Musculoskeletal manifestations of scleroderma are common although variable and are a major contributor to morbidity 7.
For a general discussion of scleroderma, please refer to the parent article: scleroderma.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Symptomatic joints are present in ~40% (range 12-65%) of patients when diagnosed and overall are present in ~60% (range 24-97%) of patients at sometime during their illness course 6,8.
Clinical presentation
Musculoskeletal presentations of scleroderma stiffness, pain, reduced dexterity, reduced power, which is often multifactorial in etiology 6-8:
-
joints:
arthralgia/arthritis in a non-specific oligo- or poly-articular pattern
fingers (particularly proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints), wrist and ankles are most commonly involved although any joint can be affected 8
tendons: tenosynovitis, tendon friction rub
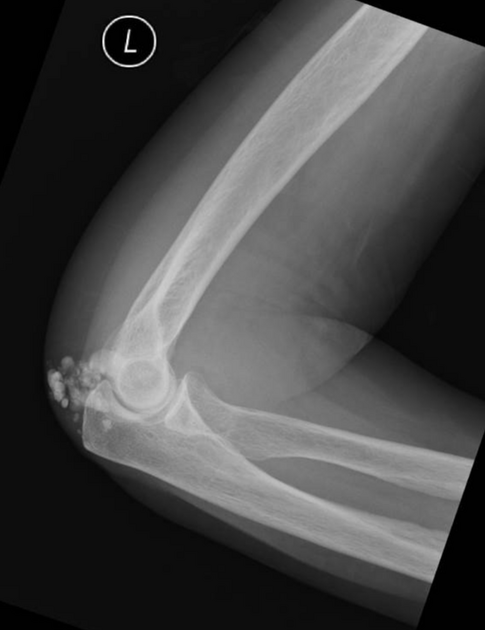
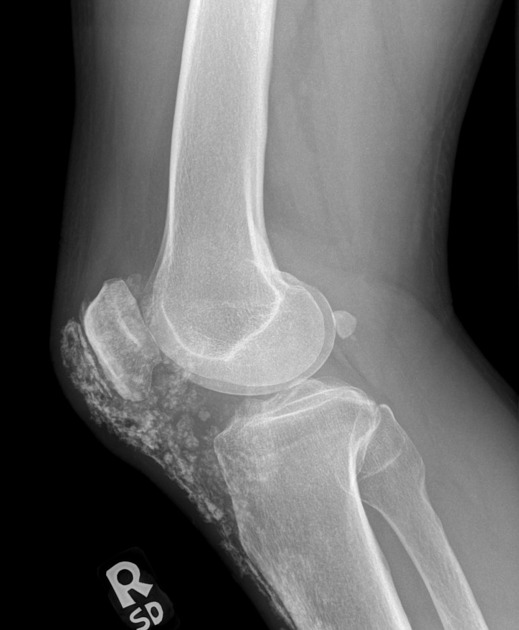
bursae: trochanteric and/or olecranon bursitis 8
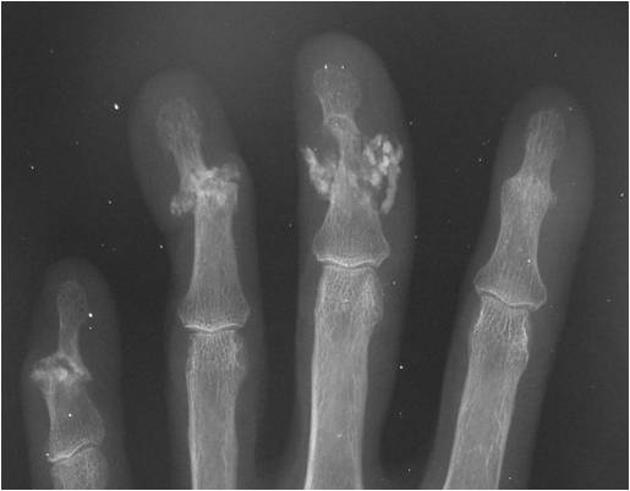
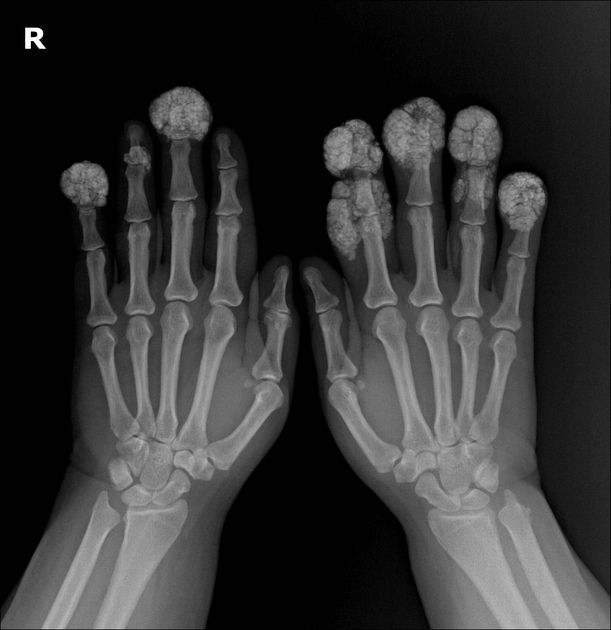
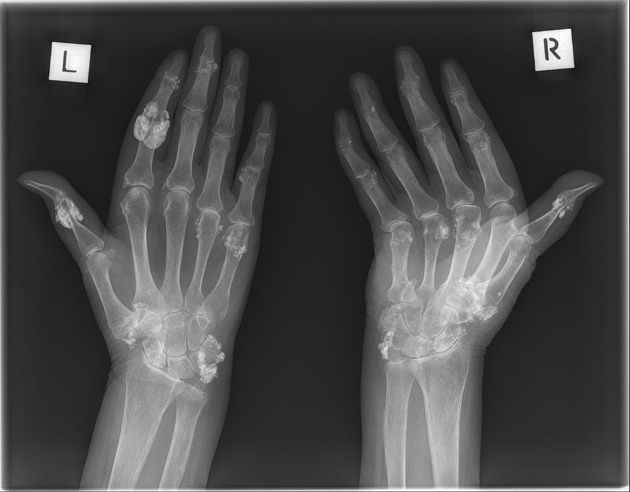
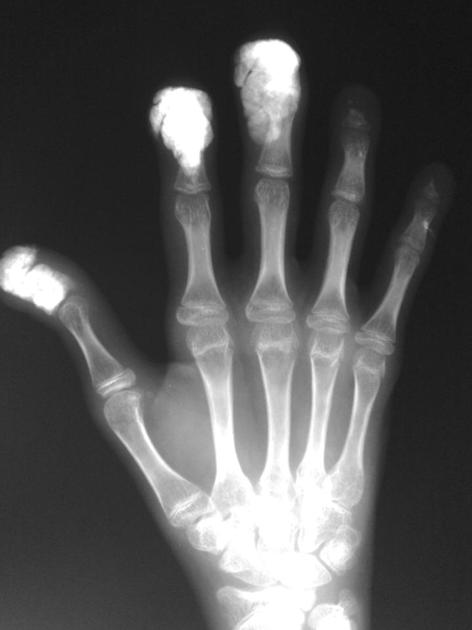
skin: cutaneous thickening resulting in contractures, soft tissue calcification
muscles: fibromyalgia, myositis (also see overlap myositis)
-
nerves:
carpal tunnel syndrome: thought to be from flexor tendon abnormalities in the cubital tunnel 8
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
Articular findings
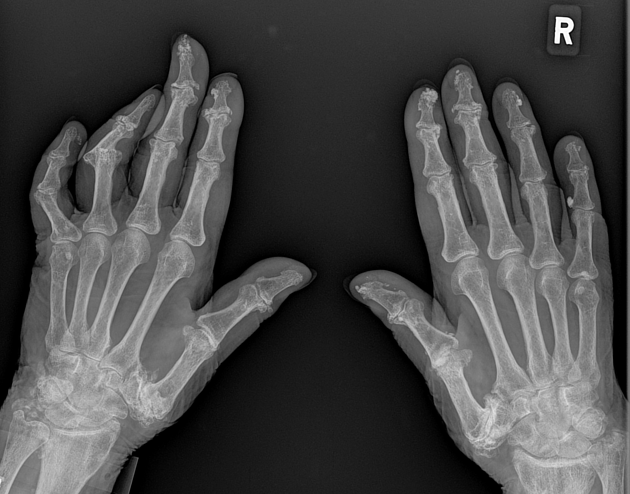
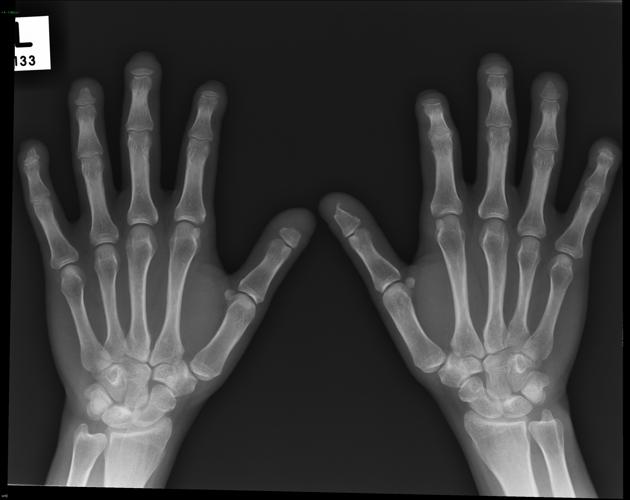
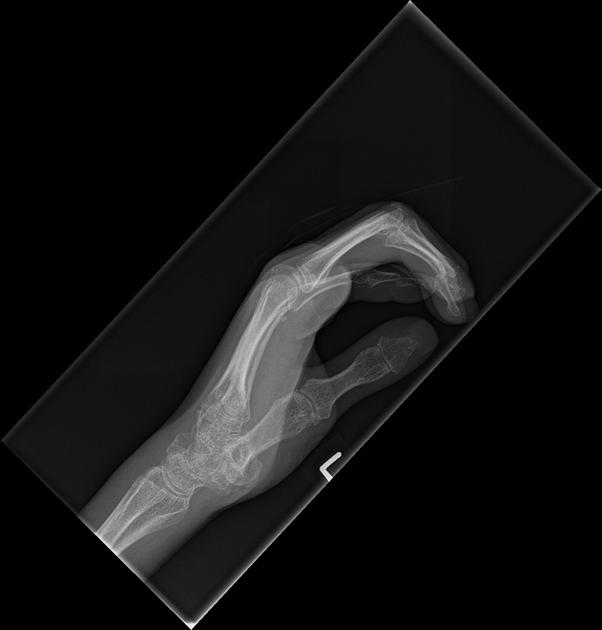
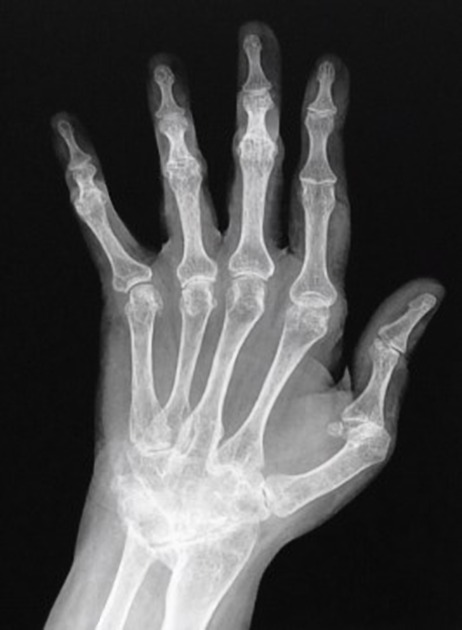
acro-osteolysis (resorption of the distal phalanges) 2-4
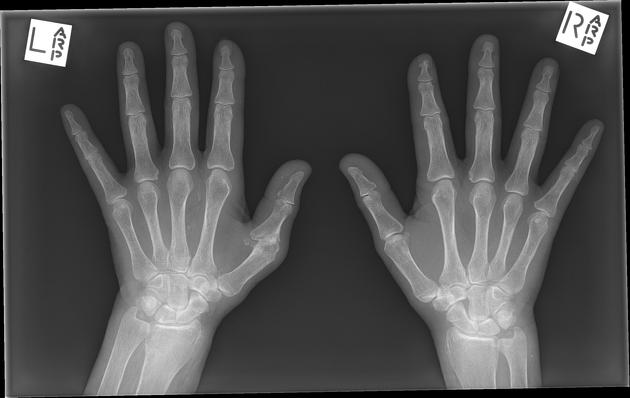
periarticular osteopenia 2-4,6
joint space narrowing 2-4,6
rheumatoid arthritis-like joint erosions 2-4,6
severe resorption of the first carpometacarpal joint with radial subluxation is common 2-4,7
Extra-articular findings
soft tissue atrophy, especially at tips of fingers 2-4
flexion contractures: small joint contractures present in ~30% 6,8
Less common musculoskeletal findings
rib resorption (bilateral superior rib notching, predominantly along posterior surface), mandibular angle resorption (+/- loss of lamina dura), radius and ulna resorption
Ultrasound
Articular findings
joint effusion (common) 6
synovial thickening/synovitis (common) 6
joint erosion 6
Extra-articular findings
-
tenosynovitis (common) 6
tendon sheath thickening and fibrinous deposits may be present 8
may be a stenosing tenosynovitis 6
may be an inflammatory tenosynovitis predisposing to tendon rupture 8
A1 flexor pulley thickening (associated with reduced hand mobility) 7
Differential diagnosis
rheumatoid arthritis: similar appearance with joint erosions and anti-CCP positivity 1




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.