IgA vasculitis (formerly known as Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP)) is a type of non-thrombocytopenic immune complex-mediated small vessel acute leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
On this page:
Epidemiology
IgA vasculitis tends to occur in the pediatric population (peak incidence 3-10 years) 3. In predominantly White populations, it is the most common type of vasculitis in children (Kawasaki disease is the most common type of vasculitis in children worldwide) 10,15.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of IgA vasculitis is based on a combination of typical clinical and pathological features.
Diagnostic criteria
In order to differentiate from other types of vasculitides, the 1990 diagnostic criteria by the American College of Rheumatology require two or more of 13,14:
age of onset less than 20 years (although some case series show disease involvement in older individuals)
palpable skin purpura
acute abdominal pain
biopsy showing granulocytes around small arteriolar/venular walls
The presence of two or more of these criteria has a sensitivity and specificity of 87% for IgA vasculitis 14.
Clinical presentation
IgA vasculitis tends to present as:
a palpable, purpuric rash primarily of the extremities
acute abdominal pain, ileoileal intussusception may be present
arthralgia
Pathology
In IgA vasculitis, there is deposition of IgA immune complexes in small vessels.
Location
The most common organ systems to be involved are:
skin: 95-100%, usually the first organ to get involved
gastrointestinal tract: 50-75%
joints: ~80% 6
kidneys
Rare sites:
central nervous system 5,7
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
May show evidence of bowel wall thickening due to hemorrhage and/or evidence of bowel obstruction. Plain radiograph features are however non-specific.
Fluoroscopy
Small bowel follow-through may show evidence of separation of bowel loops, "thumbprinting" and/or mucosal thickening.
Ultrasound
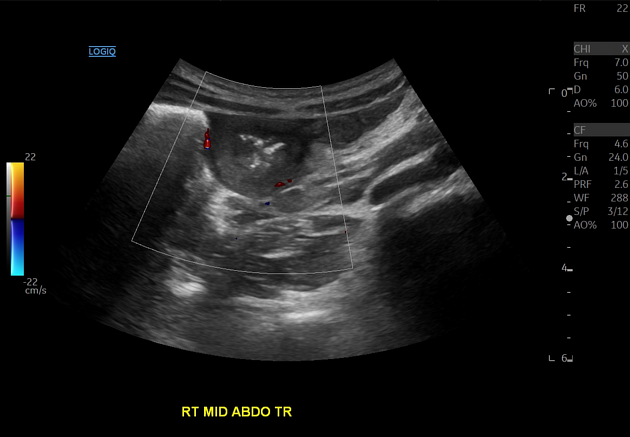
May show echogenic kidneys, target or doughnut sign in case of intussusception. IgA vasculitis has also been shown to cause massive scrotal edema and can be a source of severe pain in young boys 9.
CT
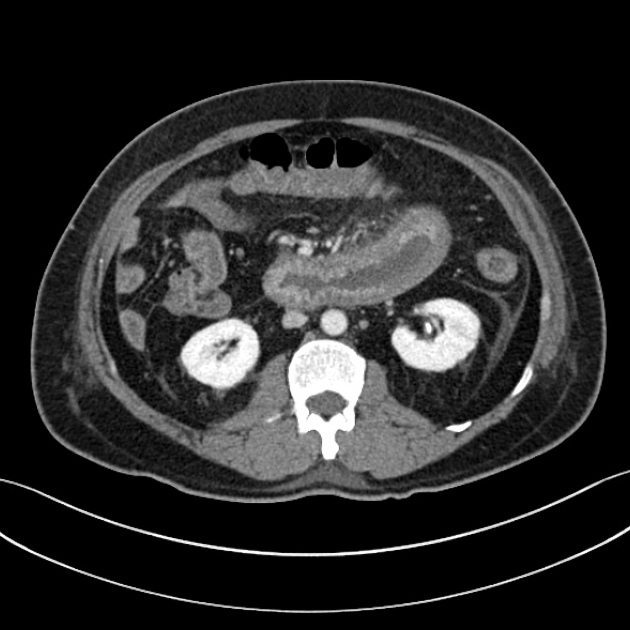
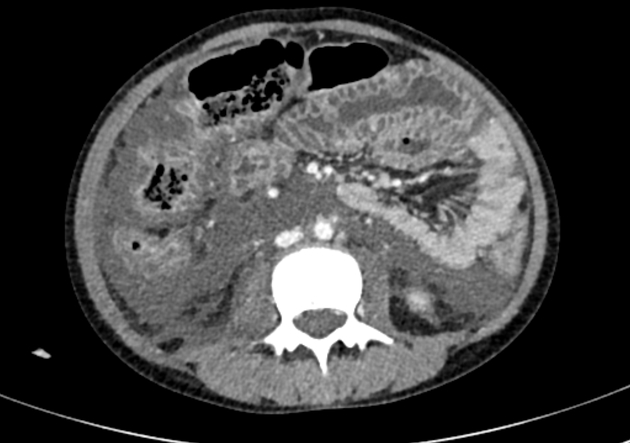
May show multifocal bowel thickening, lymphadenopathy, mesenteric edema and vascular engorgement. Although non-specific, CT findings may aid in the diagnosis of IgA vasculitis in a young patient with acute gastrointestinal illness along with other cutaneous features of IgA vasculitis. Intussusception, typically ileoileal type, is also seen.
Treatment and prognosis
The disease is self-limiting in most instances. Treatment is usually supportive including fluids and pain relief in the pediatric population. Steroids are used in adults due to the risk of serious renal involvement 10.
Complications
Gastrointestinal tract
small bowel intussusception
gastrointestinal hemorrhage
small bowel infarction: 3-5% 3
Renal
renal failure (HSP nephritis)
History and etymology
Henoch-Schönlein purpura was named after Eduard Heinrich Henoch, German pediatrician (1820-1910), and Johann Lukas Schönlein, German physician (1793-1864) 11, whom Henoch was the protégé of, although neither was the first to describe this condition 11,12.
Differential diagnosis
On a CT/contrast study for the bowel consider:





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.