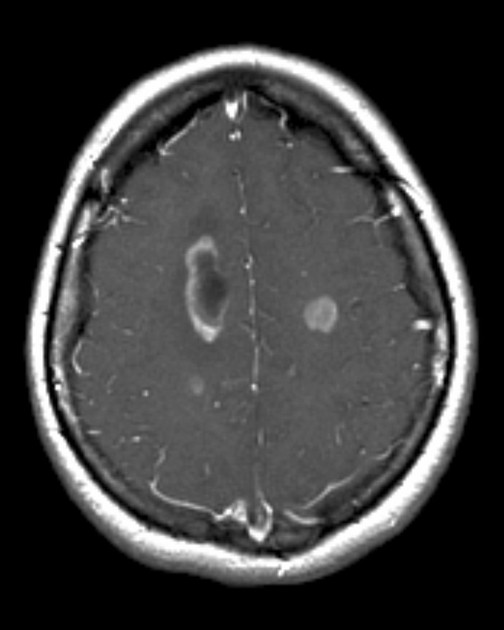
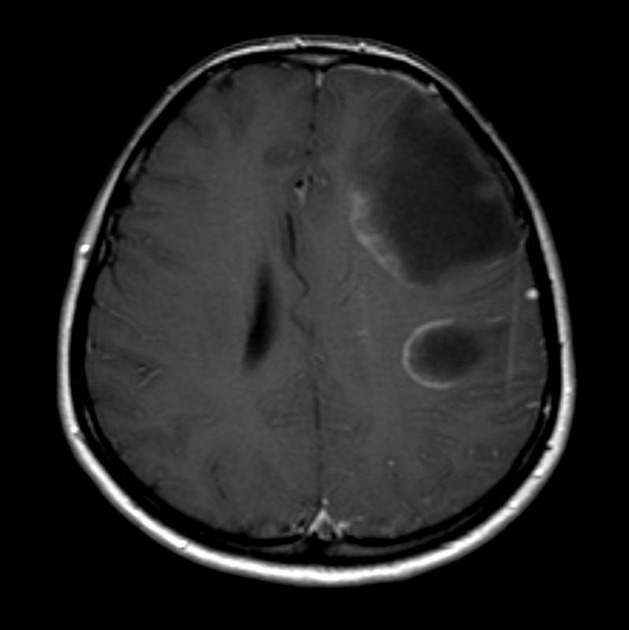
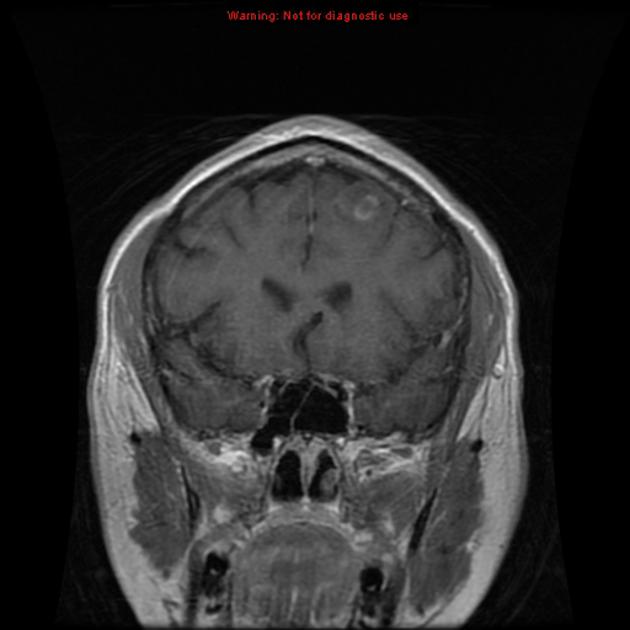
Open ring sign
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Frank Gaillard had the following disclosures:
- Biogen Australia Pty Ltd, Investigator-Initiated Research Grant for CAD software in multiple sclerosis: finished Oct 2021 (past)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosures- Incomplete ring enhancement sign
- Open ring enhancement
The open ring sign is a relatively specific sign for demyelination, most commonly multiple sclerosis (MS), and is helpful in distinguishing between the causes of ring-enhancing lesions.
Radiographic features
The enhancing component is thought to represent advancing front of demyelination and thus favors the white matter side of the lesion. The open part of the ring will therefore usually point towards the grey matter 3.
Treatment and prognosis
Often patients with such lesions undergo biopsy, where the histology can be difficult to interpret. Abundant bizarre astrocytes with frequent mitoses can suggest the diagnosis of glioblastoma. Toxoplasmosis may also be suggested by the presence of giant cells (Creutzfeldt cells).
As such, careful assessment of imaging is essential to avoid unnecessary and misleading intervention.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Masdeu JC, Quinto C, Olivera C et-al. Open-ring imaging sign: highly specific for atypical brain demyelination. Neurology. 2000;54 (7): 1427-33. Neurology (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Siddiqui A, Sahni A, Khadilkar S. The open-ring sign. Neurol India. 2005;53 (2): 253-4. Neurol India (link) - Pubmed citation
- 3. Given CA, Stevens BS, Lee C. The MRI appearance of tumefactive demyelinating lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182 (1): 195-9. AJR Am J Roentgenol (full text) - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM)
- Demyelination protocol (MRI)
- Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder
- Marburg variant of multiple sclerosis
- Levamisole-induced leukoencephalopathy
- Cerebral ring enhancing lesions
- Tumefactive demyelinating lesion
- Multiple sclerosis
- Supratentorial intracranial mass in an adult (an approach)
- Tumefactive demyelinating lesion
- Multiple sclerosis and left optic neuritis
- Multiple sclerosis
- Tumefactive demyelinating lesion
- Tumefactive multiple sclerosis
- Tumefactive demyelination
- Tumefactive multiple sclerosis
- Multiple sclerosis
- Demyelination - incomplete ring enhancement
- Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
Related articles: White matter disorders
- white matter
- normal myelination
- terminology[+][+]
-
white matter disorders
-
demyelination
- general articles[+][+]
- acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM)[+][+]
- acute hemorrhagic encephalomyelitis (AHEM)
- anti-MOG associated encephalomyelitis (MOGAD)
- neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD)[+][+]
-
multiple sclerosis (MS)
-
McDonald diagnostic criteria for MS (2017 revision)[+][+]
- previous 2016 MAGNIMS consensus
- signs
- central vein sign
- Dawson fingers
- open ring enhancement
- paramagnetic rim lesions
- T1 black holes
- variants[+][+]
-
McDonald diagnostic criteria for MS (2017 revision)[+][+]
- radiologically isolated syndrome (RIS)
- clinically isolated syndrome (CIS)
- astrocytopathies[+][+]
- leukoaxonopathies[+][+]
- early-onset neuronal degenerative disorders
- giant axonal neuropathy
- hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum (H-ABC)
- hypomyelination with congenital cataract
- leukoencephalopathy with brainstem and spinal cord involvement and lactate elevation
- hypomyelination with brainstem and spinal cord involvement and leg spasticity
- pol III-related leukodystrophies
- leukovasculopathies[+][+]
- CADASIL
- CARASIL
- cathepsin A-related arteriopathy with strokes and leukoencephalopathy (CARASAL)
- cerebral amyloid angiopathy
- COL4A1 brain small-vessel disease
- Fabry disease
- heterozygous HTRA1-related cerebral small vessel disease
- leukoencephalopathy with calcifications and cysts (Labrun syndrome)
- pontine autosomal dominant microangiopathy with leukoencephalopathy (PADMAL)
- retinal vasculopathy with cerebral leukoencephalopathy and systemic manifestations (RVCL-S)
- microgliopathies[+][+]
- myelin disorders[+][+]
- hypomyelination
- demyelination
- myelin vacuolisation
- other[+][+]
- adult polyglucosan body disease
- adult-onset autosomal dominant leukodystrophy
- cerebrotendinous xanthomathosis
- cystic leukoencephalopathy without megalencephaly
- L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria
-
lysosomal storage diseases
- free sialic acid storage disorders (e.g. Salla disease)
- Niemann-Pick disease
- peroxisomal disorders
- Sjögren-Larsson syndrome
-
demyelination





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.