Tc-99m pertechnetate thyroid scintigraphy (thyroid scan) is a functional nuclear medicine study used to assess the thyroid gland. The uptake of the pertechnetate anion - similar in chemical-physical characteristics to the iodide ion (i. e. ionic size and negative charge) - in the thyroid parenchyma is mediated by the NIS (sodium-iodide symporter, a transmembrane glycoprotein). However, unlike iodine, pertechnetate anion is not incorporated into thyroid hormones.
On this page:
Technique
-
patient preparation
fast for 4 hours prior to exam
-
radiopharmaceutical
-
dose and route of administration
-
time of imaging
20 minutes after Tc-99m pertechnetate administration
-
equipment
camera: gamma camera
collimator: pinhole
window: 20% energy window centered at 140 KeV
-
procedure
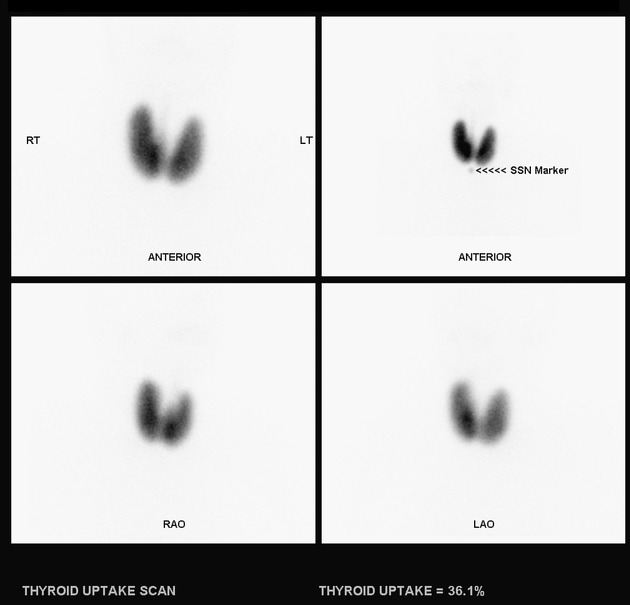
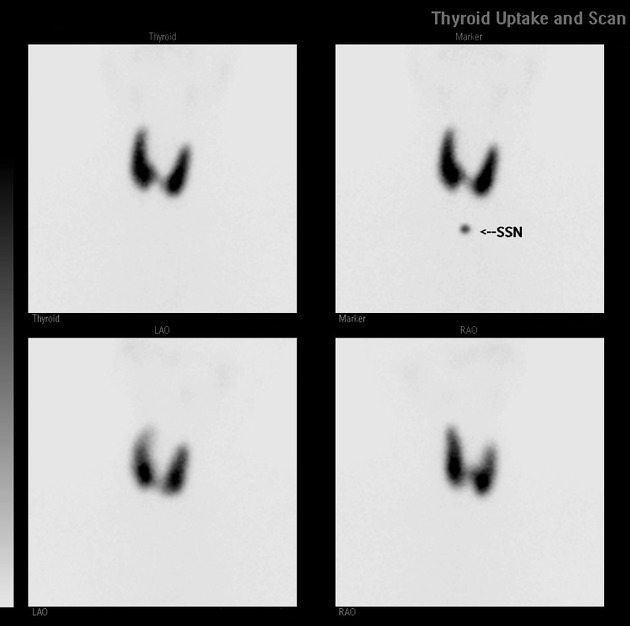
obtain anterior, LAO, and RAO views
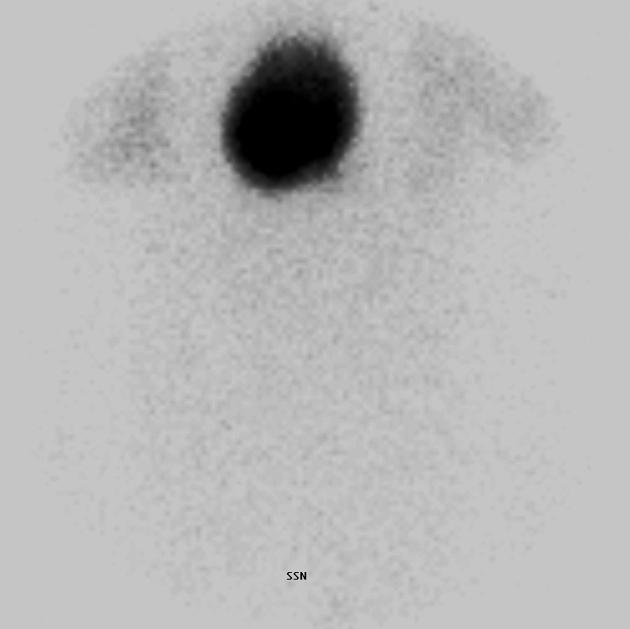
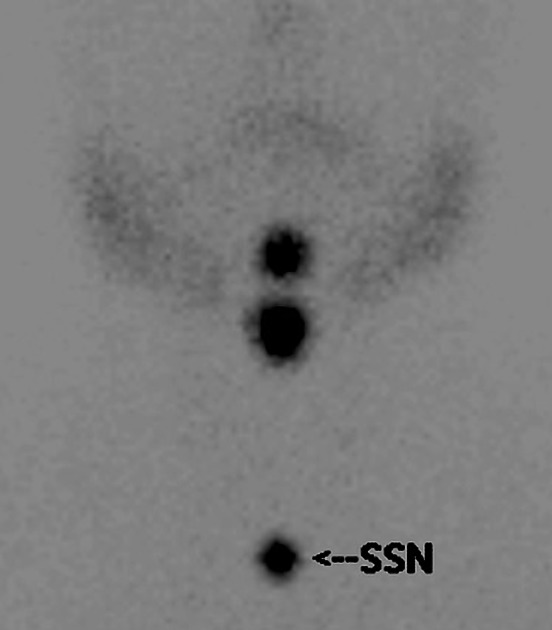
mark chin, suprasternal notch, palpable nodules, and surgical scars
Interpretation
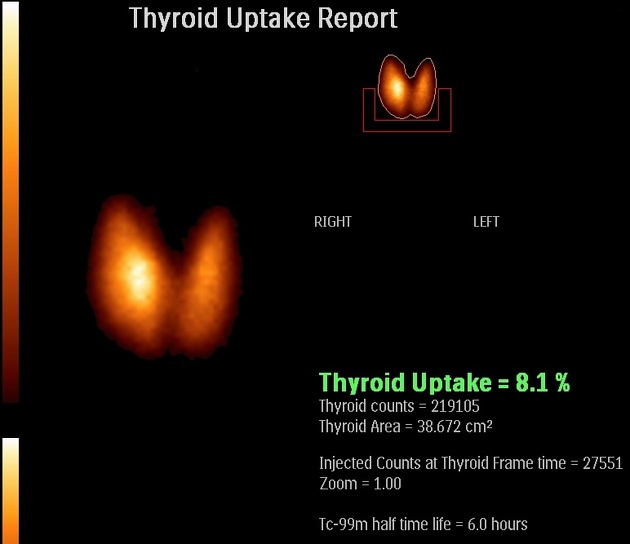
Radiotracer uptake on the thyroid scan needs to be interpreted with biochemical thyroid function tests and thyroid antibodies (e.g. antithyroglobulin, antimicrosomal, thyrotropin receptor). The combination of these results can usually distinguish between the causes of thyroid dysfunction.
Increased uptake
Hashitoxicosis
Normal uptake
following I-131 therapy
Decreased uptake
-
excess iodine intake
high iodine diet






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.