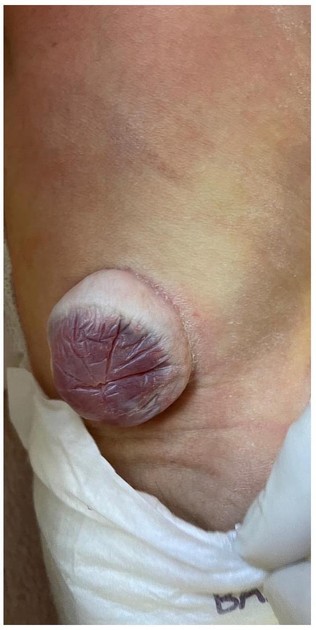
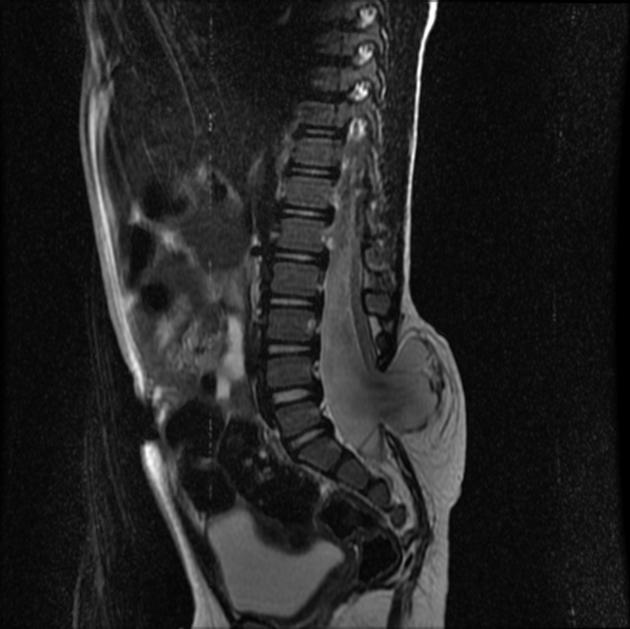
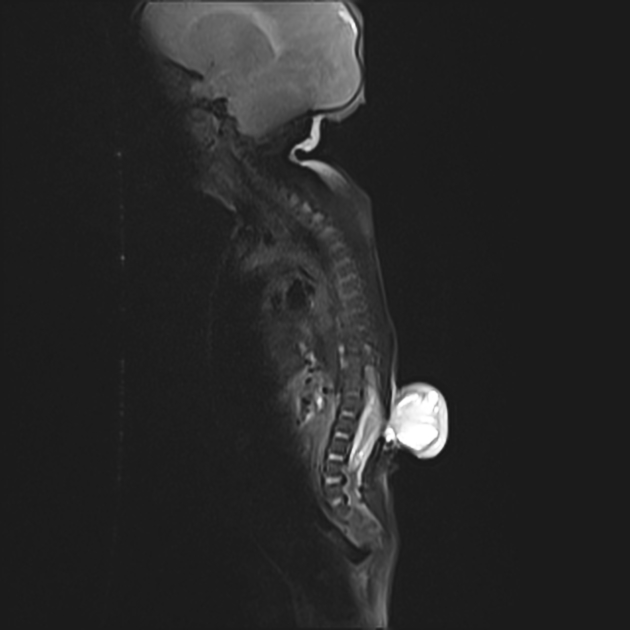
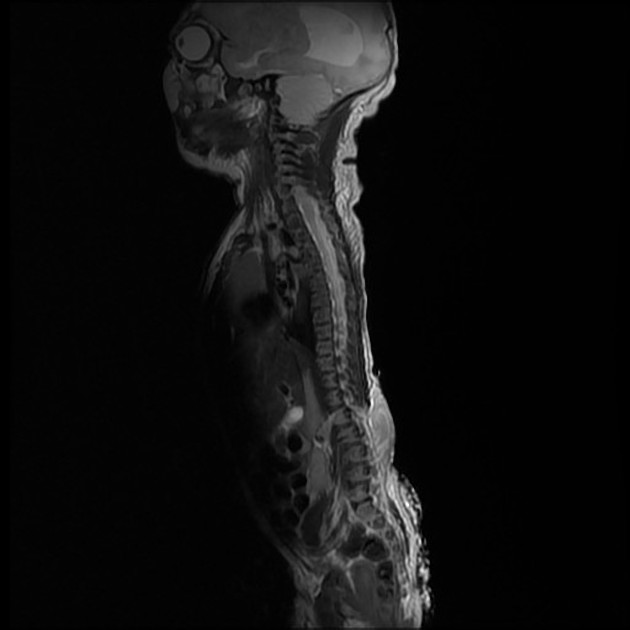
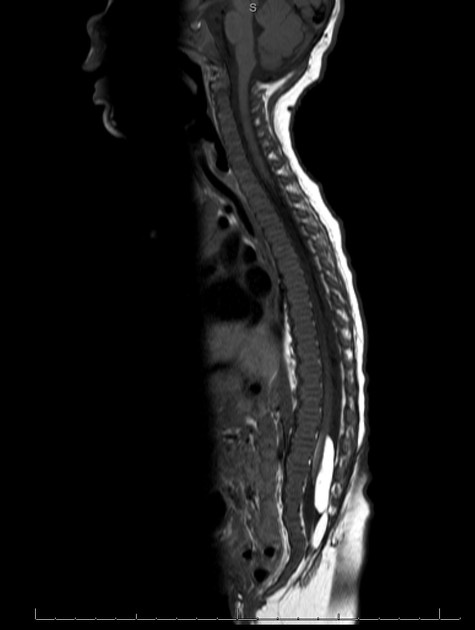
Myelomeningocele, also known as spina bifida cystica, is a complex congenital spinal anomaly that results in spinal cord malformation (myelodysplasia).
On this page:
Epidemiology
It is one of the most common congenital CNS anomalies and is thought to occur in approximately 1:500 of live births 5. There may be a slight female predilection.
Clinical presentation
Patients present with lower limb paralysis and sensory loss, bladder and bowel dysfunction as well as cognitive impairment.
Pathology
Results from failure of fusion of neural tube dorsally during embryogenesis.
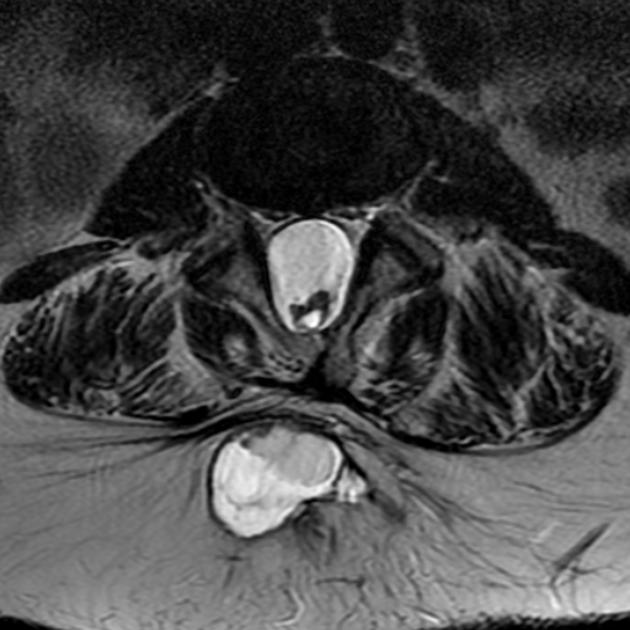
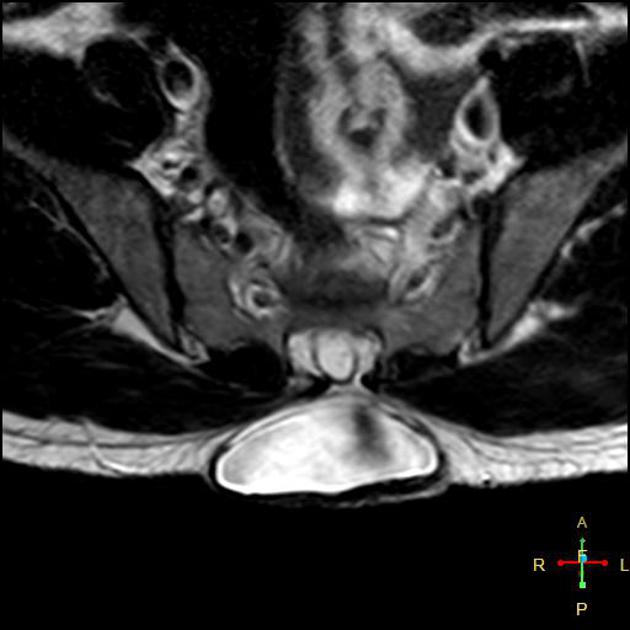
There is a localized defect of the closure of caudal neuropore with persistence of neural placode (open spinal cord).
Location
lumbosacral: ~45%
thoracolumbar: ~30%
lumbar: ~20%
cervical: ~2%
Risk factors
in utero folate deficiency
in utero teratogen exposure
Markers
Associations
-
aneuploidy anomalies
Radiographic features
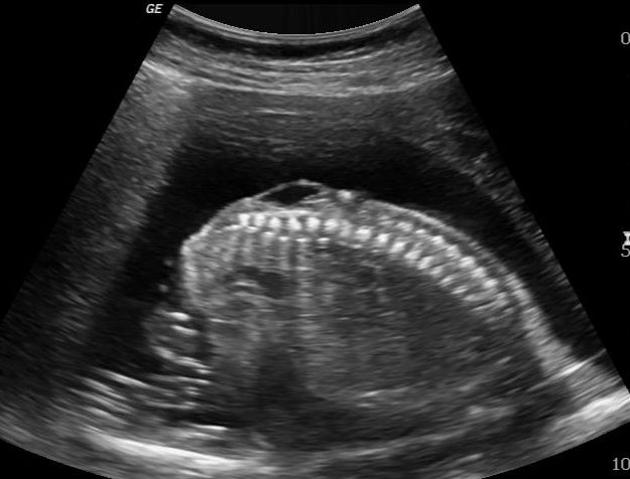
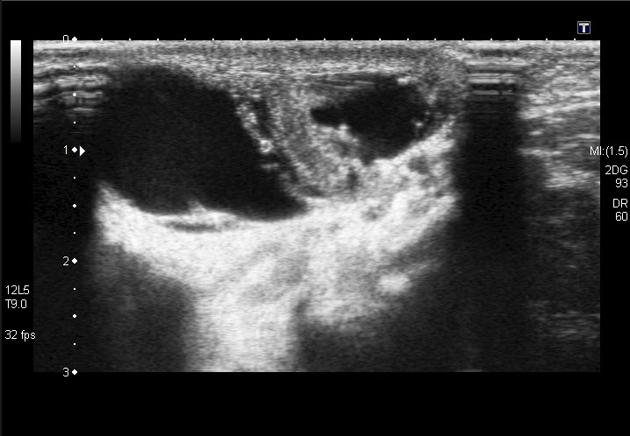
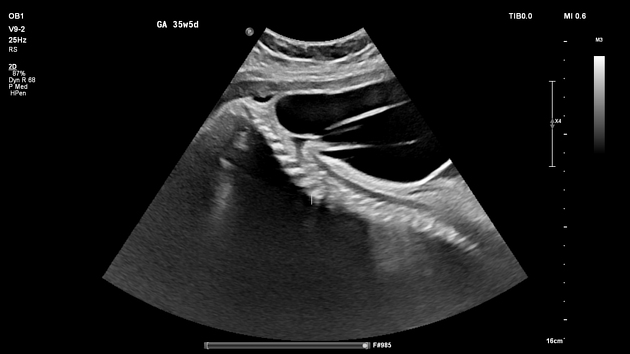
Ultrasound
may show evidence of an open neural tube defect with splayed or divergent posterior elements







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.