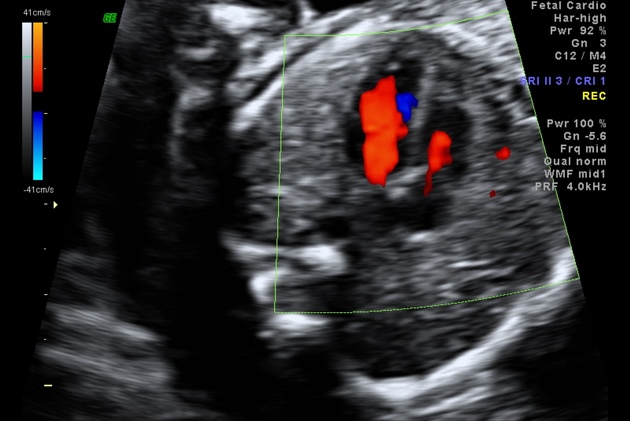
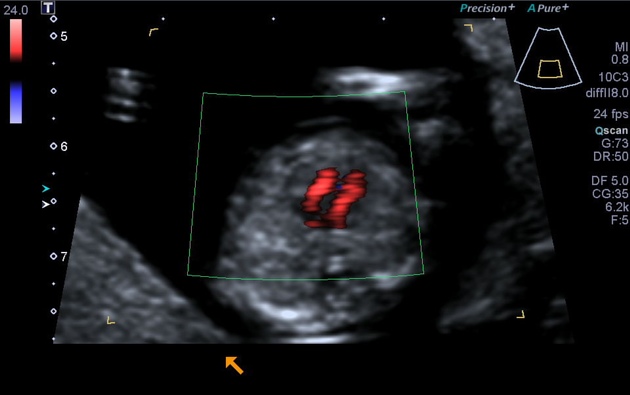
Four chamber cardiac view (fetal)
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Weerakkody Y, Elfeky M, Kang O, et al. Four chamber cardiac view (fetal). Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 21 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-15708
rID:
15708
Article created:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosures
Revisions:
15 times, by
9 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
Tags:
Synonyms:
- Four chamber view
- Four chamber view in fetal echocadiography
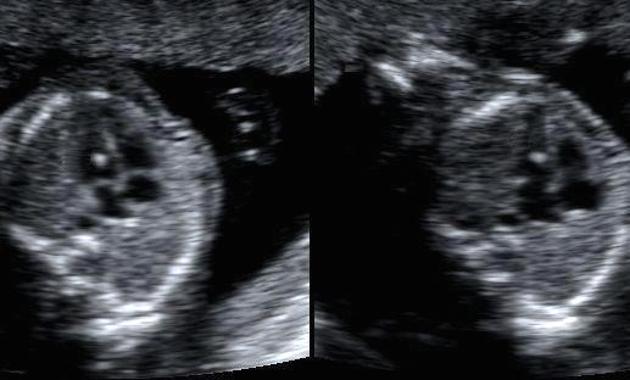
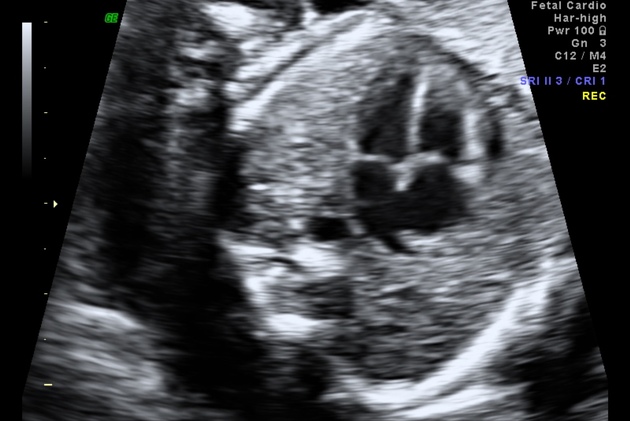
The four chamber cardiac view is an important and routinely performed view in both fetal echocardiography as well as on a standard second trimester anatomy scan.
On this page:
Detectable pathology
The four chamber view can only detect some of the congenital cardiac anomalies (~64% according to one study 2) that can be detected antenatally and these include:
- septal defects
- hypoplastic left heart syndrome
- persistent truncus arteriosus
- presence of echogenic intracardiac foci (EIF)
Anomalies that may not be apparent on the four chamber view alone include transposition of the great arteries and aortic coarctation.
Radiographic features
It is assessed on an axial (transverse) plane through the fetal thorax.
Features to evaluate:
- situs: establish heart on the left side, same side as fetal stomach
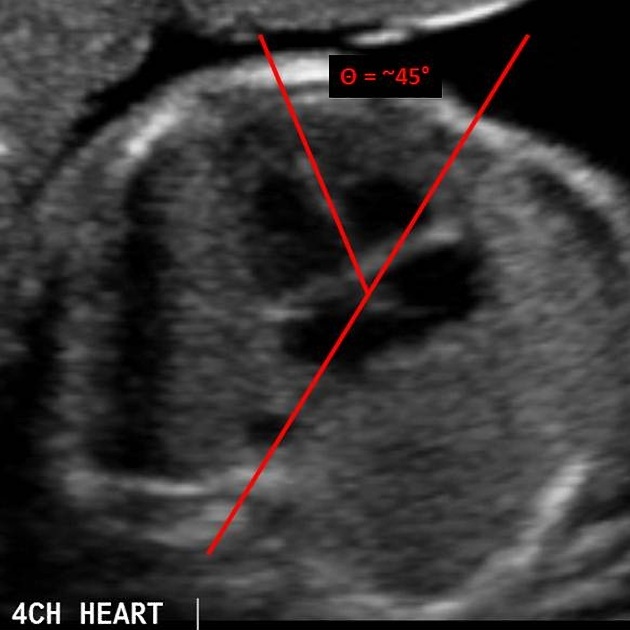
- axis: cardiac apex normally points to the left, at an angle of 45°+/-20°
- heart size: should occupy approximately 1/3rd of the thoracic area
- heart location: any mediastinal shift or ectopia cordis
- heart rate: normal 120-160 bpm
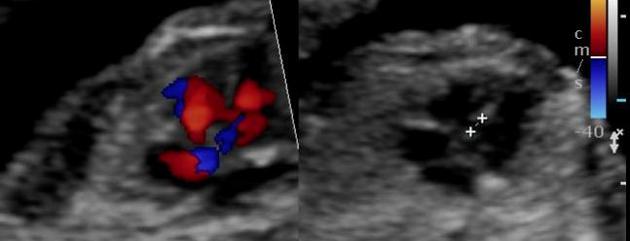
- atrial chambers: similar in size, with foramen ovale flap opening to the left atrium
- ventricular chambers: the morphologic right ventricle should be located immediately behind the sternum and is characterised by the presence of the moderator band
- interventricular and interatrial septa (with possible defects)
- atrioventricular valves: tricuspid valve (right heart) septal leaflet inserts into the septum more anterior than the mitral valve (left heart) - the normal valve offset
See also
References
- 1. Shultz SM, Pretorius DH, Budorick NE. Four-chamber view of the fetal heart: demonstration related to menstrual age. J Ultrasound Med. 1994;13 (4): 285-9. J Ultrasound Med (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Fernandez CO, Ramaciotti C, Martin LB et-al. The four-chamber view and its sensitivity in detecting congenital heart defects. Cardiology. 1998;90 (3): 202-6. Cardiology (link) - Pubmed citation
- 3. Barboza JM, Dajani NK, Glenn LG et-al. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital cardiac anomalies: a practical approach using two basic views. Radiographics. 22 (5): 1125-37. Radiographics (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 4. Mcgahan JP. Sonography of the fetal heart: findings on the four-chamber view. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991;156 (3): 547-53. AJR Am J Roentgenol (abstract) - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
Articles:
Cases:
- Right sided aortic arch - fetal ultrasound
- Transposition of the great arteries (TGA) - fetal echocardiogram
- Transposition of the great arteries (fetal echocardiogram)
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS)
- Common atrium (fetal echo)
- Normal second trimester ultrasound
- Fetal echocardiograph views
- Truncus arteriosus (fetal echocardiogram)
- Fetal echocardiography - normal views
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta praevia
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynaecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumours
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumours of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumours
- mixed germ cell tumour
- yolk sac tumour (endodermal sinus tumour)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumour
- sex cord / stromal tumours of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumour of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumours (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumours
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.