Portosystemic collateral pathways
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Donna D'Souza had no recorded disclosures.
View Donna D'Souza's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Nicholas Verikios had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Nicholas Verikios's current disclosures- Porto-systemic collateral pathways
- Portal-systemic collaterals
- Porto-systemic collaterals
- Portosystemic shunts
- Porto-systemic shunts
- Porto-systemic shunt
- Portal-systemic collateral pathways
- Portosystemic collaterals
- Portosystemic collateral pathways
- Portosystemic shunt
- Varices (portosystemic shunts)
- Spontaneous portosystemic shunt
- Spontaneous portosystemic shunts
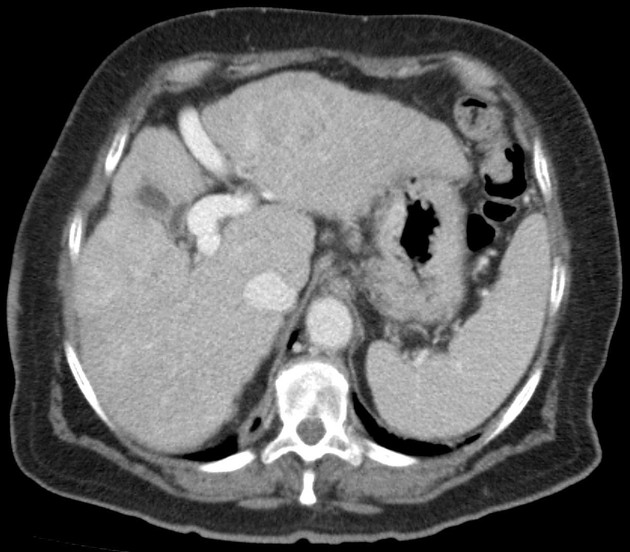
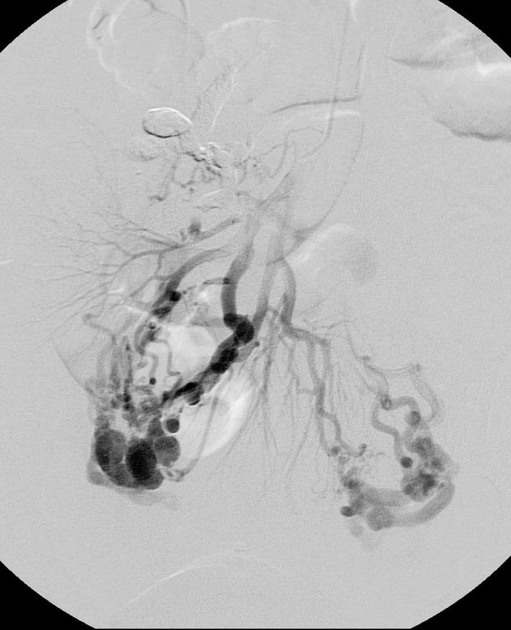
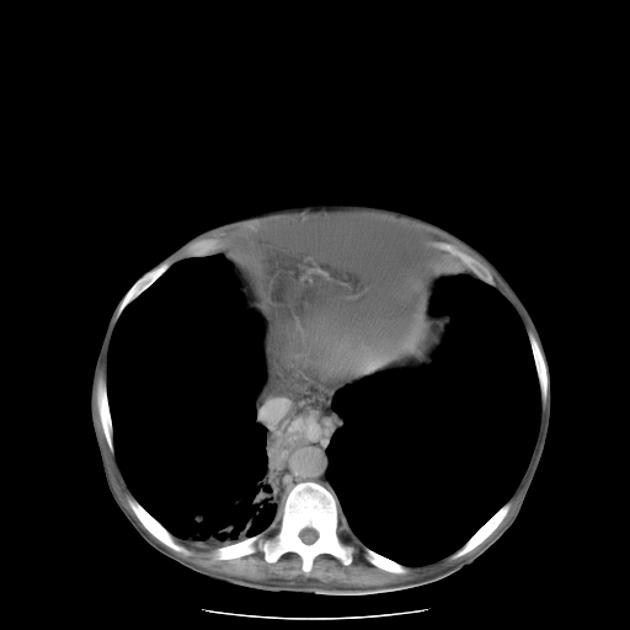
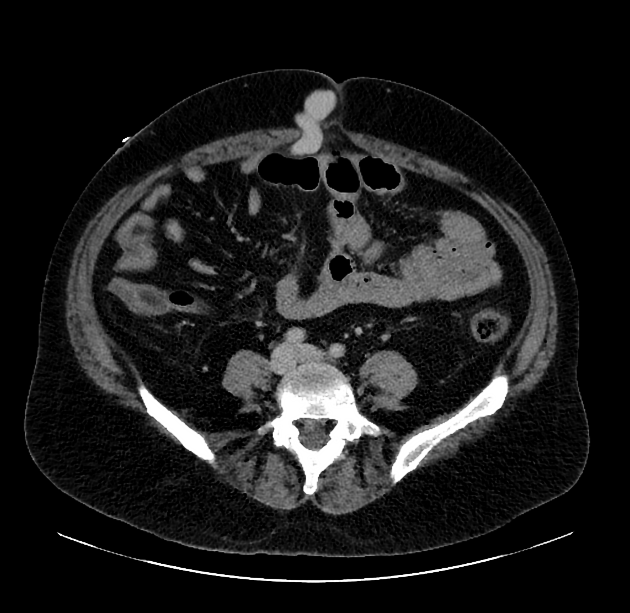
Portosystemic collateral pathways, also called spontaneous portosystemic shunts or varices, develop spontaneously via dilatation of pre-existing anastomoses between the portal and systemic venous systems. This facilitates shunting of blood away from the liver into the systemic venous system in portal hypertension, as a means for reducing portal venous pressure. However, these are not sufficient for normalizing portal venous pressure.
The main sites of portosystemic collateral pathways are:
-
left gastric (see gastric varices)
left gastric (coronary) vein and short gastric veins to distal esophageal veins
located between medial wall of gastric body and posterior margin of left hepatic lobe in lesser omentum
usually accompanied by esophageal/paraesophageal varices (see below)
esophageal: dilated submucosal venous plexus of distal esophagus (see esophageal varices)
-
paraesophageal
coronary vein to azygos and hemiazygos veins and vertebral venous plexus
located posterior to esophagus in posterior mediastinum
perisplenic: splenic vein to left renal vein, traversing splenocolic ligament; may eventuate in a spontaneous splenorenal shunt
-
retrogastric
left gastric (coronary) vein or gastroepiploic vein to esophageal or paraesophageal veins
located in posterior/posteromedial aspect of gastric fundus
retroperitoneal-paravertebral: colic or mesenteric branches of superior mesenteric vein to retroperitoneal/lumbar veins to the inferior vena cava
paraumbilical: left portal vein to paraumbilical veins in anterior ridge of falciform ligament
anterior abdominal wall: paraumbilical and omental veins to subcutaneous periumbilical veins and superior and inferior epigastric veins; collaterals appear to radiate from the umbilicus (caput medusae)
mesenteric: dilated branches of superior mesenteric vein
anal canal: superior rectal vein (from the inferior mesenteric vein) to upper anal canal veins (hemorrhoids)
Differential diagnosis
Dilatation of splenic veins at the splenic hilum mimicking splenic hilar varices without splenomegaly may occur in situations such as increased perfusion of splenic tissue associated with an immune response 4.
References
- 1. Kaufman JA, Lee MJ. Vascular & interventional radiology. Mosby Inc. (2004) ISBN:0815143699. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Sinnatamby CS, Last RJ. Last's anatomy, regional and applied. Churchill Livingstone. (2006) ISBN:0443100330. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Schuenke M, Schulte E, Schumacher U et-al. Neck and Internal Organs. Thieme. ISBN:1604062940. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Stella SM, Giunta S, Galetta F et-al. Dilation of venous vessels at the splenic hilum in normal sized spleens as an indication of pathologic splenic involvement: preliminary results. J Ultrasound Med. 1993;12 (6): 349-53. Pubmed citation
- 5. Sharma M, Rameshbabu CS. Collateral pathways in portal hypertension. Journal of clinical and experimental hepatology. 2 (4): 338-52. doi:10.1016/j.jceh.2012.08.001 - Pubmed
- 6. Lee W, Chang S, Duddalwar V et al. Imaging Assessment of Congenital and Acquired Abnormalities of the Portal Venous System. Radiographics. 2011;31(4):905-26. doi:10.1148/rg.314105104 - Pubmed
- 7. Stephanie Ryan, Michelle McNicholas, Stephen J. Eustace. Anatomy for Diagnostic Imaging. (2011). ISBN: 9780702029714 - Google Books
- 8. Nardelli S, Riggio O, Turco L et al. Relevance of Spontaneous Portosystemic Shunts Detected with CT in Patients with Cirrhosis. Radiology. 2021;299(1):133-40. doi:10.1148/radiol.2021203051 - Pubmed
- 9. Philips C, Arora A, Shetty R, Kasana V. A Comprehensive Review of Portosystemic Collaterals in Cirrhosis: Historical Aspects, Anatomy, and Classifications. Int J Hepatol. 2016;2016:1-15. doi:10.1155/2016/6170243 - Pubmed
- 10. Grant E, Tessler F, Gomes A et al. Color Doppler Imaging of Portosystemic Shunts. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990;154(2):393-7. doi:10.2214/ajr.154.2.2105035 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension
- Upper gastrointestinal bleeding (differential)
- Splenic vein
- Hepatic encephalopathy
- Caroli disease
- Ascending colon
- Esophagus
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
- Hepatopulmonary syndrome
- Gastric varix
- Congenital portosystemic shunt
- Rectum
- Portal hypertension
- Spontaneous splenorenal shunt
- Esophageal balloon tamponade device
- Schistosomiasis (hepatic manifestations)
- Anterior abdominal wall
- Portal hypertensive gastroenterocolopathy
- Upper gastrointestinal bleeding
- Portal vein
- Recanalised paraumbilical vein
- Recurrent pyogenic cholangiohepatitis
- Gallbladder varices
- Vesical varices
- Cirrhosis with portal hypertension and dilation of paraumbilical veins
- Diffuse hepatocellular carcinoma with malignant portal vein thrombus
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Hepatic abscesses and large splenic abscess
- Nutcracker syndrome
- Gallbladder varices
- Cavernous transformation of portal vein
- Intramural gastric haematoma with haemoperitoneum
- Retroperitoneal teratoma
- Portosystemic shunt syndrome in liver cirrhosis
- Appendiceal mucocele
- Extrahepatic portosystemic shunt
- Ovarian vein thrombosis
- Congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunt
- Portal hypertension
- Intrahepatic portal vein-hepatic vein fistula
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- benign epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumors
- primary malignant epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumors
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumors
- hematopoietic and lymphoid tumors
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumors
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumors
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic hemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumor
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumor
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumor
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumors
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumors
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.