clinico-radiological features and mimics. (2018) Journal of medical imaging and radiation oncology. doi:10.1111/1754-9485.12726 - Pubmed
-
9. Fanout EM, Coutinho JM, Shannon P, et al. Critical Illness-Associated Cerebral Microbleeds. (2017) Stroke. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.016289 - Pubmed
-
10. Radmanesh A, Derman A, Lui Y et al. COVID-19-Associated Diffuse Leukoencephalopathy and Microhemorrhages. Radiology. 2020;297(1):E223-7. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020202040 - Pubmed
-
11. Igarashi S, Ando T, Takahashi T et al. Development of Cerebral Microbleeds in Patients with Cerebral Hyperperfusion Following Carotid Endarterectomy and Its Relation to Postoperative Cognitive Decline. J Neurosurg. 2021;135(4):1122-8. doi:10.3171/2020.7.jns202353 - Pubmed
-
12. Bathla G, Watal P, Gupta S, Nagpal P, Mohan S, Moritani T. Cerebrovascular Manifestations of Neurosarcoidosis: An Underrecognized Aspect of the Imaging Spectrum. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018;39(7):1194-200. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A5492 - Pubmed
-
13. Kammeyer R & Schreiner T. Cortical Vein Thrombosis, Tortuous Venous Vasculature, and Microhemorrhages in Neurosarcoidosis. JAMA Neurol. 2021;78(4):491. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.5440
-
14. Giyab O, Balogh B, Bogner P, Gergely O, Tóth A. Microbleeds Show a Characteristic Distribution in Cerebral Fat Embolism. Insights Imaging. 2021;12(1):42. doi:10.1186/s13244-021-00988-6 - Pubmed
-
15. Patel N, Banahan C, Janus J et al. Perioperative Cerebral Microbleeds After Adult Cardiac Surgery. Stroke. 2019;50(2):336-43. doi:10.1161/strokeaha.118.023355 - Pubmed
-
16. Sperling R, Jack C, Black S et al. Amyloid-Related Imaging Abnormalities in Amyloid-Modifying Therapeutic Trials: Recommendations from the Alzheimer's Association Research Roundtable Workgroup. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7(4):367-85. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2011.05.2351 - Pubmed
-
17. Richie M, Guterman E, Shah M, Cha S. Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging of Intravascular Lymphoma of the Central Nervous System. JAMA Neurol. 2022;79(1):86-7. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.4391 - Pubmed
-
18. Llufriu S, Cervera A, Capurro S, Chamorro A. Neurological Picture. Familial Sneddon's Syndrome with Microbleeds in MRI. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79(8):962. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2007.131912 - Pubmed
-
19. Yao M, Zhao J, Jiang N, Li L, Ni J. Superficial Siderosis and Microbleed Restricted in Cortex Might Be Correlated to Atrophy and Cognitive Decline in Sneddon's Syndrome. Front Neurol. 2020;11:547600. doi:10.3389/fneur.2020.01035
-
20. Wen L, Yuan J, Li S et al. Case Report: Diffuse Cerebral Microbleeds in Cerebral Autosomal Recessive Arteriopathy With Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy. Front Neurol. 2022;13:818332. doi:10.3389/fneur.2022.818332 - Pubmed
-
21. Nozaki H, Sekine Y, Fukutake T et al. Characteristic Features and Progression of Abnormalities on MRI for CARASIL. Neurology. 2015;85(5):459-63. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000001803 - Pubmed
-
22. Mori N, Miki Y, Kikuta K et al. Microbleeds in Moyamoya Disease: Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging Versus T2*-Weighted Imaging at 3 Tesla. Invest Radiol. 2008;43(8):574-9. doi:10.1097/RLI.0b013e31817fb432 - Pubmed
-
23. Khan N, Saherwala A, Chen M et al. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Cerebral Microbleeds in Moyamoya Disease and Syndrome in the American Population. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2019;9(3):139-47. doi:10.1159/000504530 - Pubmed
-
24. Greenberg S, Vernooij M, Cordonnier C et al. Cerebral Microbleeds: A Guide to Detection and Interpretation. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8(2):165-74. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70013-4 - Pubmed
-
25. Legendre L, Cuinat L, Curot J, Tanchoux F, Bonneville F, Mazereeuw-Hautier J. [Facial Linear Scleroderma Associated with Neurological Abnormalities Relating to Microangiopathy]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2016;143(12):831-5. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2016.02.032 - Pubmed
-
26. Pesaresi I, Sabato M, Desideri I, Puglioli M, Moretti P, Cosottini M. 3.0T MR Investigation of CLIPPERS: Role of Susceptibility Weighted and Perfusion Weighted Imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;31(9):1640-2. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2013.06.012 - Pubmed
-
27. Zhao Y, Duan R, Ji L, Liu Q, Yan C. Cervical Spinal Involvement in a Chinese Pedigree With Pontine Autosomal Dominant Microangiopathy and Leukoencephalopathy Caused by a 3' Untranslated Region Mutation of COL4A1 Gene. Stroke. 2019;50(9):2307-13. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.024875 - Pubmed
-
28. Ding X, Hagel C, Ringelstein E et al. MRI Features of Pontine Autosomal Dominant Microangiopathy and Leukoencephalopathy (PADMAL). J Neuroimaging. 2010;20(2):134-40. doi:10.1111/j.1552-6569.2008.00336.x - Pubmed
-
29. Bugiani M, Kevelam S, Bakels H et al. Cathepsin A-Related Arteriopathy with Strokes and Leukoencephalopathy (CARASAL). Neurology. 2016;87(17):1777-86. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000003251 - Pubmed
-
30. Budhdeo S, de Paiva A, Wade C et al. A Rare Cause of Monogenic Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Stroke: Cathepsin A-Related Arteriopathy with Strokes and Leukoencephalopathy (CARASAL). J Neurol. 2022;269(12):6673-7. doi:10.1007/s00415-022-11302-9 - Pubmed
-
31. De Sciscio M, De Sciscio P, Vallat W, Kleinig T. Cerebral Microbleed Distribution Following Cardiac Surgery Can Mimic Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy. BMJ Neurol Open. 2021;3(2):e000166. doi:10.1136/bmjno-2021-000166 - Pubmed
-
32. Yoon J, Smith D, Tirumani S, Caimi P, Ramaiya N. CAR T-Cell Therapy: An Update for Radiologists. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;217(6):1461-74. doi:10.2214/AJR.21.26091 - Pubmed
-
33. Wilms A, de Boer I, Terwindt G. Retinal Vasculopathy with Cerebral Leukoencephalopathy and Systemic Manifestations (RVCL-S): An Update on Basic Science and Clinical Perspectives. Cereb Circ Cogn Behav. 2022;3:100046. doi:10.1016/j.cccb.2022.100046 - Pubmed
-
34. Yan Y, Jiang S, Wang R, Wang X, Li P, Wu B. Serial Magnetic Resonance Imaging Changes of Pseudotumor Lesions in Retinal Vasculopathy with Cerebral Leukoencephalopathy and Systemic Manifestations: A Case Report. BMC Neurol. 2021;21(1):219. doi:10.1186/s12883-021-02250-4 - Pubmed
-
35. Kono Y, Wakabayashi T, Kobayashi M et al. Characteristics of Cerebral Microbleeds in Patients with Fabry Disease. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;25(6):1320-5. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.02.019 - Pubmed
-
36. Cocozza S, Russo C, Pontillo G, Pisani A, Brunetti A. Neuroimaging in Fabry Disease: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Insights Imaging. 2018;9(6):1077-88. doi:10.1007/s13244-018-0664-8 - Pubmed
-
37. Trivedi S & Chakravarty A. Neurological Complications of Dengue Fever. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2022;22(8):515-29. doi:10.1007/s11910-022-01213-7 - Pubmed
-
38. Eran A, Hodes A, Izbudak I. Bilateral Temporal Lobe Disease: Looking Beyond Herpes Encephalitis. Insights Imaging. 2016;7(2):265-74. doi:10.1007/s13244-016-0481-x - Pubmed
-
39. Hackett P, Yarnell P, Weiland D, Reynard K. Acute and Evolving MRI of High-Altitude Cerebral Edema: Microbleeds, Edema, and Pathophysiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019;40(3):464-9. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A5897 - Pubmed
-
40. Uemura M, Nozaki H, Kato T et al. HTRA1-Related Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Review of the Literature. Front Neurol. 2020;11:545. doi:10.3389/fneur.2020.00545 - Pubmed
-
41. Benson J, Payabvash S, Thalken G et al. Delineation of Microhemorrhage in Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy Using Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2016;85(3):629-34. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.12.025 - Pubmed
Multiple choice questions:
Related articles: Stroke and intracranial haemorrhage
Promoted articles (advertising)





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.