AFS classification of Müllerian anomalies
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Henry Knipe had the following disclosures:
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (past)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures- Müllerian duct anomaly classification (AFS classification)
- Classification of Mullerian duct anomalies
- Mullerian duct anomaly classification
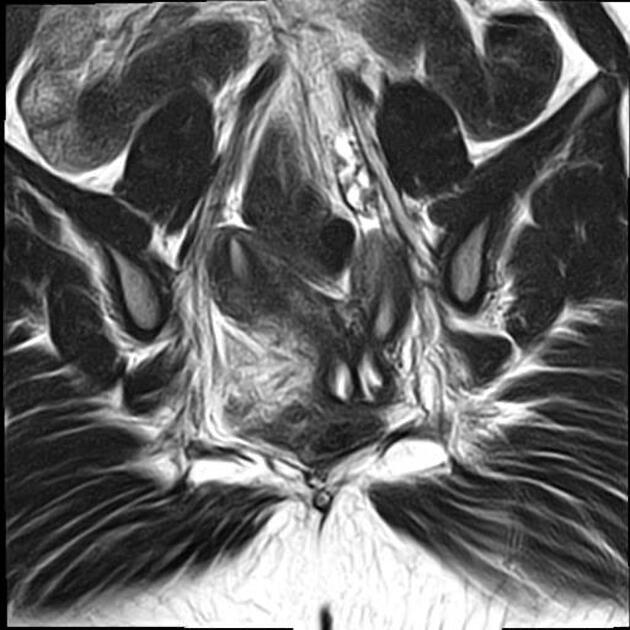
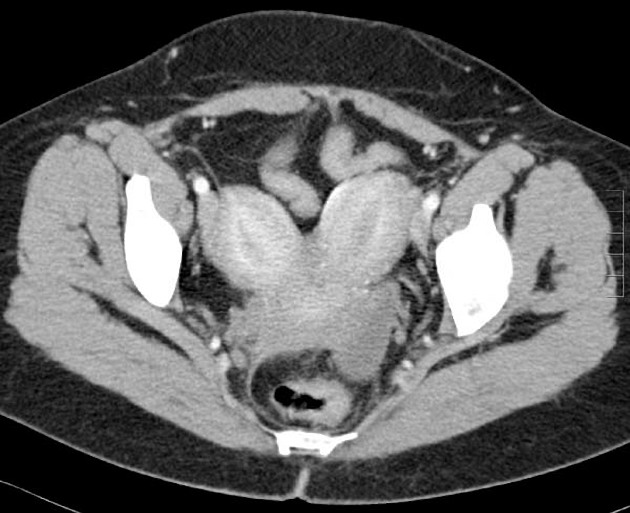
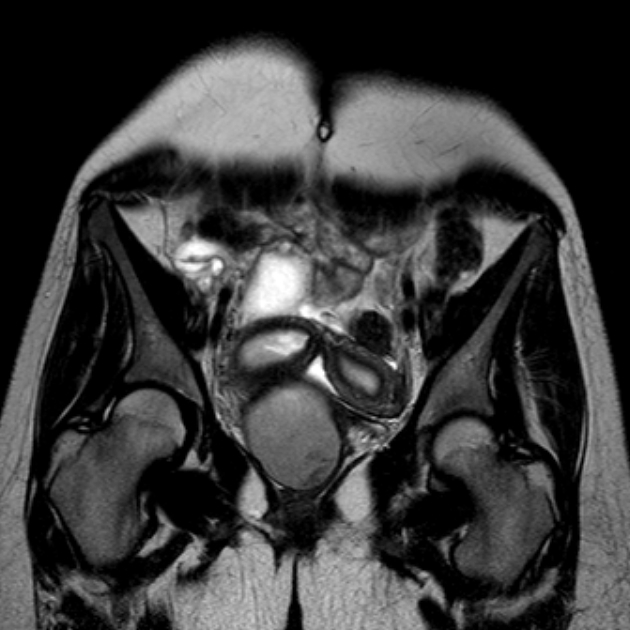
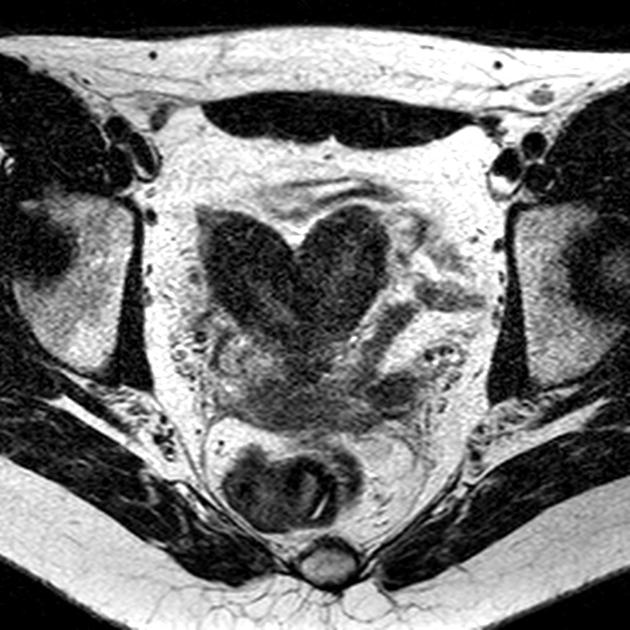
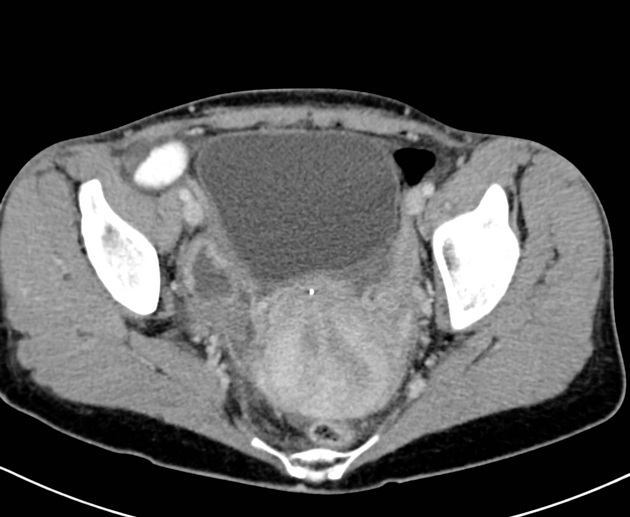
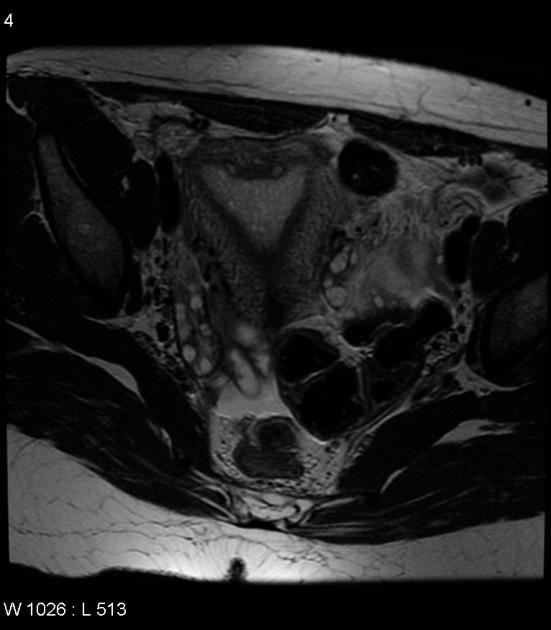
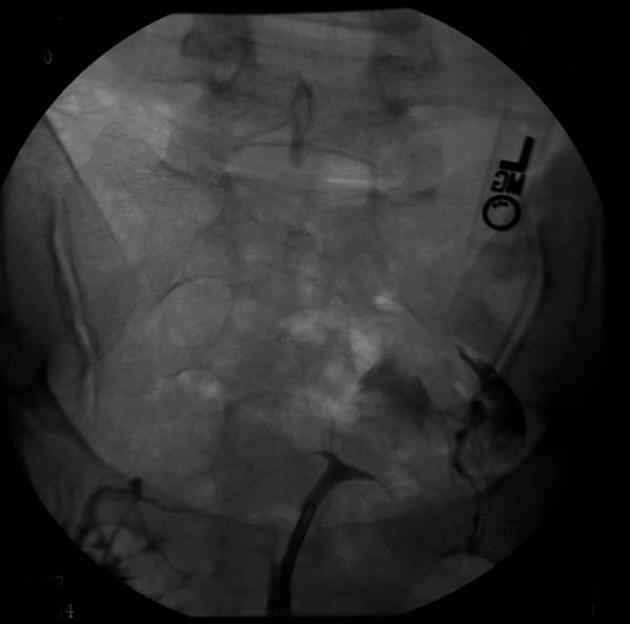
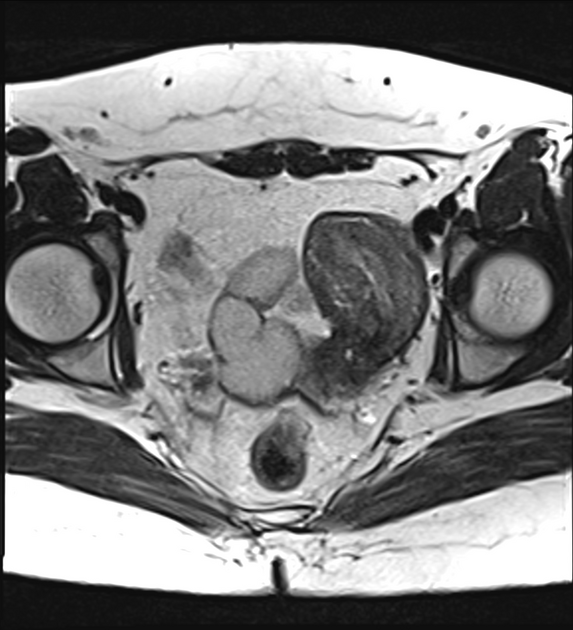
The American Fertility Society (AFS) classification of Müllerian anomalies is a seven-class system published in 1988, which is used to describe several embryonic Müllerian duct anomalies.
The American Fertility Society is now known as the American Society of Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), and the AFS classification is sometimes referred to as the ASRM classification 11. However, using "AFS classification" is preferred to differentiate the 1988 classification from the more recent ASRM Müllerian anomalies classification 2021 12.
On this page:
Usage
The AFS classification, published in 1988, is one of the most widely used and recognised (c. 2022) classification systems for Mullerian duct anomalies. However, there are other classification systems with no clear consensus on use 9-11. It is based on a classification system published in 1979 by Buttram and Gibbons 1,9. Criticisms of this system include the focus on uterine anomalies only (excluding cervical and uterine anomalies), unclear criteria, and complex anomalies being difficult to classify 9.
Classification
-
class I: uterine agenesis/uterine hypoplasia
a: vaginal (uterus: normal/variety of abnormal forms)
b: cervical
c: fundal
d: tubal
e: combined
-
class II: unicornuate uterus/unicornis unicollis, ~15% (range 6-25%)
a: communicating contralateral rudimentary horn contains endometrium
b: non-communicating contralateral rudimentary horn contains endometrium
c: contralateral horn has no endometrial cavity
d: no horn
class III: uterus didelphys, ~7.5% (range 5-11%)
-
class IV: bicornuate uterus: 2nd most common type ~25% (range 10-39%)
a: complete division, all the way down to the external os (bicornuate bicollis)
b: partial division, not extending to the internal os (bicornuate unicollis)
-
class V: septate uterus: commonest anomaly, ~45% (range 34-55%)
a: complete division, all the way down to the internal or external os
b: incomplete division, involving the endometrial cavity but not the cervix
class VI: arcuate uterus, ~7%
class VII: in utero diethylstilboestrol (DES) exposure (T-shaped uterus)
See also
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Buttram V & Gibbons W. Müllerian Anomalies: A Proposed Classification. (An Analysis of 144 Cases). Fertil Steril. 1979;32(1):40-6. doi:10.1016/s0015-0282(16)44114-2 - Pubmed
- 2. Carrington B, Hricak H, Nuruddin R, Secaf E, Laros R, Hill E. Müllerian Duct Anomalies: MR Imaging Evaluation. Radiology. 1990;176(3):715-20. doi:10.1148/radiology.176.3.2202012 - Pubmed
- 3. Ronald J. Zagoria. Genitourinary Radiology. (2004) ISBN: 9780323018425 - Google Books
- 4. Troiano R & McCarthy S. Mullerian Duct Anomalies: Imaging and Clinical Issues. Radiology. 2004;233(1):19-34. doi:10.1148/radiol.2331020777 - Pubmed
- 5. Mueller G, Hussain H, Smith Y et al. Müllerian Duct Anomalies: Comparison of MRI Diagnosis and Clinical Diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189(6):1294-302. doi:10.2214/AJR.07.2494 - Pubmed
- 6. Steinkeler J, Woodfield C, Lazarus E, Hillstrom M. Female Infertility: A Systematic Approach to Radiologic Imaging and Diagnosis. Radiographics. 2009;29(5):1353-70. doi:10.1148/rg.295095047 - Pubmed
- 7. Saleem S. MR Imaging Diagnosis of Uterovaginal Anomalies: Current State of the Art. Radiographics. 2003;23(5):e13. doi:10.1148/rg.e13 - Pubmed
- 8. Imaoka I, Wada A, Matsuo M, Yoshida M, Kitagaki H, Sugimura K. MR Imaging of Disorders Associated with Female Infertility: Use in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management. Radiographics. 2003;23(6):1401-21. doi:10.1148/rg.236025115 - Pubmed
- 9. Acién M & Acién P. Classification of Müllerian Anomalies: Is a Consensus Possible? Case Rep Womens Health. 2022;34:e00413. doi:10.1016/j.crwh.2022.e00413 - Pubmed
- 10. Ludwin A & Ludwin I. Comparison of the ESHRE-ESGE and ASRM Classifications of Mullerian Duct Anomalies in Everyday Practice. Hum Reprod. 2014;30(3):569-80. doi:10.1093/humrep/deu344 - Pubmed
- 11. Behr S, Courtier J, Qayyum A. Imaging of Müllerian Duct Anomalies. Radiographics. 2012;32(6):E233-50. doi:10.1148/rg.326125515 - Pubmed
- 12. Pfeifer S, Attaran M, Goldstein J et al. ASRM Müllerian Anomalies Classification 2021. Fertil Steril. 2021;116(5):1238-52. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2021.09.025 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Herlyn-Werner-Wunderlich syndrome
- Uterine hypoplasia
- Persistent Mullerian duct syndrome
- Uterine didelphys with pregnancy
- Septate uterus
- Androgen insensitivity syndrome
- Robert's uterus
- Uterus didelphys
- Bicornuate uterus
- Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome
- Bicornuate uterus
- Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome
- Unicornuate uterus (3D ultrasound)
- Subseptate uterus
- Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome (MRKH)
- Ovarian torsion - Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser Syndrome
- Unicornuate uterus
- Unicornuate uterus - type B
- Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome
- Bicornuate, unicollis uterus
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta praevia
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynaecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumours
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumours of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumours
- mixed germ cell tumour
- yolk sac tumour (endodermal sinus tumour)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumour
- sex cord / stromal tumours of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumour of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumours (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumours
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys










 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.