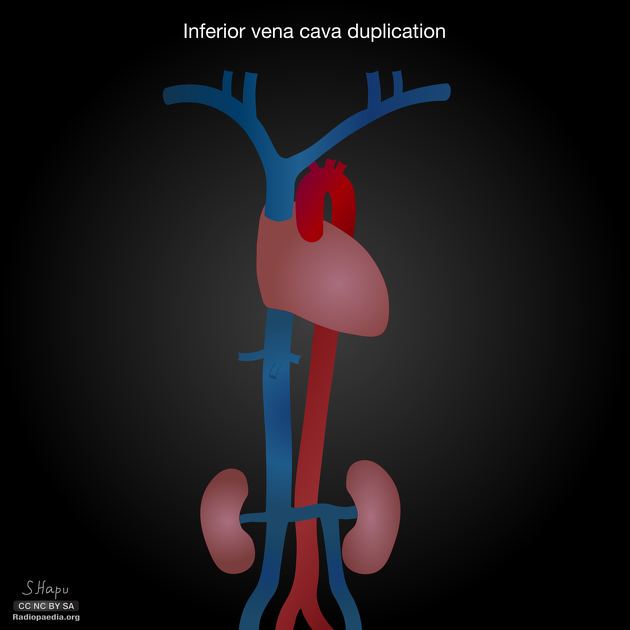
Duplication of the inferior vena cava
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Praveen Jha had no recorded disclosures.
View Praveen Jha's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures- IVC duplication
- Duplicated IVC
- Duplicated inferior vena cava
- Inferior venacava duplication
- Duplication of IVC
- Duplication of the inferior vena cava
- Inferior vena caval duplication
- Double inferior vena cava
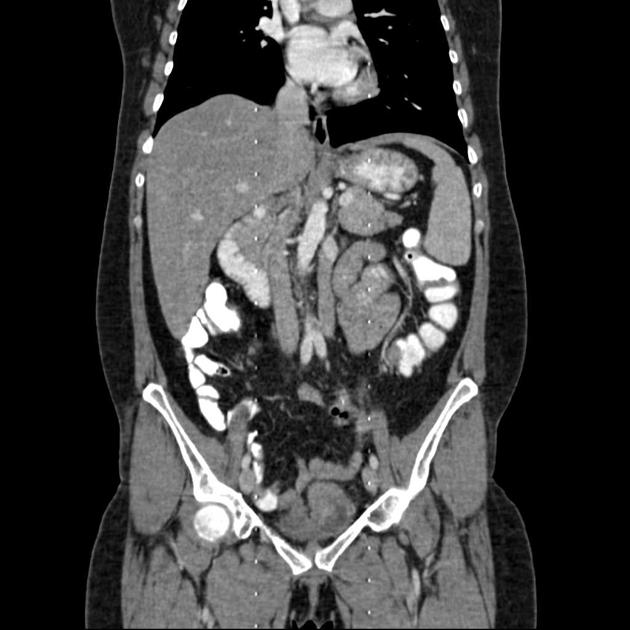
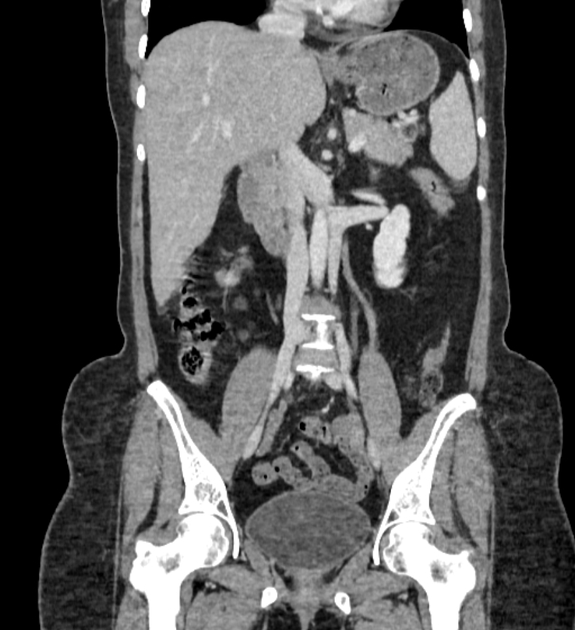
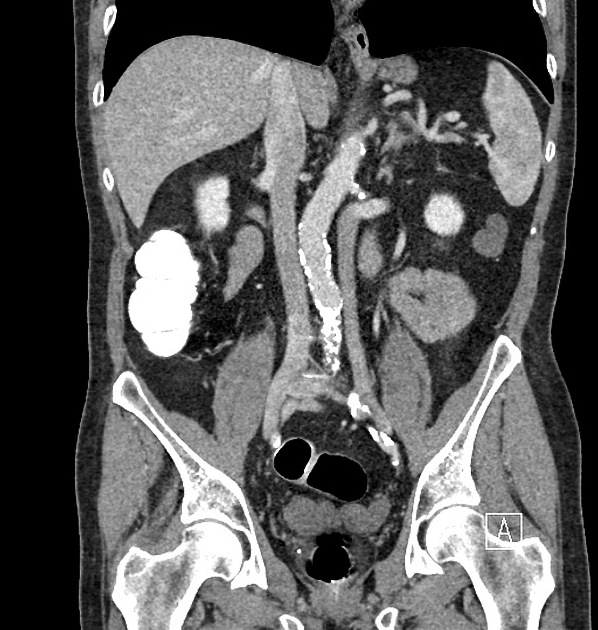
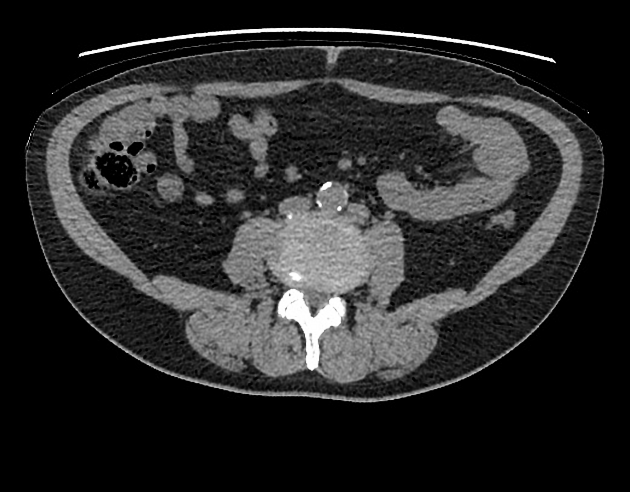
Duplication of the inferior vena cava is a relatively rare but well described vascular anomaly. This caval abnormality had an increased association with renal anomalies like crossed fused ectopia or circumaortic renal collar 1,2.
On this page:
Epidemiology
The incidence of inferior vena cava duplication is reported to be ~1.5% (range 0.2-3%) 3.
Associations
Case reports of association with ureteropelvic junction anomaly and retrocaval ureters have been described 5.
Clinical presentation
Usually, an incidental detection, while evaluating genitourinary anomalies.
Pathology
The inferior vena cava has a convoluted development during the 7-10th weeks of gestation 4.
posterior cardinal vein appears first but forms only the distal IVC i.e. iliac bifurcation.
subcardinal veins (2) appear next, left subcardinal vein regresses, and right subcardinal vein forms the suprarenal IVC.
supracardinal veins (2) appear last, left supracardinal vein regresses, and right supracardinal vein forms infrarenal IVC.
IVC duplication results from a persistent left supracardinal vein.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
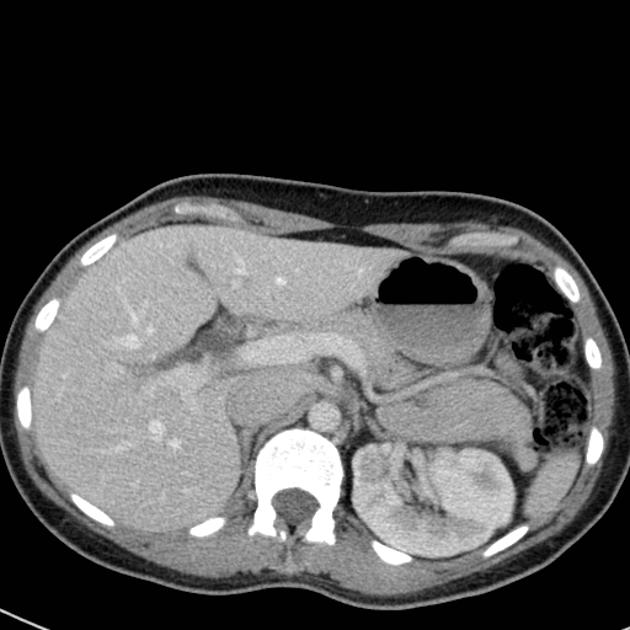
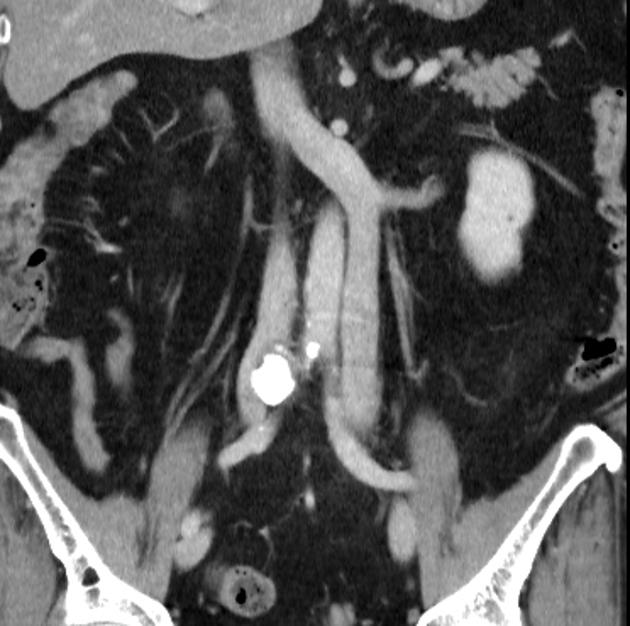
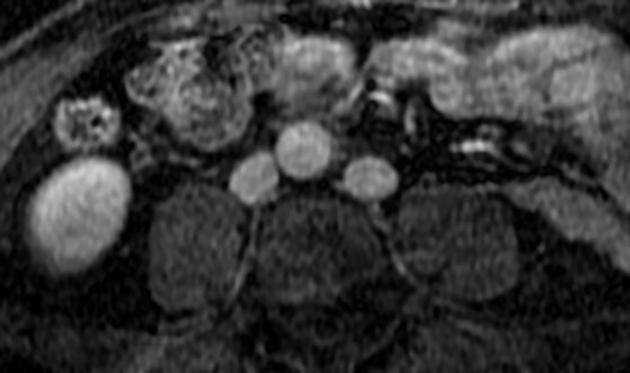
Radiographic features
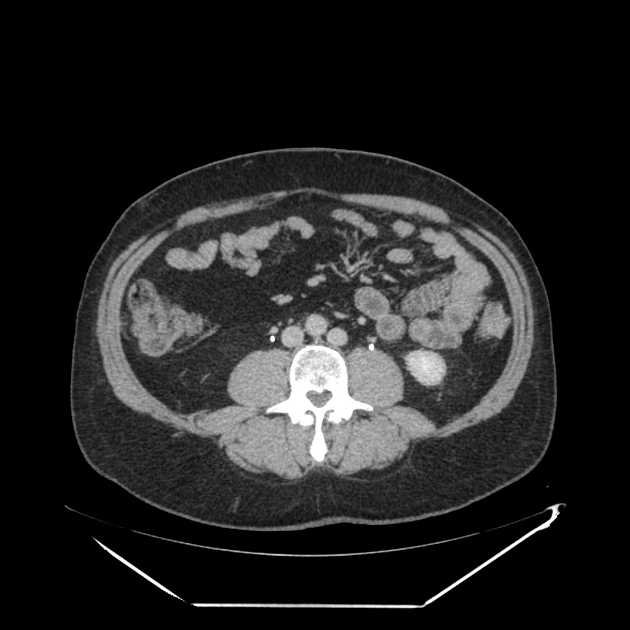
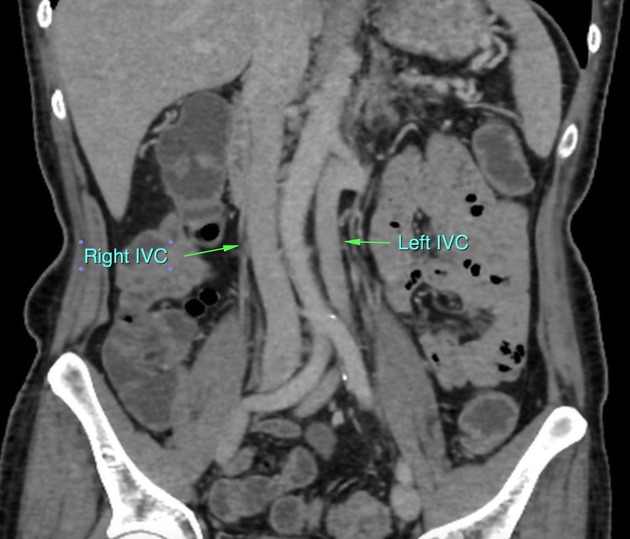
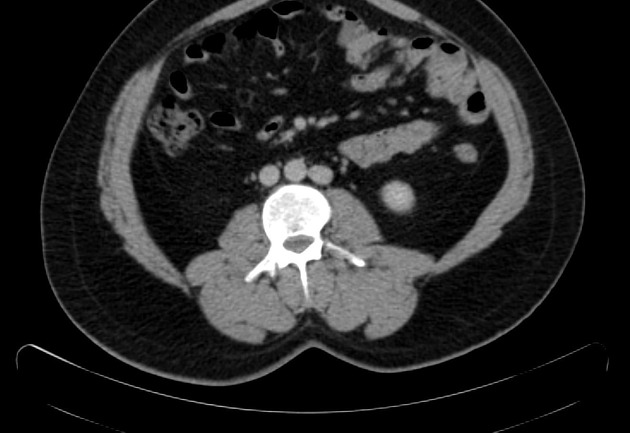
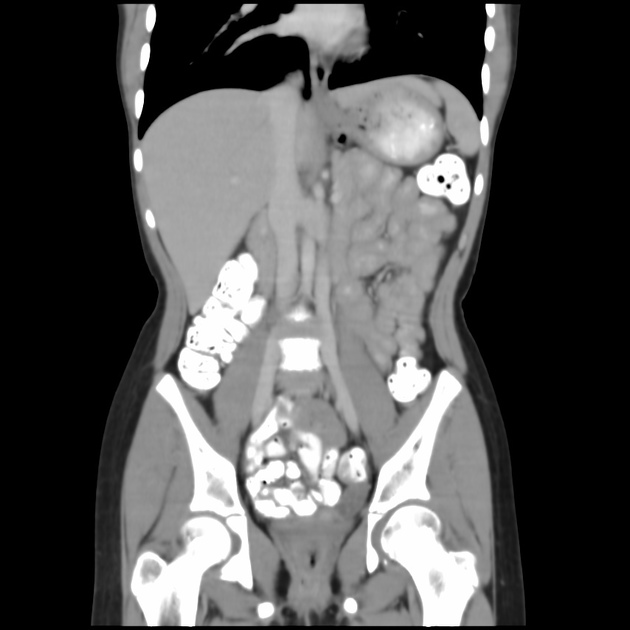
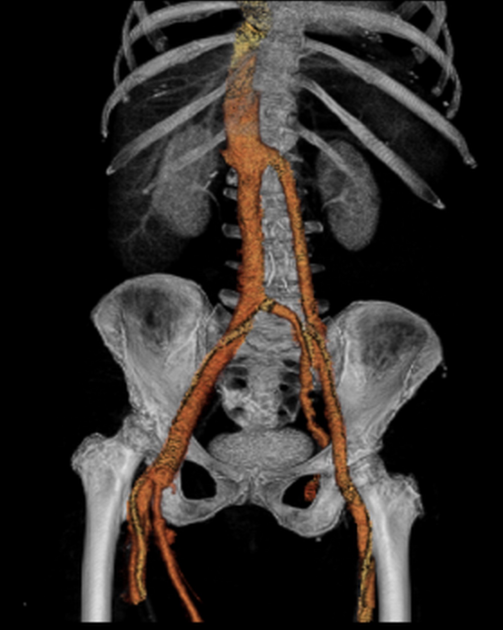
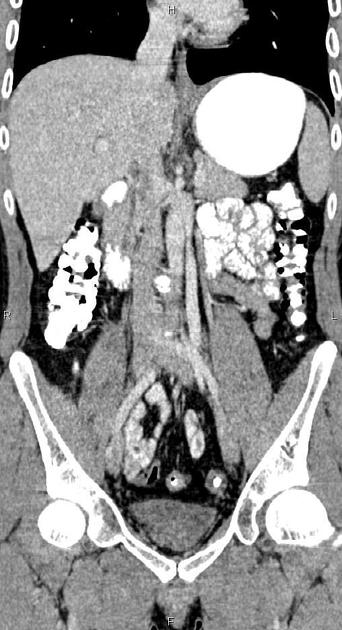
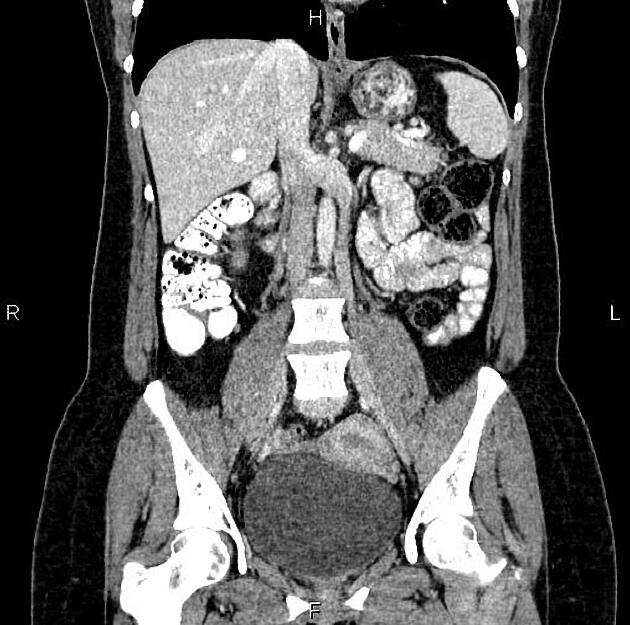
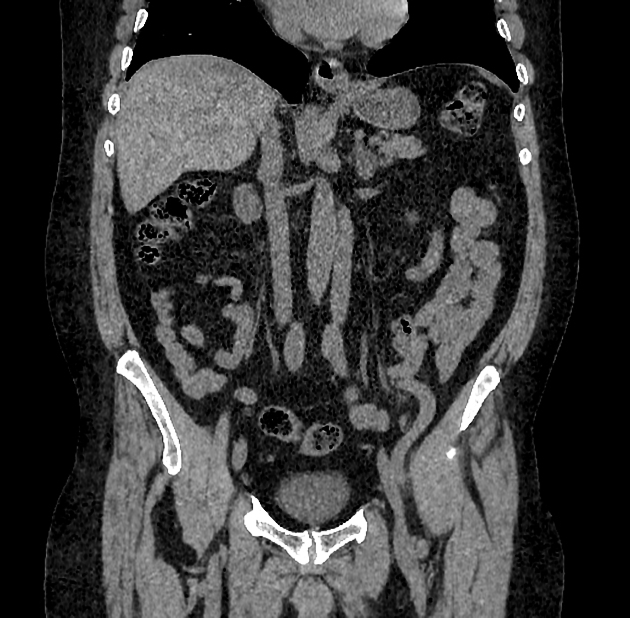
Duplicated left sided IVC is usually seen as a continuation of the left common iliac vein, crossing anterior to the aorta at the level of renal vein to join the right sided IVC.
Differential diagnosis
An important differential is transposition of IVC. The renal vein is an important landmark for this differential. IVC continues on both sides of the aorta, in duplicated IVC. However, in transposition of the IVC, it continues on the left side of the aorta only.
References
- 1. Royal S & Callen P. CT Evaluation of Anomalies of the Inferior Vena Cava and Left Renal Vein. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979;132(5):759-63. doi:10.2214/ajr.132.5.759 - Pubmed
- 2. Smith TR, Frost A. Anomalous inferior vena cava associated with horseshoe kidneys. Clin Imaging. 20 (4): 276-8. Clin Imaging (link) - Pubmed citation
- 3. Mayo J, Gray R, St louis E et-al. Anomalies of the inferior vena cava. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983;140 (2): 339-45. AJR Am J Roentgenol (citation) - Pubmed citation
- 4. Chuang V, Mena C, Hoskins P. Congenital Anomalies of the Inferior Vena Cava. Review of Embryogenesis and Presentation of a Simplified Classification. Br J Radiol. 1974;47(556):206-13. doi:10.1259/0007-1285-47-556-206 - Pubmed
- 5. Chou CT, Yang AD, Hong YC et-al. Bilateral retrocaval ureters with IVC duplication. Abdom Imaging. 31 (5): 596-7. doi:10.1007/s00261-005-0122-1 - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Duplication of inferior vena cava
- Duplicated IVC
- Duplicated inferior vena cava with complex vascular malformation
- Duplication of the inferior vena cava
- Retroperitoneal lymphangiectasia and transposition of inferior vena cava
- Duplicated inferior vena cava
- Polysplenia syndrome
- Crossed fused renal ectopia and duplicated IVC
- Duplicated inferior vena cava filter placement
- Duplicated inferior vena cava (type 2c)
- Duplicated inferior vena cava
- Accessory right inferior hepatic vein
- Duplication of inferior vena cava
- Duplicated inferior vena cava
- Duplicated inferior vena cava
- Horseshoe kidney and inferior vena cava duplication
- Left IVC with SVC duplication
- Arrested inferior vena cava duplication
- Inferior vena cava duplication
- Caval variants (illustrations)
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.