Nasogastric tube position on chest x-ray (summary)
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Henry Knipe had the following disclosures:
- Radiopaedia Events Pty Ltd, Speaker fees (past)
- Integral Diagnostics, Shareholder (ongoing)
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures- NG tube position on chest x-ray (summary)
This is a basic article for medical students and other non-radiologists
Nasogastric (NG) tube position on chest x-ray should be assessed following initial placement and on subsequent radiographs.
Reference article
This is a summary article; we have a more in-depth reference article NGT.
Summary
-
confirming position
- x-rays are only performed when the position is uncertain
- most tube positions are checked by assessing pH of tube aspirate
-
normal
- tube descends the thorax in the midline
- tube bisects the carina
- tube crosses the diaphragm in the midline
- the tip sits below the diaphragm
-
viewing the tube
- you need to be confident that you can see the tip
- most tubes are visible on a chest x-ray without a guide wire
- changing the windowing of the radiograph is helpful
- if you are not sure, discuss with a senior
-
malposition
- nasogastric tubes may end up in the airways
- feeding through a malpositioned tube can be disastrous
Quiz questions
Question 2099
A premature male neonate (born at 33 weeks gestation) underwent CXR which confirmed the presence of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and a left-sided pneumothorax. Subsequently, as a part of the treatment, multiple tubes/lines were placed. Which of the following tube/line is malpositioned on the shown chest x-ray?
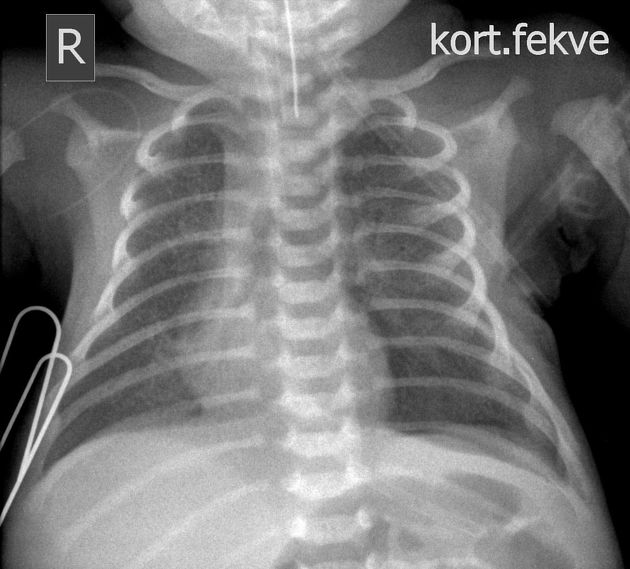
References
- 1. NHS National Patient Safety Alert (2011) PDF
Incoming Links
- Malpositioned nasogastric tube in right main bronchus
- Misplaced nasogastric tube
- Nasogastric tube in the right lung
- Surfactant deficiency disorder and Broviac line
- Overlying densities simulating pneumothorax
- Malpositioned nasogastric tube
- Kinked nasogastric tube
- Spinnaker sign - pneumomediastinum
- Nasogastric tube terminating in left bronchus
- Misplaced nasogastric tube - right main bronchus
- Nasogastric tube position confirmation
- Misplaced nasogastric tube
- Normal positioning of chest lines and tubes (portable radiograph)
- Feeding tube in the pleural space
- Misplaced nasogastric tube - pharyngeal perforation
- Nasogastric tube in left lower lobar bronchus
- Incorrect nasogastric tube positioning
- Nasogastric tube in right main bronchus
- Misplaced nasogastric tube into the left lung
- Misplaced nasogastric tube resulting in pneumothorax
Related articles: Education: Medical student curriculum
- radiology for students
-
neuroradiology
- imaging
- key findings
- conditions
- presentations
- cardiac radiology
-
chest radiology
- imaging
- key findings
- conditions
- presentations
-
abdominal radiology
- imaging
- key findings
- conditions
- upper GI
- lower GI
- hepatopancreatobiliary
- genitourinary
- vascular
- breast
- presentations
-
musculoskeletal radiology
- imaging
- key findings
- interpretation
- conditions
- upper limb
- lower limb
- pelvic fractures
- proximal femoral fractures
- distal fibula fracture
- 5th metatarsal fracture
- paediatrics
- spine
- major trauma
- joint pain/arthritis
- presentations
- upper limb
- lower limb
- hip trauma
- lower limb injury
- foot and ankle injury
- joint pain/arthritis
-
obstetrics and gynaecology imaging
- imaging
- pelvic US - transabdominal
- pelvic US - transvaginal
- hysterosalpingogram
- CT abdomen
- MRI pelvis
- key findings
- endometrial thickening
- ovarian cysts
- conditions
- non-obstetric
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- tubo-ovarian abscess
- ovarian torsion
- ovarian neoplasms
- endometriosis
- endometrial hyperplasia
- endometrial carcinoma
- cervical cancer
- obstetric
- normal pregnancy
- abnormal first trimester
- ectopic pregnancy
- heterotopic pregnancy
- twins
- non-obstetric
- presentations
- PV bleeding
- pelvic pain
- PV discharge
- early pregnancy
- imaging
-
paediatric radiology
- imaging
- key findings
- conditions
- presentations






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.