Pseudomeningoceles are abnormal collections of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that occur due to a defect in the dura surrounding the brain and/or spinal cord. They most commonly occur as a result of trauma or surgery and can result in a variety of local or distant complications.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Psuedomeningoceles are fairly commonly seen following posterior fossa decompression surgery (e.g. Chiari 1 malformation decompression). Spinal pseudomeningoceles occur after accidental and unrecognised durotomies during spinal surgery (e.g. laminectomy or discectomy) 4,5.
Pseudomeningoceles can also occur following trauma (e.g. nerve root avulsions and intraosseous pseudomeningoceles).
Clinical presentation
Pseudomeningoceles can present in a variety of ways depending on their location, size, and whether they communicate with other body cavities or surfaces.
Some may merely present as soft swellings deep to a surgical wound. If the wound dehises, CSF may leak out, potentially resulting in intracranial hypotension and/or meningitis 5.
If left untreated, the walls of the pseudomeningocele, not being lined by dura, can cause a chronic leak of blood products in the CSF, resulting in superficial siderosis, which can present in a variety of ways, most commonly sensorineural hearing loss 7.
Large pseudomeningoceles may also cause sudden rise of intracranial pressure when external pressure is applied to the collection 8.
Pathology
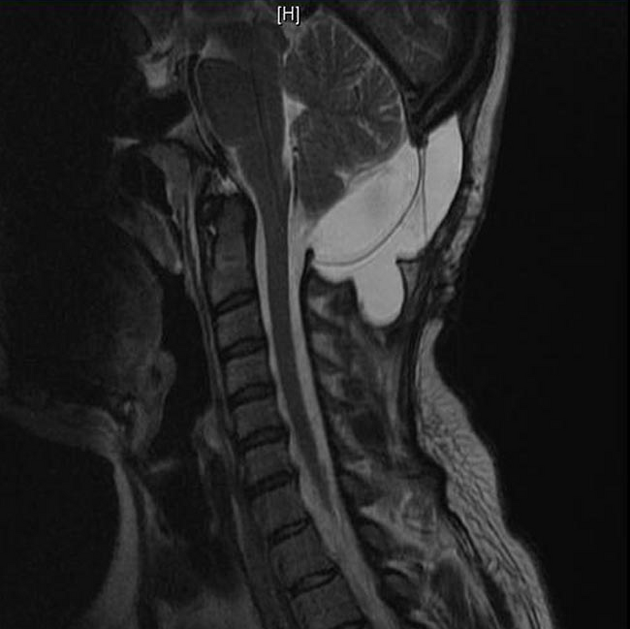
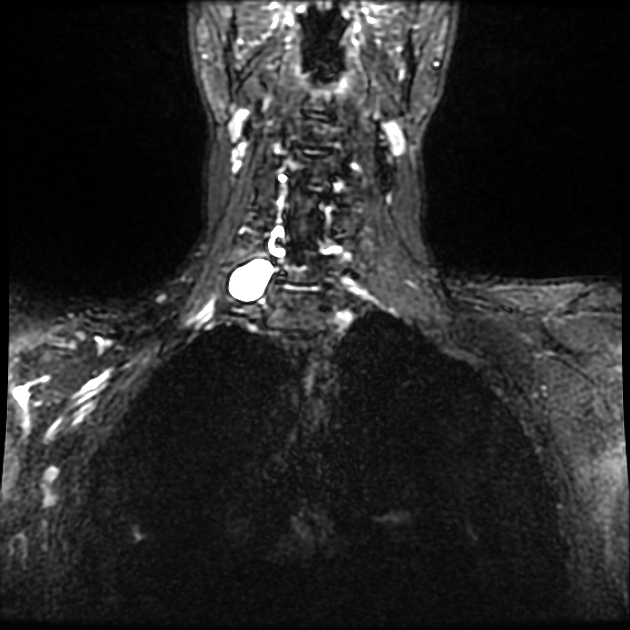
A pseudomeningocele is a collection of CSF that communicates with the CSF surrounding the brain or spinal cord. Unlike meningoceles, pseudomeningoceles are not lined by dura.
Radiographic features
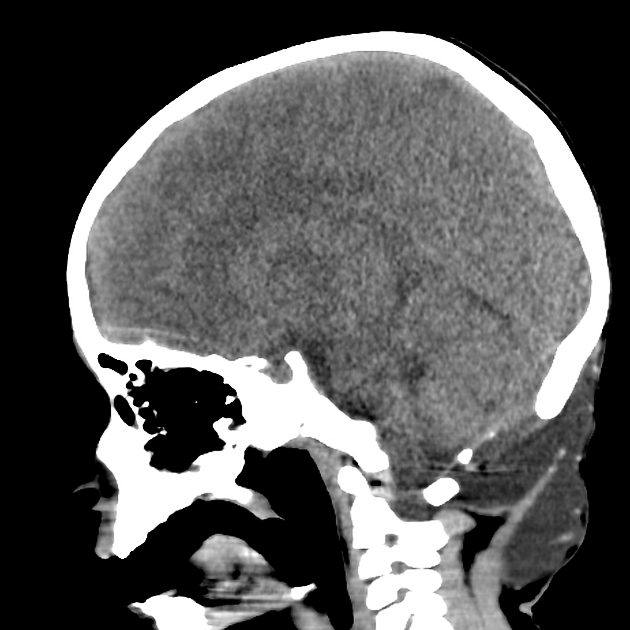
CT
Typically appears as a hypoattenuating collection that extends to the dura with minimal peripheral enhancement and with similar attenuation to CSF elsewhere.
MRI
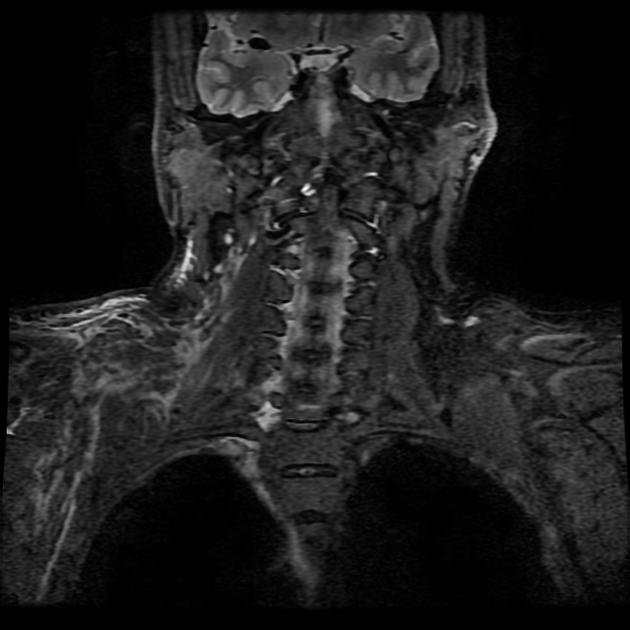
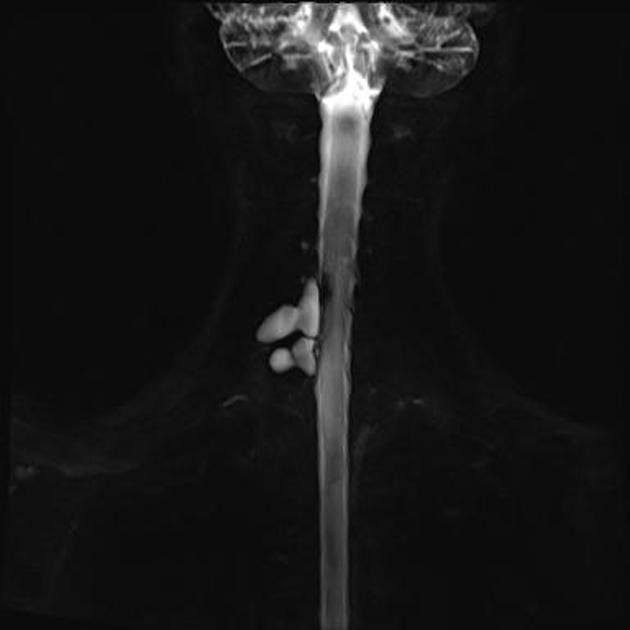
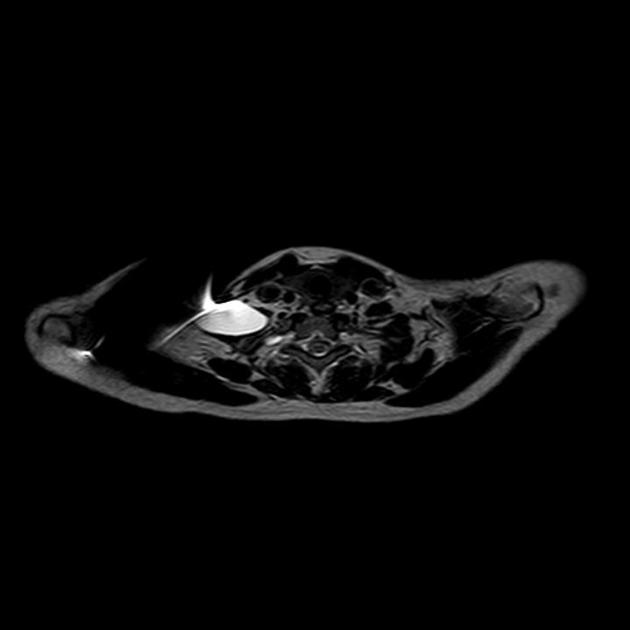
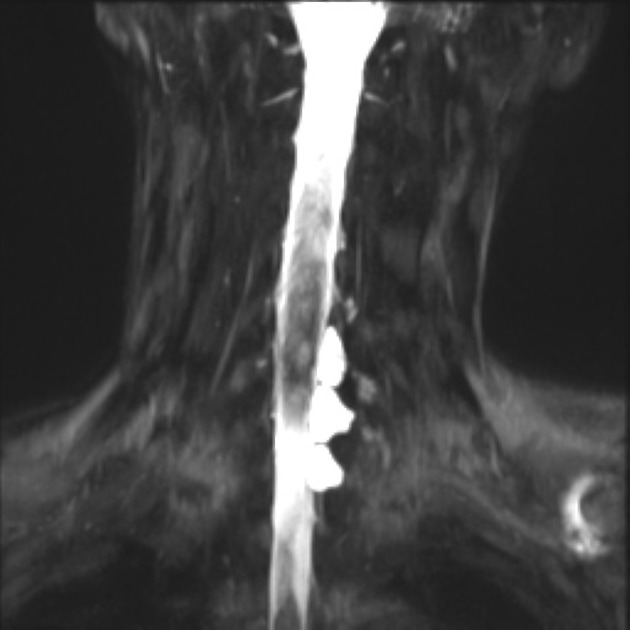
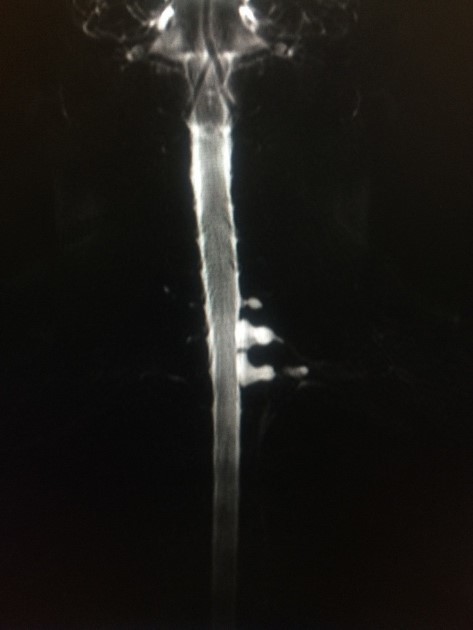
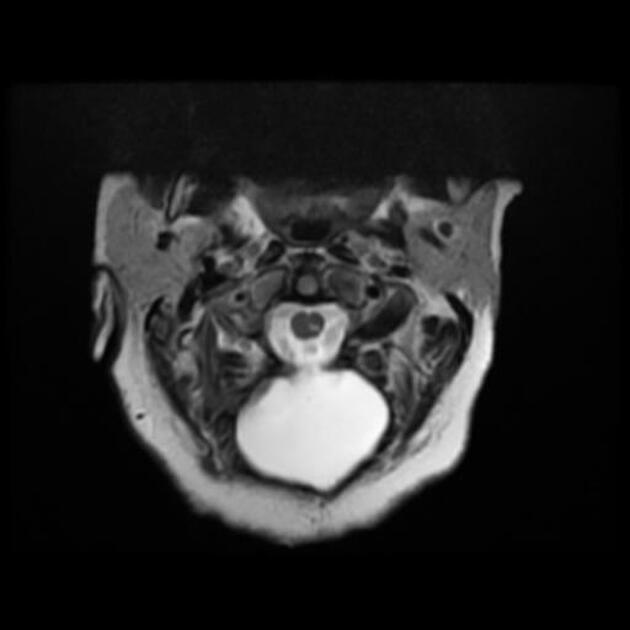
The pseudomeningocele follows CSF signal on all sequences. A communication with the subarachnoid space may be directly visualized as a fluid signal tract or as a jet of signal loss on T2 weighted sequences 9.
An important feature to look for is signs of superficial siderosis, typically seen in the posterior fossa or on the surface of the cord 7.
Treatment and prognosis
How pseudomeningoceles are treated depends on size, etiology and location. For example, early in the postoperative period spinal pseudomeningoceles can be treated with bed rest, introduction of a lumbar drain or targetted epidural blood patch 5. Alternatively, surgical exploration with dural repart can be performed, which may include oversewing the defect or the introduction of various dural substitutes (autograft, allograft, xenograft or artificial grafts) or tissue glues 6.
Differential diagnosis
postoperative seroma/abscess





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.