Deep brain stimulation is used in a variety of clinical settings, predominantly in patients with poorly controlled movement disorders. Although effective, its exact mode of function continues to be poorly understood 2.
Careful patient selection and target selection are essential if the procedure is to have good efficacy.
On this page:
Indications
-
pedunculopontine nucleus
globus pallidus internus
-
ventral intermediate nucleus 2,12
posterior subthalamic area (caudal zona incerta) 12
-
dystonia syndromes (e.g. DYT1 dystonia) 4,10
globus pallidus internus
-
thalamus: centromedian nucleus–nucleus ventrooralis internus complex, centromedian nucleus–parafascicular complex
globus pallidus internus: posteroventrolateral, anteromedial portion
-
epilepsy 11
thalamic anterior nucleus
thalamic centromedian nucleus
-
chronic pain 5
-
neuropsychiatric disorders: largely experimental 4
-
white-matter tracts adjacent to cingulate gyrus
medial forebrain bundle 8
-
anterior limb of internal capsule
subthalamic nucleus
striatum
-
Procedure
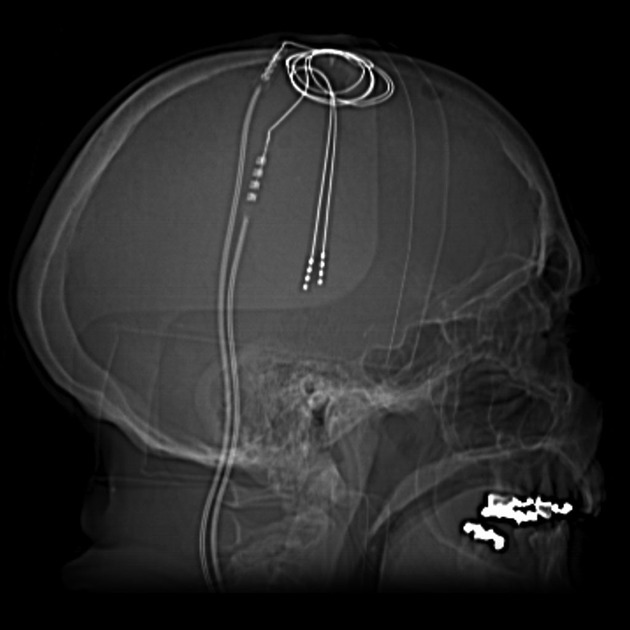
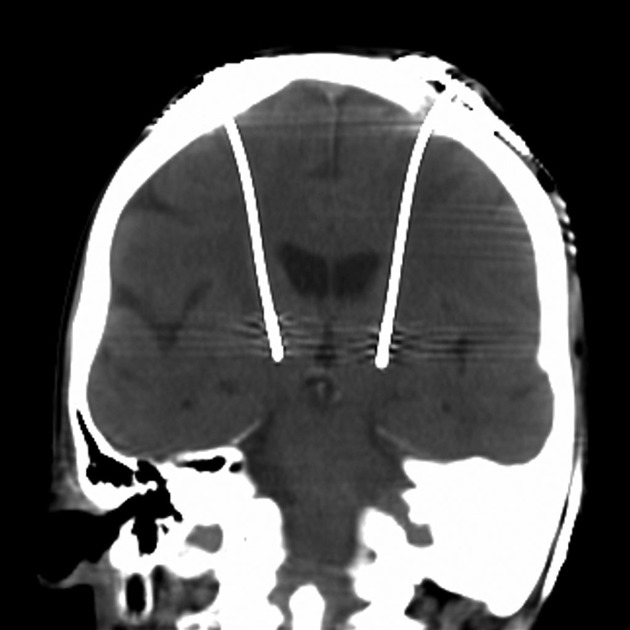
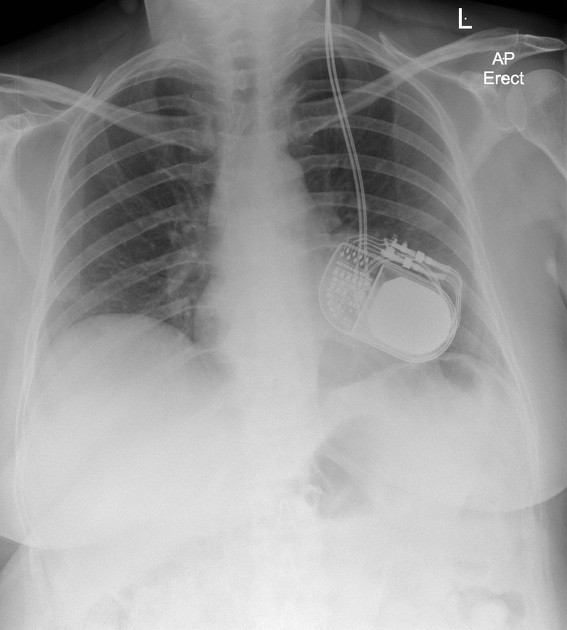
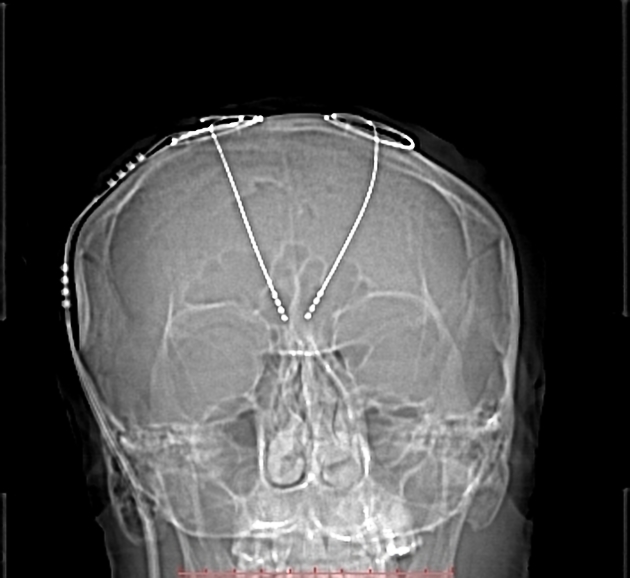
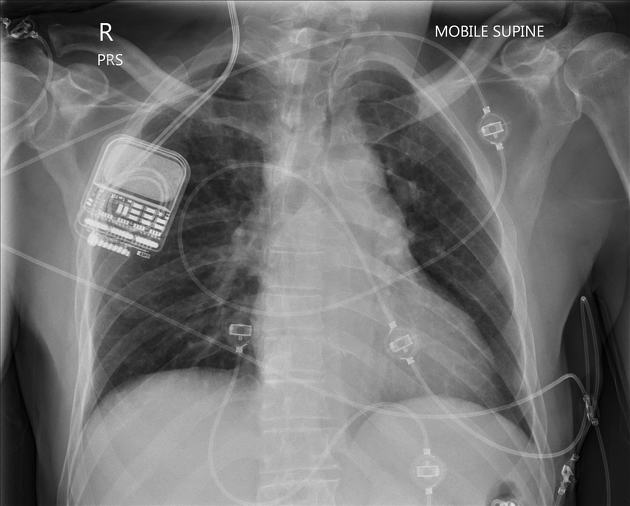
A stereotactic frame is applied and imaging obtained to enable accurate target selection. With the aid of multiplanar reformats and operative stereotaxis, a burr hole is made for each probe and the electrode passed to the desired target, avoiding the lateral ventricles, vessels and sulci. Intraoperative stimulation is then performed to ensure adequate positioning. Leads are tunneled under the skin and the internal pulse generator implanted in a similar location to a pacemaker.
Complications
Complications can be immediate or delayed 12:
-
immediate
-
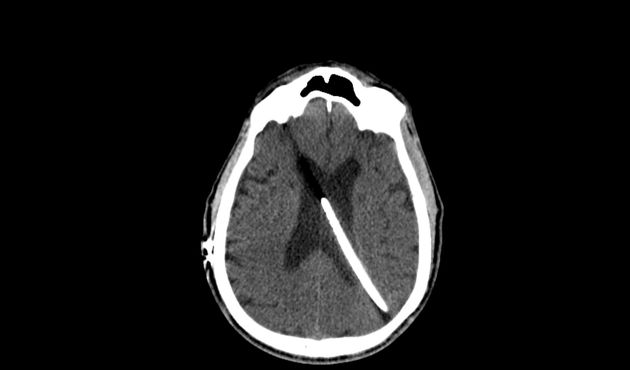
hemorrhage (~1.5%)
can be secondary to venous infarction
-
local brain parenchymal edema (~3%)
unilateral or bilateral
4-120 days postoperatively
asymptomatic or present with headache, seizure
-
-
delayed
infection (~12.5%): most commonly the pulse generator pocket
lead fracture (~10%)
Side effects predominantly relate to the stimulation itself, which may lead to dysarthria, disequilibrium, motor disturbances and paresthesia. These symptoms vary with the location of the probes.






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.