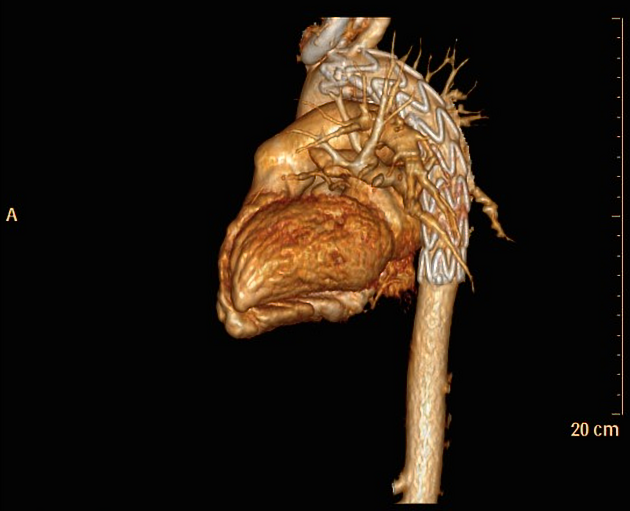
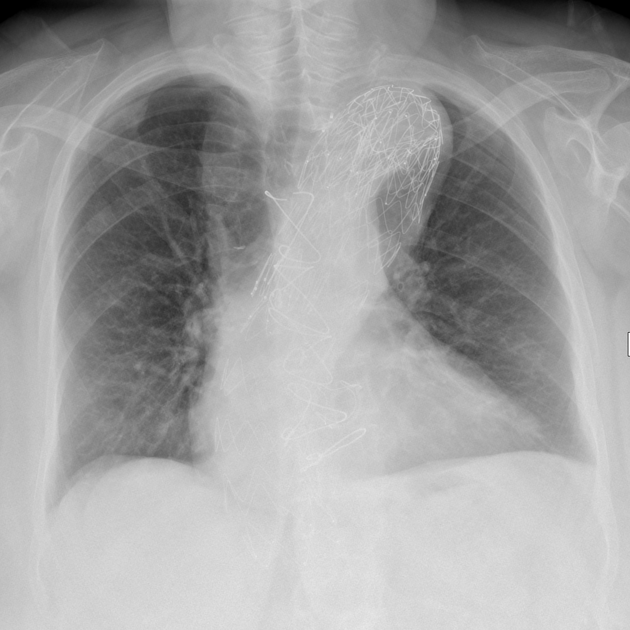
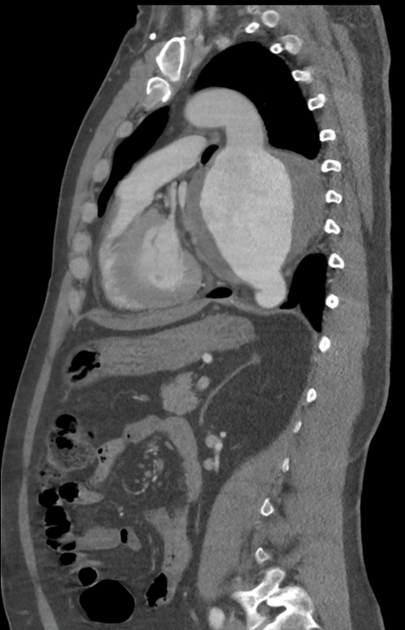
A thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) is a type of endovascular aneurysm repair of the thoracic aorta by insertion of a stent.
On this page:
Images:
Indications
TEVAR is an effective treatment for a wide variety of thoracic aortic pathologies, including:
type A and type B thoracic aortic dissections
penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of thoracic aorta
Contraindications
Recognized contraindications include 3:
-
unfavorable anatomy
inadequate proximal or distal seal zones
tortuosity
lack of vascular access options or extremes of aortic diameter.
placement into infected regions
Landing zones
An understanding of landing zones is useful for a reporting radiologist in pre-operative and post-operative assessment.
These zones are often numbered as:
zone 0: from distal to the coronary ostia to proximal edge of innominate artery
zone 1: from distal to innominate artery to proximal and involving the left common carotid artery
zone 2: from distal to the left common carotid artery to proximal and involving the left subclavian artery
zone 3: from distal margin of the left subclavian artery to 2 cm distal to the left subclavian artery
zone 4: from 2 cm distal to the left subclavian artery to midpoint of the descending thoracic aorta
zone 5: from midpoint of descending thoracic aorta to proximal margin of the celiac artery
zone 6: from celiac artery origin to proximal margin of the superior mesenteric artery
zone 7: from superior mesenteric artery to the remainder of suprarenal aorta
Complications
enlarging aneurysmal sac / aortic outer luminal growth - without a visible endoleak
incomplete or missed coverage of the primary intimal tear
stent / graft migration
infection
arterial thromboembolism




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.