Sciatic nerve
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yuranga Weerakkody had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosures- Sciatic nerves
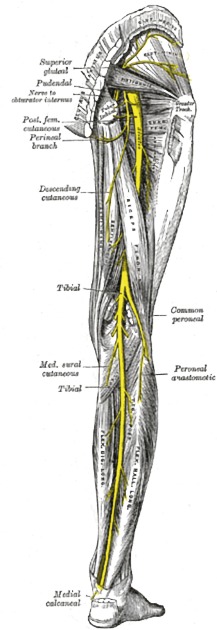
The sciatic nerve arises from the sacral plexus from the roots of L4-S3 and runs through the buttock and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the body.
On this page:
Summary
origin: sacral plexus (L4-S3)
course: exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen to enter the leg between ischial tuberosity and femoral greater trochanter, then courses inferiorly through the posterior compartment of the thigh
-
major branches
tibial nerve (L4-S3)
common peroneal nerve (L4-S2)
motor supply: see motor supply of the sciatic nerve
sensory supply: no direct sensory function. Indirect sensory supply to the foot (plantar surface: tibial nerve, dorsal surface: common peroneal nerve) and the leg (except its inner side, which is supplied by the saphenous nerve)
Gross anatomy
Origin
The nerve forms from the anterior divisions of the L4-S3 roots (which form the tibial component) and posterior divisions of the L4-S2 roots (which form the common peroneal component) of the sacral plexus.
Course
The sciatic nerve enters the lower limb by exiting the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen, below the piriformis muscle and above the superior gemellus muscle.
It descends midway in between the greater trochanter of the femur and the tuberosity of the ischium and in the posterior compartment of the thigh to the apex of the popliteal fossa, where it divides into two large terminal branches:
Relations
-
anteriorly
upper part: posterior surface of the ischium, nerve to quadratus femoris, obturator internus, the gemelli
lower part: adductor magnus
-
posteriorly
upper part: gluteus maximus
lower part: long head of biceps femoris (crosses obliquely)
In the upper part of its course, it is accompanied by the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve and the inferior gluteal artery, and is covered by the gluteus maximus muscle.
Branches
The nerve gives off articular and muscular branches before dividing into two terminal branches - the tibial nerve and the common peroneal nerve.
Articular branches
The articular branches arise from the upper part of the nerve and supply the hip joint, perforating the posterior part of its capsule; they are sometimes derived from the sacral plexus.
Muscular branches
The sciatic nerve supplies the following muscles:
biceps femoris: supply to short head arises from the common peroneal part, supply to long head arises from the tibial part
semitendinosus: arises from the tibial part
semimembranosus: arises from the tibial part
adductor magnus: arises from the tibial part
Variant anatomy
The division of the sciatic nerve into the common peroneal and tibial nerves may take place at any point between the sacral plexus and the lower third of the thigh. When it occurs at the sacral plexus, the common peroneal nerve usually pierces the piriformis muscle.
A range of other variants exist based on the relationship to the piriformis muscle.3
-
division in the pelvis with
common peroneal nerve piercing piriformis muscle and tibial nerve exiting below (mentioned above)
common peroneal nerve travelling above piriformis muscle and tibial nerve below
common peroneal nerve travelling above piriformis muscle and tibial nerve piercing pirformis muscle
both common peroneal nerve and tibial nerve travelling below piriformis muscle separately
sciatic nerve courses over piriformis muscle
sciatic nerve pierces piriformis muscle
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
appears as a hypoechoic round structure, situated deep to piriformis and gluteus maximus muscles 4
Related pathology
Pain and functional symptoms may be caused by a compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve. This may be caused by:
spinal disc herniation
degenerative disc disease
spinal stenosis
References
- 1. Standring S (editor). Gray's Anatomy (39th edition). Churchill Livingstone. (2011) ISBN:0443066841. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Chen CP, Shen CY, Lew HL. Ultrasound-guided injection of the piriformis muscle. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011;90 (10): 871-2. doi:10.1097/PHM.0b013e31822de72c - Pubmed citation
- 3. Tomaszewski KA, Graves MJ, Henry BM, Popieluszko P, Roy J, Pękala PA, Hsieh WC, Vikse J, Walocha JA. Surgical anatomy of the sciatic nerve: A meta-analysis. (2016) Journal of orthopaedic research : official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society. 34 (10): 1820-1827. doi:10.1002/jor.23186 - Pubmed
- 4. Rosse C, Gaddum-Rosse P. Hollinshead's textbook of anatomy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. (1997) ISBN:0397512562. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
- Superior gluteal nerve
- Greater sciatic foramen
- Inferior gluteal nerve
- Adductor magnus muscle
- Lumbosacral trunk
- Common peroneal nerve
- Persistent sciatic artery
- Soleus muscle
- Nerve to piriformis
- Judet and Letournel classification for acetabular fractures
- Nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus
- Obturator internus muscle
- Adductor minimus muscle
- Inferior gluteal artery
- Sciatic neuropathy
- Infrapiriform foramen (mnemonic)
- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour
- Medial circumflex femoral artery
- Flexor hallucis longus
- Gastrocnemius muscle
- Pseudoaneurysm of the left inferior gluteal artery with coil embolization
- Traumatic sciatic neuropathy
- Piriformis syndrome
- Piriformis syndrome
- Sacral plexus (Gray's illustration)
- Lower limb nerves (Gray's illustrations)
- Proximal hamstring injury and incidental intermuscular lipoma
- Post-injection sciatic nerve injury
- Hamstring injury
- Sciatica due to bilateral gluteal vein varicosities
- Sciatic nerve injury
- Sciatic nerve schwannoma
- Peripheral nerve sheath tumour - sciatic nerve
- Sciatic nerve injury
- Popliteal fossa (diagram)
- Sciatic nerve injury
- Atypical lipomatous tumor - thigh
- Sciatic neuropathy - orthopaedic hardware induced
- Sciatic nerve entrapment by soft tissue tumor
- Traumatic sciatic nerve injury
Related articles: Anatomy: Lower limb
- skeleton of the lower limb
- joints of the lower limb
-
hip joint
- ligaments
- muscles
- additional structures
- hip joint capsule
- zona orbicularis
- iliotibial band
-
hip bursae
- anterior
- iliopsoas bursa (iliopectineal bursa)
- lateral
- subgluteal bursae
- greater trochanteric bursa (subgluteus maximus bursa)
- subgluteus medius bursa
- subgluteus minimus bursa
- gluteofemoral bursa
- subgluteal bursae
- postero-inferior
- anterior
- ossification centres
-
knee joint
- ligaments
- anterior cruciate ligament
- posterior cruciate ligament
- medial collateral ligament
- lateral collateral ligament
- meniscofemoral ligament (mnemonic)
-
posterolateral ligamentous complex
- arcuate ligament
- patellar tendon and quadriceps tendon
- anterolateral ligament
- posterior oblique ligament
- oblique popliteal ligament
- medial patellofemoral ligament
- additional structures
- extensor mechanism of the knee
- groove for the popliteus tendon
- knee bursae
- anterior bursae
- medial bursae
- lateral bursae
- posterior bursae
- knee capsule
- lateral patellar retinaculum
- medial patellar retinaculum
- menisci
- pes anserinus (mnemonic)
- ossification centres
- ligaments
- tibiofibular joints
-
ankle joint
- regional anatomy
- medial ankle
- lateral ankle
- anterior ankle
- ligaments
- medial collateral (deltoid) ligament
- lateral collateral ligament
- additional structures
- ankle bursae
- ossification centres of the ankle
- variants
- regional anatomy
- foot joints
- subtalar joint
- mid-tarsal (Chopart) joint
-
tarsometatarsal (Lisfranc) joint
- ligaments
- intermetatarsal joint
- metatarsophalangeal joint
- interphalangeal joint
- ossification centres
-
hip joint
- spaces of the lower limb
-
muscles of the lower limb
- muscles of the pelvic group
- muscles of the thigh
- muscles of the leg
- anterior compartment of the leg
- posterior compartments of the leg
- lateral compartment of the leg
- muscles of the foot
- dorsal muscles
- plantar muscles
- 1st layer
- 2nd layer
- 3rd layer
- 4th layer
- accessory muscles of the lower limb
- accessory gluteal muscles
-
accessory muscles of the ankle
- accessory peroneal muscles
- accessory flexor digitorum longus muscle
- accessory soleus muscle
- peroneocalcaneus internus muscle
- tibiocalcaneus internus muscle
- extensor hallucis capsularis tendon
- anterior fibulocalcaneus muscle
- accessory extensor digiti secundus muscle
- tibioastragalus anticus of Gruber muscle
- vascular supply of the lower limb
- arterial supply of the lower limb
- venous drainage of the lower limb
- innervation of the lower limb
- lymphatic system of the lower limb
- lymphatic pathways
- anteromedial group
- anterolateral group
- posteromedial group
- posterolateral group
- lower limb lymph nodes
- lymphatic pathways
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- coeliac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses










 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.