Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is a condition that is associated with an impaired immune system. It is considered the most common symptomatic primary immunodeficiency and is characterized by recurrent respiratory tract infections.
Clinical presentation
The commonest presentation is that of frequent respiratory tract infections.
Pathology
The exact cause is unknown in at least 90% of cases, while a genetic cause may be present in <10% of cases. The conditions involve:
- low levels of most or all of the immunoglobulin (Ig) classes - hypogammaglobulinaemia
- lack of B lymphocytes or plasma cells that are capable of producing antibodies
- frequent bacterial infections
Serology
The following serological abnormalities may be present:
- serum IgA and IgG: decreased but not absent
- serum IgM: occasionally decreased
- circulating T and B lymphocytes: present
Manifestations
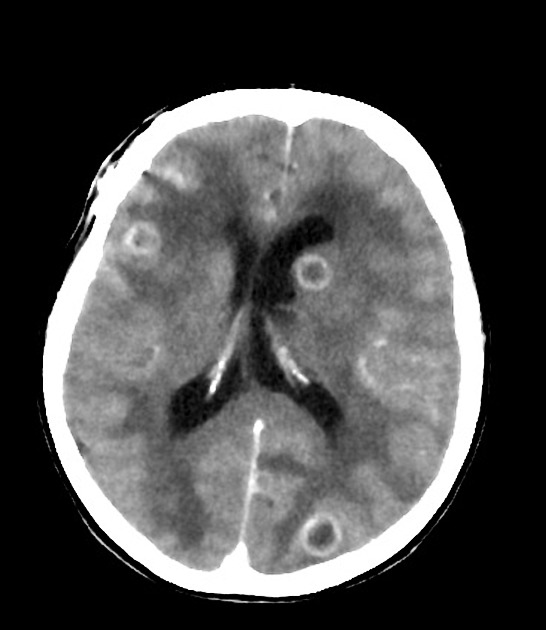
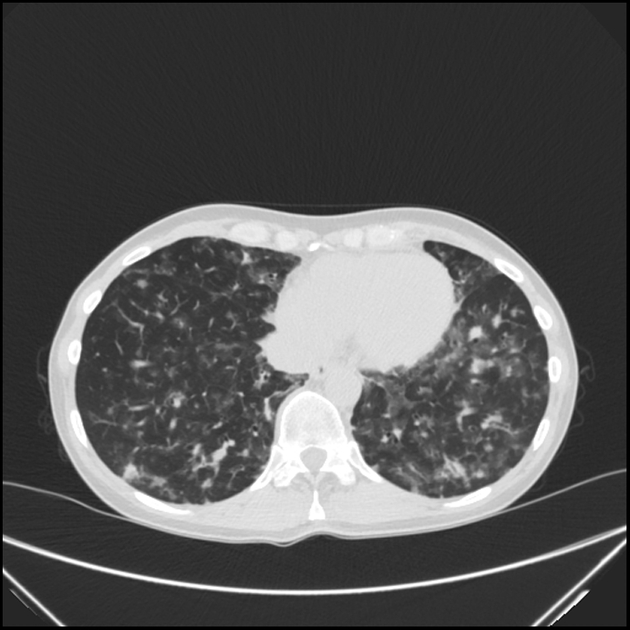
It can affect multiple organ systems:
- cutaneous manifestations of common variable immunodeficiency
- sinonasal manifestations of common variable immunodeficiency
- pulmonary manifestations of common variable immunodeficiency
- hepatic manifestations of common variable immunodeficiency
- hematological manifestations of common variable immunodeficiency




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.