Crossed renal ectopia
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Ayush Goel had no recorded disclosures.
View Ayush Goel's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised David Bassett had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View David Bassett's current disclosures- Cross ectopia
- Cross renal ectopy
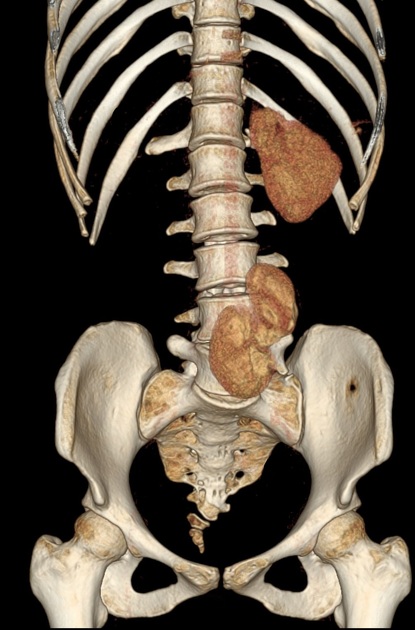
Crossed renal ectopia is said to be present when the kidney is seen in the opposite retroperitoneal space. It is more common for the left kidney to be ectopically located on the right side. More than 85% of these get fused resulting in crossed fused renal ectopia. Less than 15% cases are non-fused.
Clinical presentation
Crossed renal ectopia is usually asymptomatic and incidentally found on imaging workup. It is usually seen fixed to iliac crest, but below the level of L2.
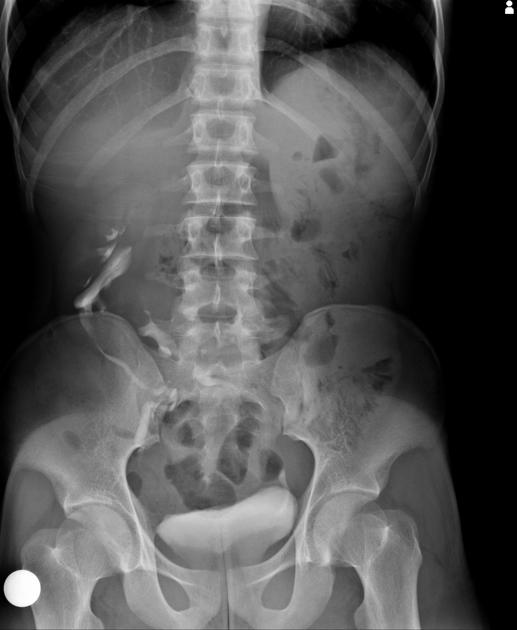
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
Absent kidney in its respective renal fossa. On careful examination, it is seen on the opposite side in the lumbar or iliac region.
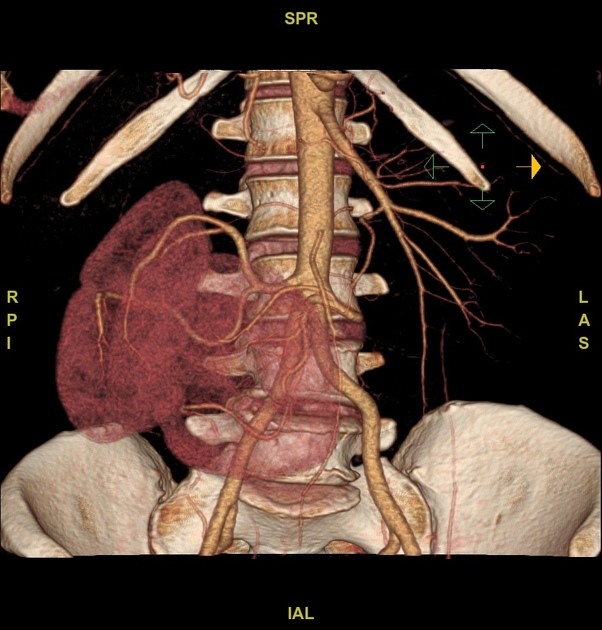
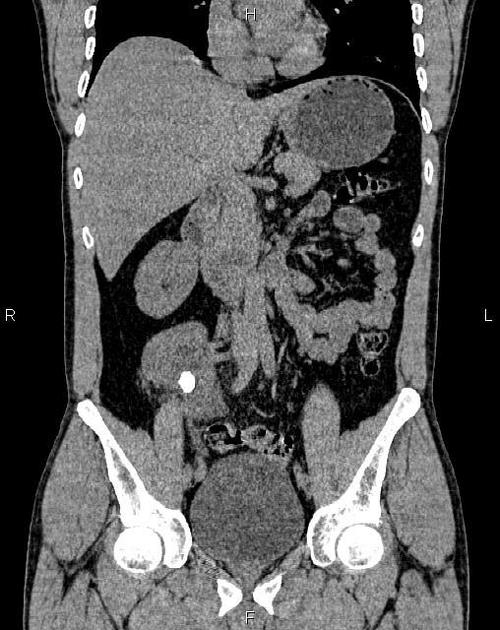
CT
Demonstrates the kidney in its ectopic location in the contralateral retroperitoneal space. The detail of the collecting system is beautifully illustrated with delayed phase imaging. This can be important in the planning of surgical procedures.
References
- 1. Nursal GN, Büyükdereli G. Unfused renal ectopia: a rare form of congenital renal anomaly. Ann Nucl Med. 2005;19 (6): 507-10. Pubmed citation
- 2. Pellicé i Vilalta C, Veicat i Porcar M. Crossed renal ectopia. Actas Urol Esp. 1999;23 (7): 640. Pubmed citation
- 3. WINRAM RG, WARD-McQUAID JN. Crossed renal ectopia without fusion. Can Med Assoc J. 1998;81: 481-3. Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Crossed fused renal ectopia
- Crossed non-fused renal ectopia
- Crossed fused renal ectopia
- Crossed renal ectopia - antenatal ultrasound
- Crossed renal ectopia
- Cross fused renal ectopia
- Crossed fused renal ectopia
- Bilateral pelvic kidneys with PUJ obstruction, fusion and right-sided duplex system
- Hematometrosalpynx
- Pancreatic serous cystadenoma
- Crossed fused renal ectopia
- Crossed fused renal ectopia
- Crossed fused renal ectopia with hydronephrosis
- Budd-Chiari syndrome
- Crossed unfused renal ectopia
- Crossed lumbar dystopia of the left kidney
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.