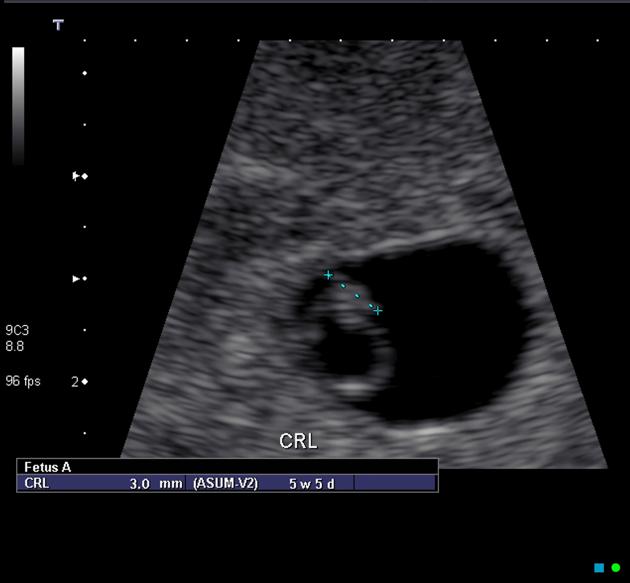
Fetal pole
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Radswiki T, Jones J, Stanislavsky A, et al. Fetal pole. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 28 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-14871
Permalink:
rID:
14871
Article created:
1 Sep 2011,
The Radswiki ◉
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created The Radswiki had no recorded disclosures.
View The Radswiki's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosures
Revisions:
11 times, by
8 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
The fetal pole is the first direct imaging manifestation of the fetus and is seen as a thickening on the margin of the yolk sac during early pregnancy. It is often used synonymously with the term "embryo".
The fetal pole is usually identified at ~6.5 weeks with transabdominal ultrasound imaging and at ~6 weeks 2 with transvaginal ultrasound imaging, although it may not be seen until ~9 weeks in some cases.
- a fetal pole should be seen when MSD ≥16 mm on TVS (by RCOG criteria), or MSD ≥25 mm on TAS
- pregnancy failure is not diagnosed until a fetal pole is not seen when MSD ≥25 mm on TVS
When the fetal pole measures ≥7 mm, a fetal heartbeat should be detected.
References
- 1. Hung N. Winn (Editor), John C. Hobbins (Editor). Clinical Maternal-Fetal Medicine. (2000) ISBN: 1850707987
- 2. F. Bahlmann (Contributor), R. Bollmann (Contributor), R. Chaoui (Contributor). Ultrasound in Obstetrics and GynecologyDiagnostic Ultrasound in Obstetrics: Obstetrics. (2005) ISBN: 1588901475
- 3. Jain K, Hamper U, Sanders R. Comparison of Transvaginal and Transabdominal Sonography in the Detection of Early Pregnancy and Its Complications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988;151(6):1139-43. doi:10.2214/ajr.151.6.1139
Incoming Links
Articles:
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta previa
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumors
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumors of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumors
- mixed germ cell tumor
- yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumor
- sex cord / stromal tumors of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumor of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumors (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumors
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.