Fourth ventricle
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Kajanan Nithiyananthan had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Kajanan Nithiyananthan's current disclosures- 4th ventricle
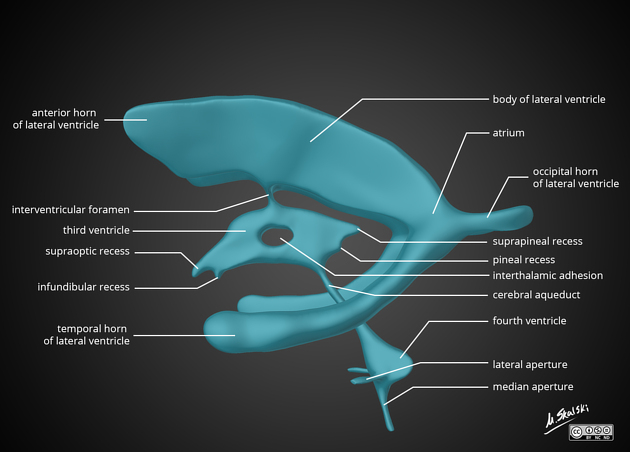
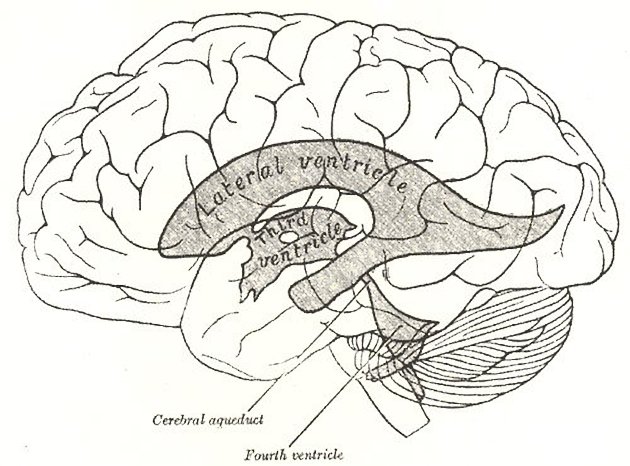
The fourth ventricle is one of the components of the ventricular system in the brain, along with the lateral and third ventricles. It extends from the cerebral aqueduct (of Sylvius) rostrally to the obex caudally and is filled with CSF.
CSF enters the ventricle via the cerebral aqueduct and leaves via one of four routes:
via the obex and into the central canal
via the median aperture (of Magendie) into the cisterna magna
via one of the two lateral apertures (of Luschka) into the cerebellopontine cistern
It is characteristically tent-shaped or triangular in sagittal cross-section and diamond-shaped in coronal cross-section. It is located dorsal to the pons or upper part of the medulla oblongatais the fastigium.
The roof, located dorsally, is formed by the superior medullary velum and inferior medullary velum overlying the cerebellum. These two surfaces met at an apex projecting into the cerebellum. This is the fastigium and it underlies the fastigial nucleus 3.
The floor, located ventrally, is also known as the rhomboid fossa and is diamond-shaped on the dorsal surface of the pons and upper half of the medulla. It is divided longitudinally by the median sulcus, with median eminences on either side. Each has a focal swelling known as the facial colliculus, formed by facial nerve fibers rounding the abducens nucleus.
The sidewalls are formed by the vela and cerebellar peduncles.
It is widest at the level of the pontomedullary junction. The obex is the most caudal tip of the fourth ventricle.
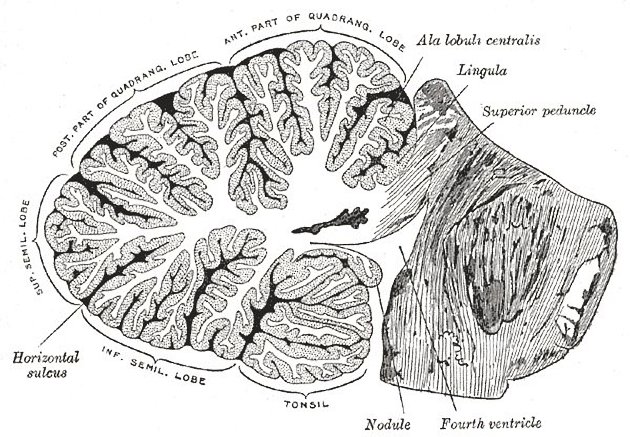
The fourth ventricle contains choroid plexus along its roof along the tela choroidea which may protrude out the lateral foramina of Luschka.
Related pathology
See also
References
- 1. Stranding S, DSc SSP. Gray's anatomy. Churchill Livingstone. (2005) ISBN:0443071683. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Ross LMMP. Atlas of anatomy. George Thieme Verlag. (2007) ISBN:3131421215. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Tsutsumi S, Fernandez-Miranda J, Ishii H, Ono H, Yasumoto Y. Dorsal Extensions of the Fastigium Cerebelli: An Anatomical Study Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Surg Radiol Anat. 2018;40(7):829-34. doi:10.1007/s00276-018-2023-3 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Rhomboid fossa (brainstem)
- Diffuse brainstem glioma (historical)
- Midline shift (summary)
- Central nervous system embryology
- Choroid plexus
- Cisterna magna
- Sagittal midline of the brain (an approach)
- Horizontal gaze palsy with progressive scoliosis
- Obex
- Pilocytic astrocytoma
- Choroid plexus papilloma
- Neurenteric cyst
- Lateral apertures (of Luschka)
- Chiari III malformation
- Inferior medullary velum
- Intraventricular haemorrhage
- Intraventricular meningioma
- Intracranial epidermoid cyst
- Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered
- Dentate nucleus
- Intracranial ventricular anatomy
- Facial colliculus syndrome
- Joubert syndrome
- Chronic lymphocytic inflammation with pontine perivascular enhancement responsive to steroids (CLIPPERS)
- Aqueduct stenosis - web
- Fourth ventricular outlet obstruction
- Epidermoid cyst - posterior cranial fossa
- Acute cerebellitis
- Aqueductal stenosis
- Acoustic neuroma with obstructive hydrocephalus
- Poretti-Boltshauser syndrome
- Dandy-Walker malformation - excessive Wharton jelly
- Pontine cavernoma
- Cerebellar mutism syndrome and pilocytic astrocytoma
- Dandy-Walker malformation with dysgenesis of the corpus callosum and arachnoid cyst
- Chiari II malformation - fetal MRI
- Aqueduct stenosis - obstructive hydrocephalus
- Diffuse pontine glioma
- Epidermoid cyst - obstructive hydrocephalus
- Subependymoma
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.