Torsion of the appendix testis
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created The Radswiki had no recorded disclosures.
View The Radswiki's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Jeremy Jones had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosures- Appendix testis torsion
- Appendicular testis torsion
- Testicular appendage torsion
- Torsion of hydatid of Morgagni
Torsion of the appendix testis (occasionally called torsion of the hydatid of Morgagni) is the most common cause of an acute painful hemiscrotum in a child. The appendix testis is located at the upper pole of the testis (between the testis and the head of the epididymis).
The normal appendix testis is 1 to 4 mm in length, and it is oval or pedunculated in shape.
On this page:
Clinical presentation
The clinical presentation is with acute scrotal pain. The blue dot sign is a classic finding on physical examination which may be present. It describes a small firm nodule palpable at the superior aspect of the testis with bluish discoloration through the overlying skin.
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
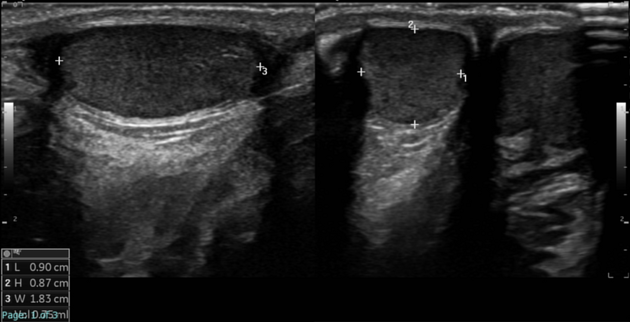
Appendix testis is increased in size with an increase or decrease in echogenicity. Torsion of the appendix testis is frequently accompanied by a hydrocele and scrotal wall thickening 3.
A spherical shape and size of 6 mm with no internal vascularity and peripheral vascularity on Doppler scan are highly suggestive of torsion.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
See also
References
- 1. Dogra V, Gottlieb R, Oka M, Rubens D. Sonography of the Scrotum. Radiology. 2003;227(1):18-36. doi:10.1148/radiol.2271001744 - Pubmed
- 2. Yang D, Lim J, Kim J, Kim J, Cho H. Torsed Appendix Testis: Gray Scale and Color Doppler Sonographic Findings Compared with Normal Appendix Testis. J Ultrasound Med. 2005;24(1):87-91. doi:10.7863/jum.2005.24.1.87 - Pubmed
- 3. Pomajzl A & Leslie S. Appendix Testis Torsion. 2025. - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics[+][+]
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta praevia
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynaecology[+][+]
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland[+][+]
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumours
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion[+][+]
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumours of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumours
- mixed germ cell tumour
- yolk sac tumour (endodermal sinus tumour)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumour
- sex cord / stromal tumours of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion[+][+]
- paratesticular lesions[+][+]
-
epididymis
- epididymo-orchitis
- epididymal abscess
- epididymal masses
- epididymal head cyst
- torsion of the epididymal appendix
- adenomatoid tumour
- epididymal leiomyoma
- other[+][+]
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumour of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumours (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion[+][+]
- penis[+][+]
- prostate gland[+][+]
- KUB[+][+]
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumours
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.