CT urography (protocol)
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Ian Bickle had no recorded disclosures.
View Ian Bickle's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosures- CT-intravenous urogram
- CT-intravenous urograms
- CT-IVU
- CT urogram
- CTU
- CT IVP
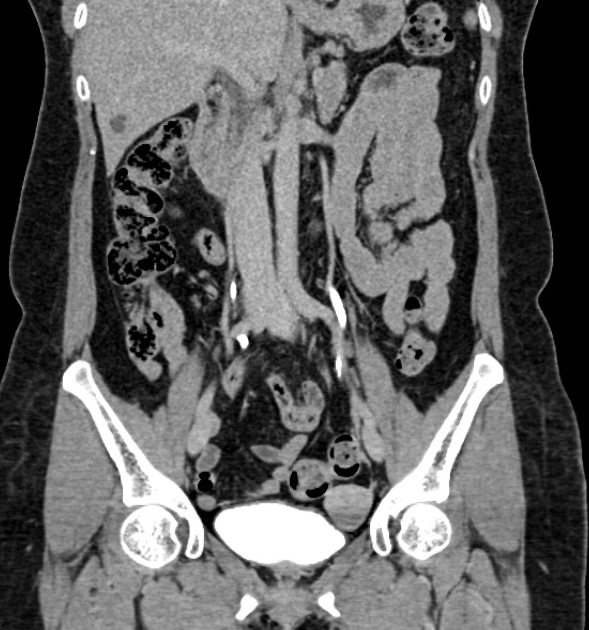
CT urography (CTU or CT IVU), also known as CT intravenous pyelography (CT IVP), has now largely replaced traditional IVU in imaging the genitourinary tract. It gives both anatomical and functional information, albeit with a relatively higher dose of radiation.
On this page:
Indications
urothelial cancer surveillance
congenital collecting system abnormality
CTU has high sensitivity (96-100%) and high specificity (94-100%) of identifying ureteric and bladder calculi 2.
Purpose
The aim is to illustrate the collecting systems, ureters and bladder with intravenous contrast, albeit in a single acquisition as opposed to the multiple and more dynamic traditional IVU. Visualization of other structures in the abdomen is also better with CTU than with traditional IVU. Upper tract tumors, strictures and to a degree the function of the kidney can be assessed.
Technique
A variety of techniques have been described 1. A CTU may be performed along with other CT studies of the genitourinary tract, such as a 3 or 4 phase or split bolus study 2.
See also
References
- 1. McTavish JD, Jinzaki M, Zou KH et-al. Multi-detector row CT urography: comparison of strategies for depicting the normal urinary collecting system. Radiology. 2002;225 (3): 783-90. Radiology (full text) - doi:10.1148/radiol.2253011515 - Pubmed citation
- 2. Moloney F, Murphy K, Twomey M, O’Connor O, Maher M. Haematuria: An Imaging Guide. Advances in Urology. 2014;2014:1-9. doi:10.1155/2014/414125 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Computed tomography curriculum
- Acute pyelonephritis
- Ileal ureter interposition
- Urolithiasis
- Cystitis cystica
- Abnormal renal rotation
- Urinary tract infection
- Delayed nephrogram
- Fungal ball of the urinary tract
- RENAL nephrometry scoring system
- Transureteroureterostomy
- Solitary filling defect of the ureter (differential)
- Ileal conduit
- Renal sinus cyst
- Hematuria (adult)
- Lobster claw sign (kidney)
- Renal tubular ectasia
- Renal papillary necrosis
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (C)
- Ureteropelvic junction obstruction
- Urothelial carcinoma - synchronus ureteral (three phase urogram)
- Urothelial carcinoma - bladder wall thickening
- Normal CT urography
- Ureteric injury post stenting
- Acute pyelonephritis - striated nephrogram
- Rupture of ureter due to calculi
- Supernumerary kidney
- Seminal vesicle and prostatic abscesses with vasitis
- Ureteric jet
- Pelviureteric junction obstruction
- Chronic pelviureteric junction obstruction
- Vesicovaginal fistula
- Normal CT intravenous urogram
- Right ureteric injury from penetrating trauma
- Transitional cell carcinoma of the renal pelvis
- Normal split bolus study
- Normal kidneys on 4-phase CT study
- Hydronephrosis due to ureteric stone
- Distal ureteric tumour
Related articles: Computed tomography
- computed tomography in practice
-
computed tomography overview
- iodinated contrast media
- CT IV contrast media administration
-
CT artifacts
- patient-based artifacts
- physics-based artifacts
- hardware-based artifacts
- ring artifact
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifacts
- CT technology
-
generations of CT scanners
- helical CT scanning
- step and shoot scanning
- ultra-high-resolution CT (UHRCT)
- CT x-ray tube
- CT fluoroscopy
- cone-beam CT
-
generations of CT scanners
- dual-energy CT
- CT image reconstruction
- CT image quality
- CT dose
-
CT protocols
- composite
- head & neck
- chest
- abdomen and pelvis
- CT abdomen-pelvis (protocol)
- CT abdominal aorta
- CT adrenals (protocol)
- CT cholangiography (protocol)
- CT colonography (protocol)
- CT enteroclysis (protocol)
- CT enterography (protocol)
- CT gastrography (protocol)
- CT kidneys, ureters and bladder (protocol)
- CT urography (protocol)
- CT Renal mass (protocol)
- CT angiography of the splanchnic vessels (protocol)
- CT renal split bolus
- CT pancreas (protocol)
- liver






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.