Meconium pseudocyst forms in response to meconium peritonitis, isolating the meconium from the rest of the peritoneum into one or several cystic lesions.
Pathology
It occurs when the extruded meconium becomes walled off within the peritoneal space.
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
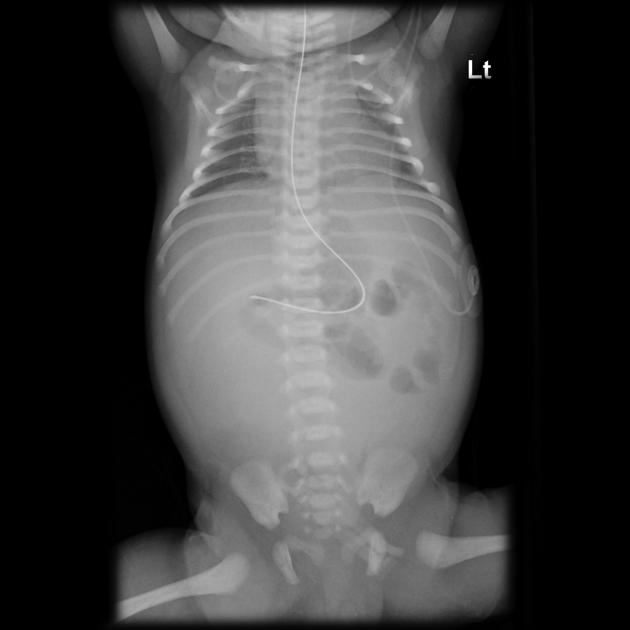
Appearance varies depending on the size of the pseudocyst and the timing of the in-utero bowel perforation. An abdominal radiograph may show:
calcification: Thin, eggshell-like rim is classic. There may also be none, amorphous, or flocculant calcifications.
air: A large air-fluid level may be present. In the absence of calcifications, this can be confused for a dilated loop of bowel or loculated pneumoperitoneum.
displaced bowel: In the absence of calcification and air, displaced bowel may be the only finding on x-ray.
Ultrasound
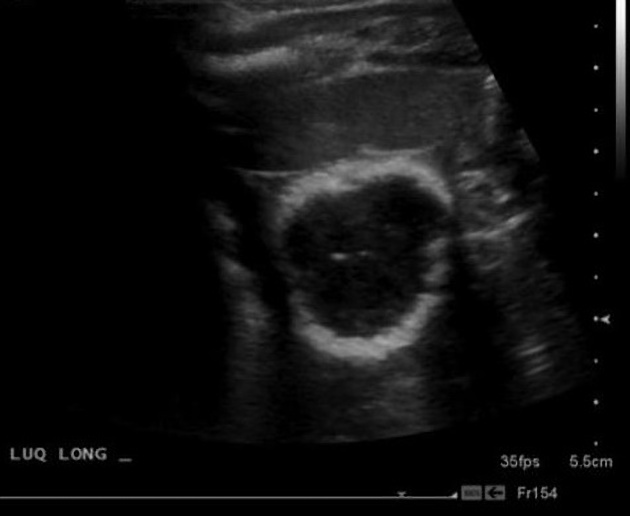
Meconium pseudocyst may be sonographically seen as a relatively well-defined avascular hypoechoic mass often surrounded by an echogenic calcified wall 2.
MRI
On Fetal MRI, meconium pseudocysts manifest as high T1, low T2 signal cystic lesions, similar to meconium, but not within bowel.





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.