An ectopic meningioma (or primary ectopic meningioma) refers to rare situations where a meningioma arises outside the dura without any connection to the dura, distinguishing it from meningiomas with extracranial or extraspinal growth.
On this page:
Clinical presentation
Ectopic meningiomas can occur at various sites but in the majority of cases, they are found in the head and neck region 1-4. Reported locations include1-6:
- scalp skin
- ear and temporal bone
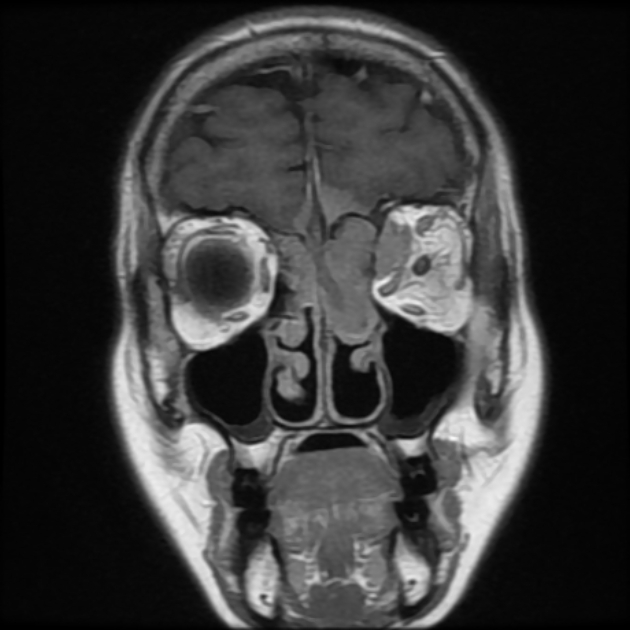
- orbit: primary orbital meningioma
- sinonasal tract
- mandible
- oral cavity
- parotid gland
Very rarely they can also arise outside the head and neck region such as:
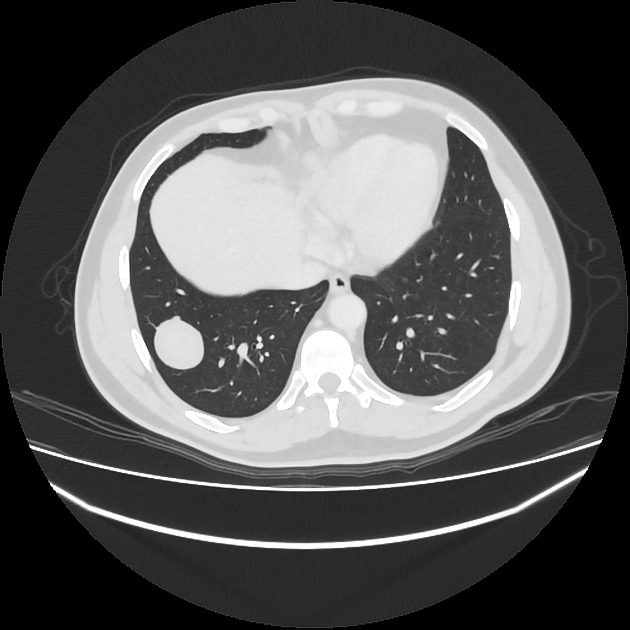
- lung: primary pulmonary meningioma 2
- mediastinum 4
Pathology
A number of theories have been proposed for ectopic meningiomas including 4:
- normal meningothelial cells that were
- entrapped within the skull, sutures or scalp tissues due to defects in neural tube closure or as a result of trauma
- located in meningoceles and meningoencephaloceles without persisting connection to the dura
- transported peripherally along nerve sheaths exiting the skull or spine
- differentiation of pluripotent mesenchymal cells into meningothelial cells
- metaplasia into meningothelial-like cells
- developmental rests of meningothelial cells (e.g. in the lung or lymph nodes).
Radiographic features
They are similar to intracranial meningiomas regarding morphology and enhancement, although they have a greater predilection for local invasion 4.
CT
- calcifications and intense enhancement
- hyperostosis of this skull, remodeling and expansion of the affected region with or without extra calvarial soft tissue mass
- purely osteolytic skull lesions are also reported and believed to be of worse prognosis, particularly if associated with a soft tissue component
MRI
Signal characteristics are similar to intracranial meningiomas.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment is with surgical resection. Unlike intracranial meningiomas, ectopic meningiomas have a relatively high metastatic rate (6%) and are more liable to malignant degeneration 4.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of these tumors is very wide and primarily based on their location.





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.