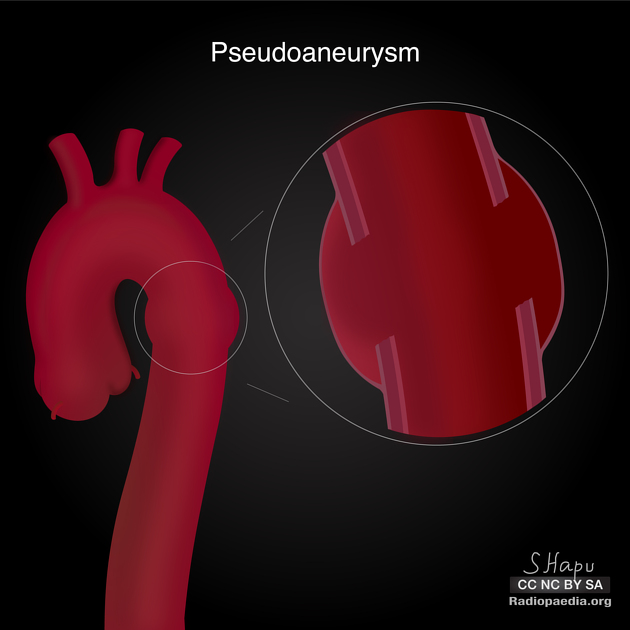
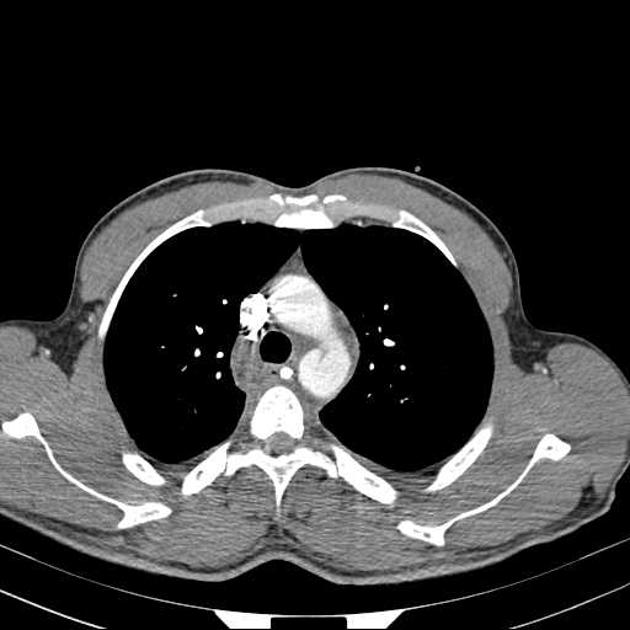
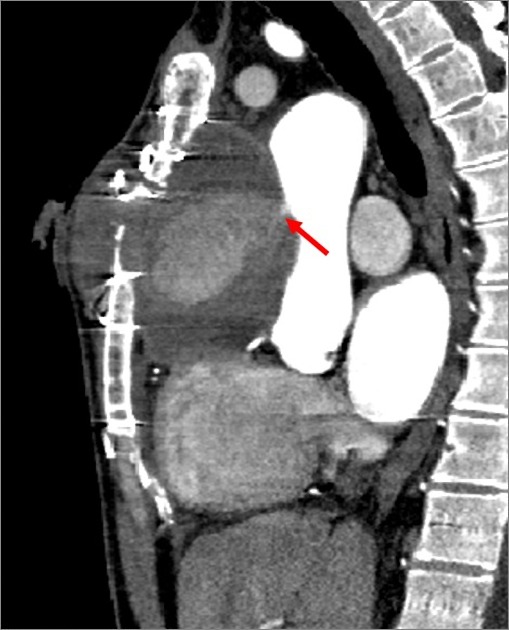
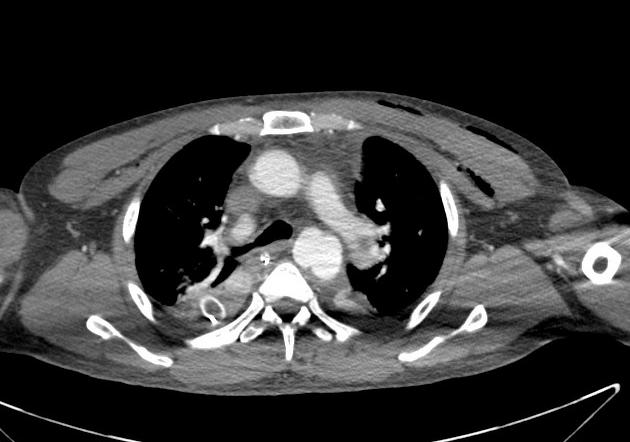
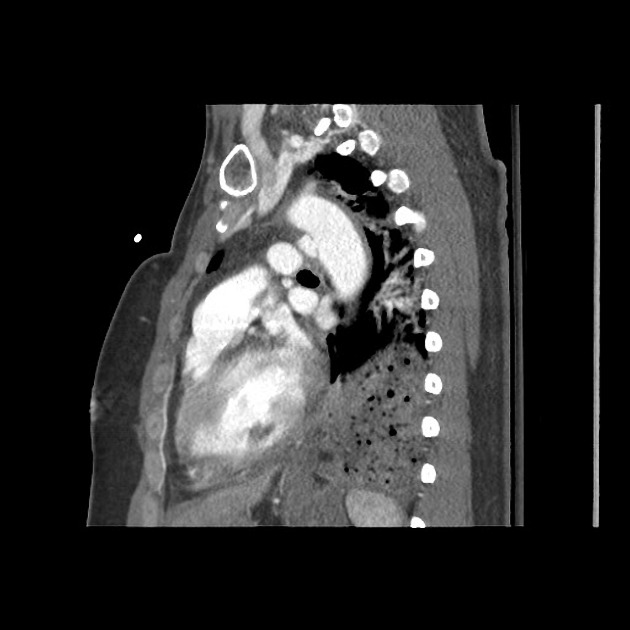
Aortic pseudoaneurysm typically occurs as a result of trauma +/- intervention, and is considered a subset of traumatic aortic injury in the majority of cases. They can be acute or chronic.
On this page:
Pathology
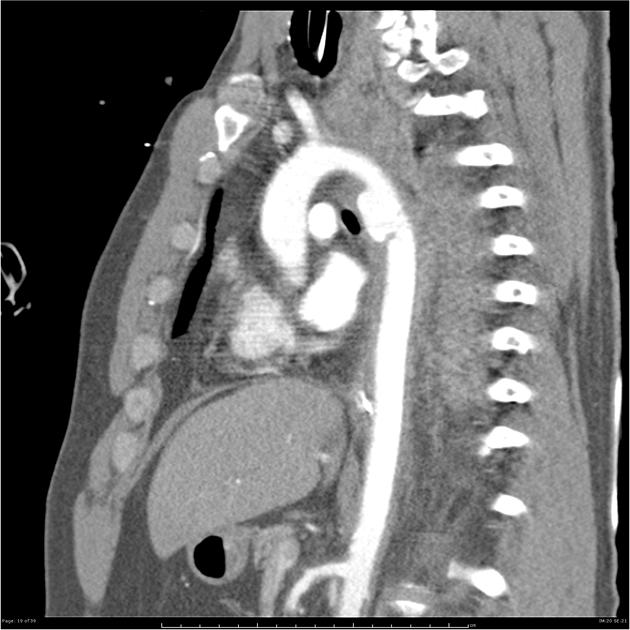
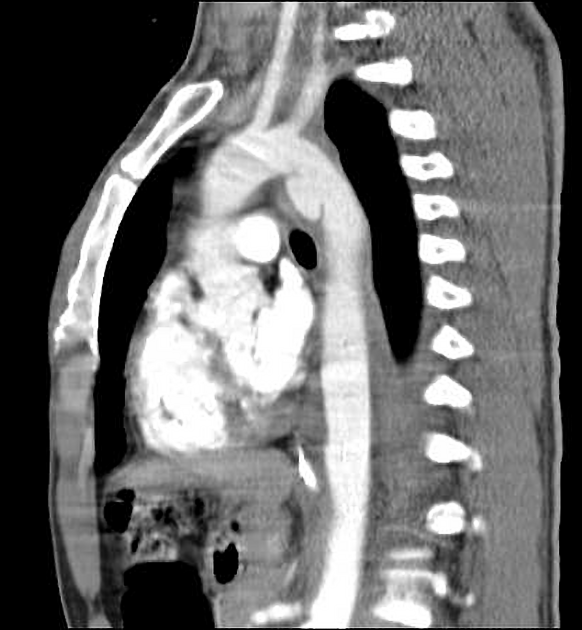
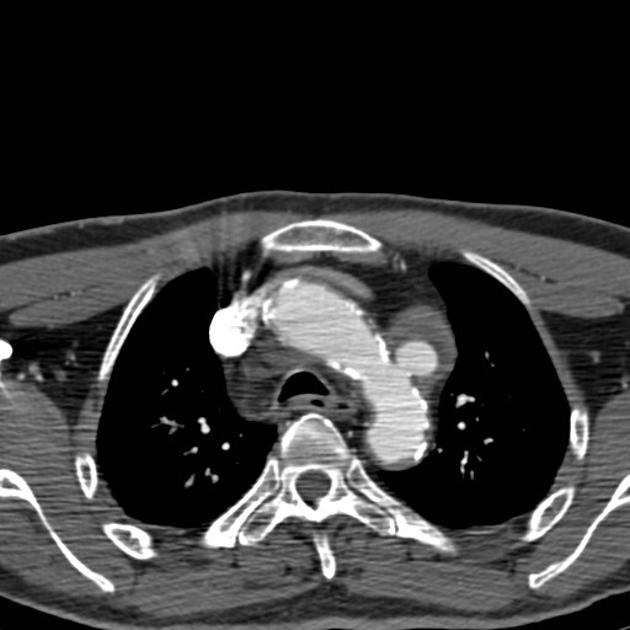
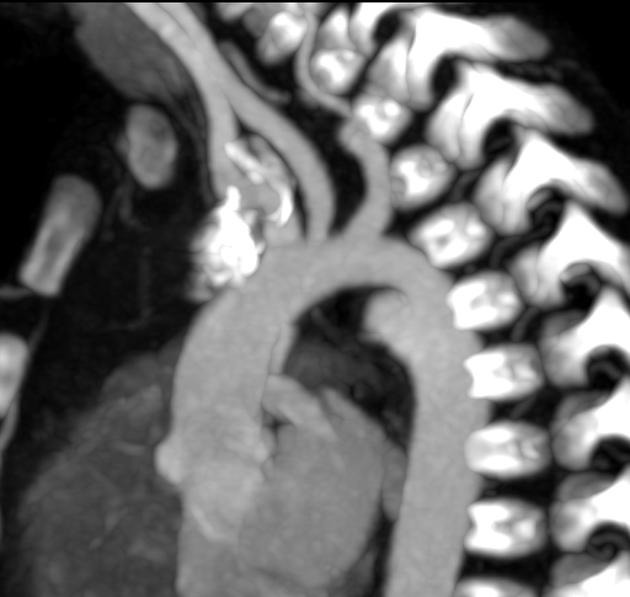
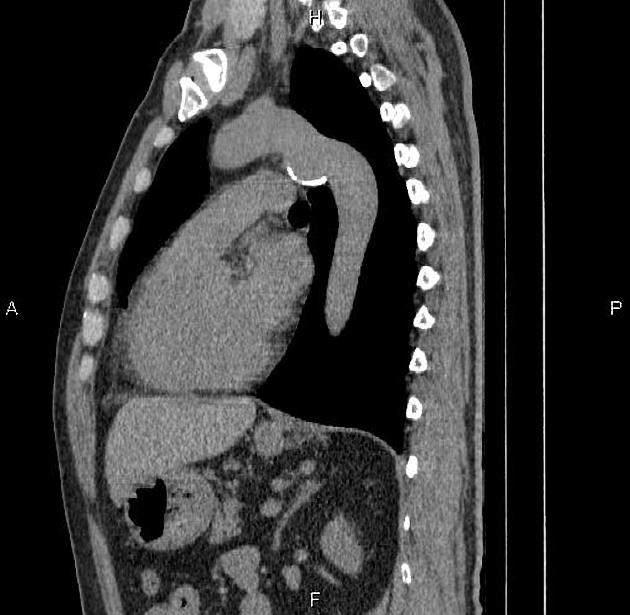
Aortic pseudoaneurysms are contained ruptures of the aorta in which the majority of the aortic wall has been breached, and luminal blood is held in only by a thin rim of the remaining wall or adventitia.
They typically occur from focal aortic transection of which 85% are the result of penetrating trauma (gunshot or stab wounds) and 15% of cases from blunt trauma (motor vehicle accidents or falls). They also occur from non-traumatic pathologies such as penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers 5.
Location
Characteristically occur along the undersurface of the aortic isthmus at or near the site of the ligamentum arteriosum 6.
Differential diagnosis
If at the level of the aortic arch, consider:
For differentiating features, see aortic pseudoaneursym vs ductus diverticulum.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.