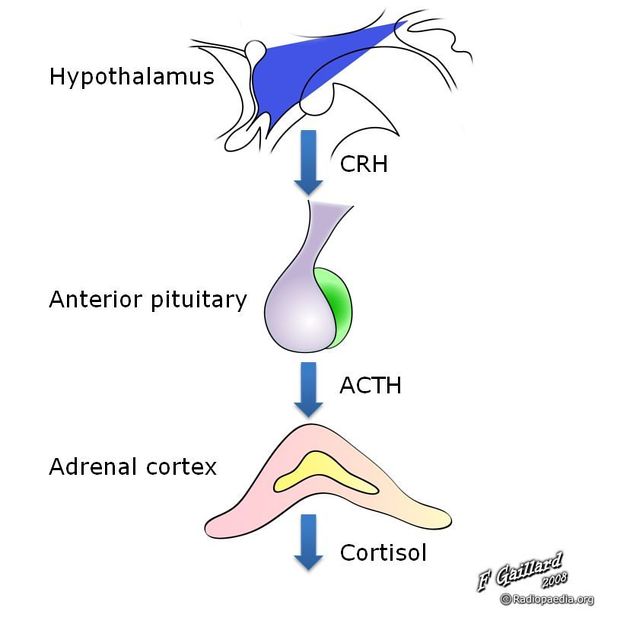
Inferior petrosal sinus sampling is an infrequently used method of confirming the presence of a hormonally active pituitary microadenoma when imaging alone has been insufficient. This technique is able to confirm that excess hormone (e.g. ACTH) is being produced by the pituitary and may also help in lateralizing the microadenoma (although the latter is more contentious).
On this page:
Images:
Indication
Inferior petrosal sinus sampling is most frequently indicated when patients have confirmed ACTH dependent Cushing's syndrome. ACTH secreting pituitary microadenomas, which may be inapparent on imaging in 40 to 50% of cases, account for 80% of non-adrenal, non-iatrogenic cases.
Technique
Although technique varies a standard modern approach would consist of:
review prior imaging to try and identify inferior petrosal sinus anatomy
-
bilateral common femoral vein punctures with a guiding catheter/microcatheter set-up
one sheath should be over-sized to allow for peripheral venous sampling, or alternatively, a peripheral IV can be located and a non-scrubbed assistant can withdraw the peripheral sample.
heparin: given the length of time catheters remain in situ, heparin is administered to prevent venous sinus thrombosis. Typically 5,000 unit bolus5.
-
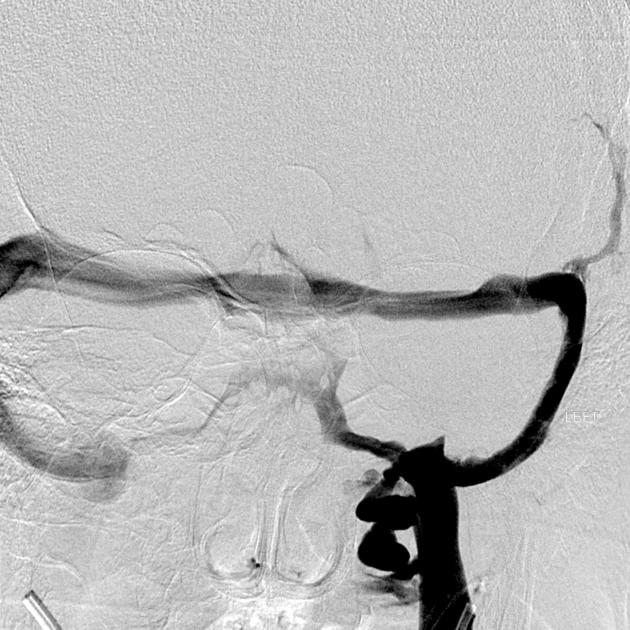
once a catheter is located in the jugular bulb rapid injection of contrast is performed to attempt to reflux contrast into the inferior petrosal sinus to guide placement of a micro-catheter
if access to the sinus is difficult then an arterial puncture can be performed to enable a common carotid injection and road mapping of the IPS
it is important to note that in ~7% of patients the inferior petrosal sinus does not drain into the jugular bulb, but rather directly into the vertebral venous plexus 4
each sinus is catheterized with the micro-catheter, a similar distance from the gland
baseline samples are obtained (one or two sets) simultaneously from both catheters and the periphery
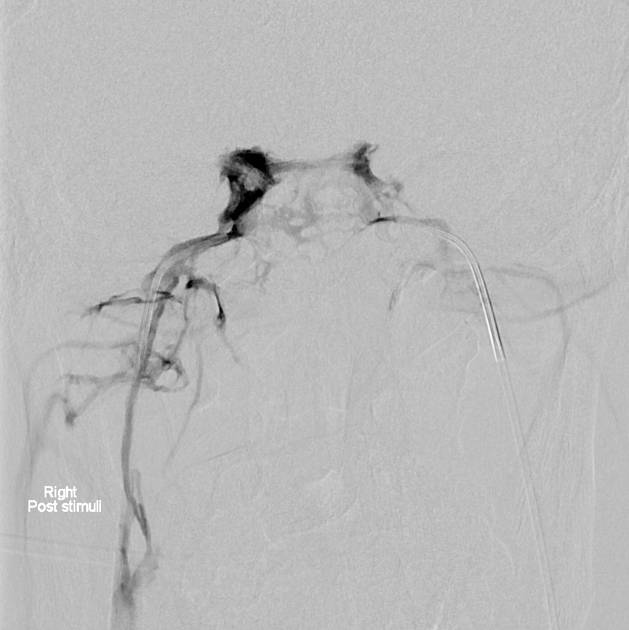
corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH) is administrated (100 µg IV 5).
-
sequential, simultaneous samples (e.g. at 3, 5, 10 and 15 minutes) are then obtained.
one of the greatest pitfalls is mislabeling the numerous samples. Ideally, 5 personnel are required. Three to aspirate, one to transfer into the EDTA tubes and another to keep track of time, etc...
submit samples for laboratory assays.
Interpretation of results
IPSS is a highly sensitive and specific examination series reporting near 100% values for both. Exact ratio values will vary between institutions. Typically published ratios are:
-
Pre CRH
>1.7:1 central:peripheral = pituitary source
<1.5:1 central:peripheral = ectopic source
-
Post CRH
>3.3:1 central:peripheral = pituitary source
<1.8:1 central:peripheral = ectopic source
-
Lateralization
>1.4:1 interpetrosal gradient
Complications
Complications are rare, but reported, and include:
In a large review of 508 patients 2, a single complication was observed (0.2%), although a conservative 1% incidence of serious complications has been suggested be quoted.






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.