Papillary renal cell carcinoma
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Hala M. Qasrawi had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Hala M. Qasrawi's current disclosures- Papillary renal cell cancer
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma (pRCC)
- Chromophil renal cell carcinoma
- Chromophil renal cell carcinomas
- Papillary renal cell carcinomas
- Papillary renal cell cancers
Papillary renal cell carcinomas (pRCC) are the second most common histological subtype of renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
On this page:
Epidemiology
This subtype may account 13-20% of all renal cell cancer 1. This subtype is also the most common in the renal transplant population 11. There is slightly increased male predilection.
Associations
Clinical presentation
As with other types of renal cell cancer, most are asymptomatic and incidentally discovered.
Pathology
There are two subtypes described according to morphology 7:
-
type I
- have papillae covered by a single layer of cuboidal or low columnar cells with scanty cytoplasm and low-grade nuclei
- carry a better prognosis than type II tumours
-
type II:
- are of a higher nuclear grade and contain more than one layer of cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm
- although mostly unilateral, this subtype is considered the most common to result in bilateral renal cell cancers 1
While it has been described to have a tendency to present at a lower stage, it still has a distinct potential for progression and aggressive behaviour 4.
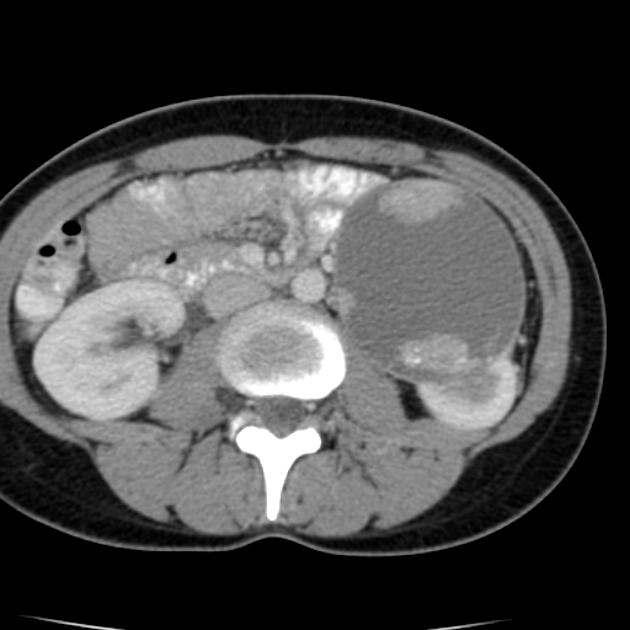
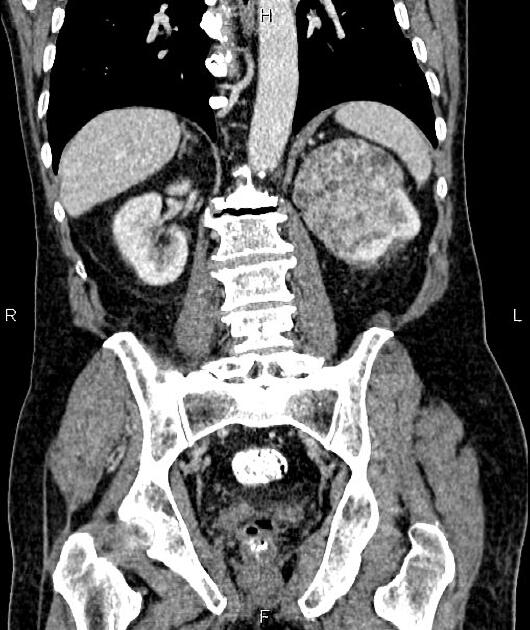
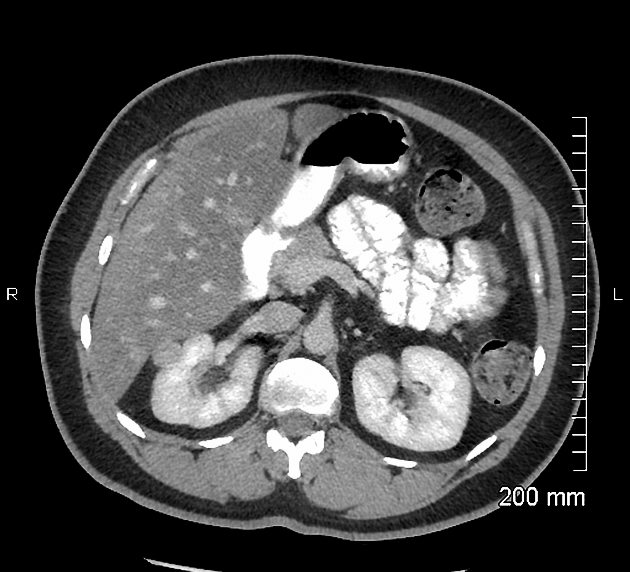
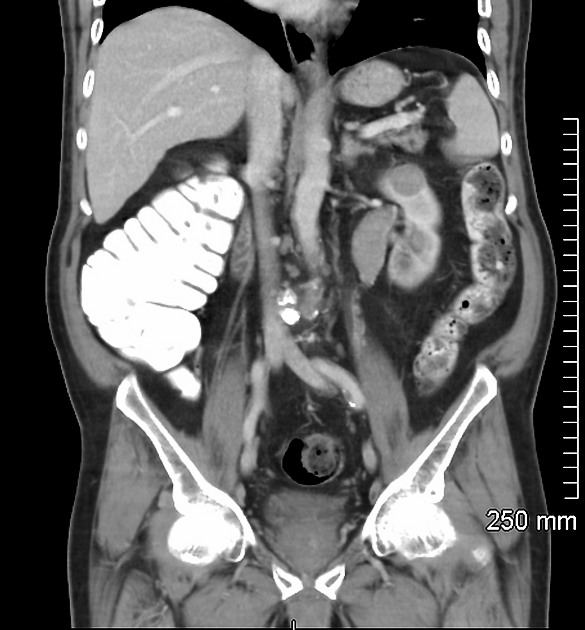
Radiographic features
Although there is no absolute rule, in general, papillary renal cancers at diagnosis tend to have a smaller mean diameter and be at a lower stage. The imaging features of type 1 and type 2 tumours may overlap.
Ultrasound
Generally tends to be hypoechoic on ultrasound 9.
CT
Smaller lesions tend to be homogeneous in attenuation with larger tumours tending to be heterogeneous.
These tumours are characteristically less vascularised than the more common clear cell subtype, showing overall hypoenhancement compared to the adjacent normal renal cortex, particularly seen in the corticomedullary phase.
When not enhancing at all, it can be difficult to differentiate from hyper-attenuating cysts 8.
MRI
The tumours generally present with a pseudo-capsule.
- T1: hypointense
- T2: hypointense
- T1 C+ (Gd): contrast enhancement tends to be less intense than in the more common clear cell RCC subtype
- DWI: restricted diffusion may be useful for differentiating from a haemorrhagic cyst
See also
References
- 1. Vikram R, Ng CS, Tamboli P et-al. Papillary renal cell carcinoma: radiologic-pathologic correlation and spectrum of disease. Radiographics. 2009;29 (3): 741-54. doi:10.1148/rg.293085190 - Pubmed citation
- 2. Ronnen EA, Kondagunta GV, Ishill N et-al. Treatment outcome for metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma patients. Cancer. 2006;107 (11): 2617-21. doi:10.1002/cncr.22340 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Delahunt B, Eble JN, McCredie MR et-al. Morphologic typing of papillary renal cell carcinoma: comparison of growth kinetics and patient survival in 66 cases. Hum. Pathol. 2001;32 (6): 590-5. doi:10.1053/hupa.2001.24984 - Pubmed citation
- 4. Amin MB, Corless CL, Renshaw AA et-al. Papillary (chromophil) renal cell carcinoma: histomorphologic characteristics and evaluation of conventional pathologic prognostic parameters in 62 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1997;21 (6): 621-35. Pubmed citation
- 5. Ng CS, Wood CG, Silverman PM et-al. Renal cell carcinoma: diagnosis, staging, and surveillance. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191 (4): 1220-32. AJR Am J Roentgenol (full text) - doi:10.2214/AJR.07.3568 - Pubmed citation
- 6. Herts BR, Coll DM, Novick AC et-al. Enhancement characteristics of papillary renal neoplasms revealed on triphasic helical CT of the kidneys. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178 (2): 367-72. doi:10.2214/ajr.178.2.1780367 - Pubmed citation
- 7. Delahunt B, Eble JN, McCredie MR et-al. Morphologic typing of papillary renal cell carcinoma: comparison of growth kinetics and patient survival in 66 cases. Hum. Pathol. 2001;32 (6): 590-5. doi:10.1053/hupa.2001.24984 - Pubmed citation
- 8. Egbert ND, Caoili EM, Cohan RH et-al. Differentiation of papillary renal cell carcinoma subtypes on CT and MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;201 (2): 347-55. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.9451 - Pubmed citation
- 9. Tsuda K, Kinouchi T, Tanikawa G et-al. Imaging characteristics of papillary renal cell carcinoma by computed tomography scan and magnetic resonance imaging. Int. J. Urol. 2005;12 (9): 795-800. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2042.2005.01126.x - Pubmed citation
- 9. Blei CL, Hartman DS, Friedman AC, Davis CJ. Papillary renal cell carcinoma: ultrasonic/pathologic correlation. Journal of clinical ultrasound : JCU. 10 (9): 429-34. Pubmed
- 10. Sidhar K, McGahan JP, Early HM, Corwin M, Fananapazir G, Gerscovich EO. Renal Cell Carcinomas: Sonographic Appearance Depending on Size and Histologic Type. Journal of ultrasound in medicine : official journal of the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine. 35 (2): 311-20. doi:10.7863/ultra.15.03051 - Pubmed
- 11. Karami S, Yanik E, Moore L et al. Risk of Renal Cell Carcinoma Among Kidney Transplant Recipients in the United States. Am J Transplant. 2016;16(12):3479-89. doi:10.1111/ajt.13862 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Renal cyst
- Tubulocystic renal cell carcinoma
- Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma
- T1 hyperintense renal lesions
- Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome
- Cystic renal tumors
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma
- International Society of Urological Pathology Vancouver classification of renal neoplasia (historical)
- Hereditary renal cancer syndromes
- WHO classification of tumours of the kidney
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Fumarate hydratase-deficient renal cell carcinoma (FH-RCC)
- Juxtaglomerular cell tumour
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma
- Right papillary renal cell carcinoma
- Fumarate hydratase-deficient renal cell carcinoma (FH-RCC)
- Synchronous ipsilateral renal cell carcinoma and renal pelvis transitional cell carcinoma
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma-type 2
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma-type 1
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma
- Renal cell carcinoma - papillary type
- Synchronous renal and colonic carcinomas
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Hypovascular renal cell carcinoma
- Renal cell carcinoma - type II papillary
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics[+][+]
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta praevia
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynaecology[+][+]
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract[+][+]
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumours
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumours of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumours
- mixed germ cell tumour
- yolk sac tumour (endodermal sinus tumour)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumour
- sex cord / stromal tumours of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumour of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumours (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
-
renal cell carcinoma
- clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- papillary renal cell carcinoma
- chromophobe renal cell carcinoma
- oncocytoma
- renal lymphoma
- renal angiomyolipoma
-
renal cell carcinoma
- renal cystic disease[+][+]
- renal infection[+][+]
- vascular[+][+]
- trauma[+][+]
- ureter[+][+]
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumours
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder[+][+]
- kidneys












 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.