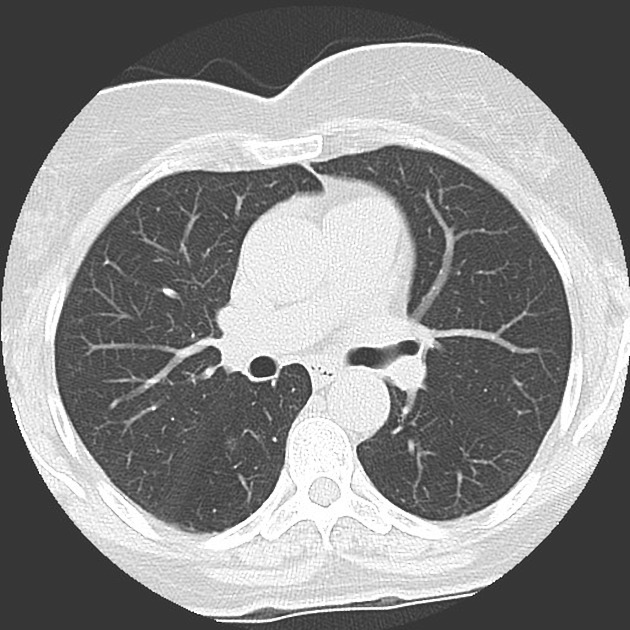
Ground-glass density nodule
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Usman Bashir had no recorded disclosures.
View Usman Bashir's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yahya Baba had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Yahya Baba's current disclosures- Ground glass density nodule (GGN)
- Ground glass density nodules (GGN)
- Ground glass density nodules
- Ground glass nodule
- Ground glass nodules
- Ground glass lung nodule
- Ground glass lung nodules
- Ground glass pulmonary nodule
- Pulmonary nodular ground-glass opacities
- Pulmonary nodular ground-glass opacities (PNGGO)
- Pulmonary nodular ground-glass opacities (NGGO's)
- Ground glass pulmonary nodules
A ground-glass density nodule (GGN) is a circumscribed area of increased pulmonary attenuation with preservation of the bronchial and vascular margins.
A ground-glass density may be:
partly solid (part of the ground-glass opacity completely obscures the parenchyma)
non-solid (no completely obscured areas): pure ground-glass nodules
Although encountered regularly, the incidence of cancer in these nodules has been reported as high as 63% (for partly solid nodules, in one study). Histologically these may represent:
-
primary (e.g. adenocarcinoma in situ, minimally invasive adenocarcinoma, and invasive adenocarcinoma)
metastases: occasionally can manifest as ground-glass nodules 6
focal pulmonary hemorrhages
See also
References
- 1. Feely MA, Hartman TE. Inappropriate application of nodule management guidelines in radiologist reports before and after revision of exclusion criteria. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196 (5): 1115-9. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.5141 - Pubmed citation
- 2. Henschke CI, Yankelevitz DF, Mirtcheva R et-al. CT screening for lung cancer: frequency and significance of part-solid and nonsolid nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178 (5): 1053-7. AJR Am J Roentgenol (citation) - Pubmed citation
- 3. Macmahon H, Austin JH, Gamsu G et-al. Guidelines for management of small pulmonary nodules detected on CT scans: a statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology. 2005;237 (2): 395-400. Radiology (full text) - doi:10.1148/radiol.2372041887 - Pubmed citation
- 4. Takahashi S, Tanaka N, Okimoto T et-al. Long term follow-up for small pure ground-glass nodules: implications of determining an optimum follow-up period and high-resolution CT findings to predict the growth of nodules. Jpn J Radiol. 2012;30 (3): 206-17. Jpn J Radiol (full text) - doi:10.1007/s11604-011-0033-8 - Pubmed citation
- 5. Park CM, Goo JM, Kim TJ et-al. Pulmonary nodular ground-glass opacities in patients with extrapulmonary cancers: what is their clinical significance and how can we determine whether they are malignant or benign lesions?. Chest. 2008;133 (6): 1402-9. doi:10.1378/chest.07-2568 - Pubmed citation
- 6. Kim SB, Lee S, Koh MJ et-al. Ground-glass opacity in lung metastasis from breast cancer: a case report. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2013;74 (1): 32-6. doi:10.4046/trd.2013.74.1.32 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 7. Kobayashi Y, Mitsudomi T. Management of ground-glass opacities: should all pulmonary lesions with ground-glass opacity be surgically resected?. (2013) Translational lung cancer research. 2 (5): 354-63. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2013.09.03 - Pubmed
- 8. Lee J, Hong J, Kim H. Guidelines for the Investigation and Management of Ground Glass Nodules. J Chest Surg. 2021;54(5):333-7. doi:10.5090/jcs.21.021 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Focal interstitial pulmonary fibrosis
- Pulmonary nodule
- Diffuse ground-glass nodules
- Chest curriculum
- Tumor pseudoprogression (lung cancer)
- Diffuse pulmonary meningotheliomatosis
- Pulmonary mucormycosis
- Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia of the lung
- Focal ground glass opacification
- Adenocarcinoma of the lung
- Adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung
- Pure ground glass nodules
- Ground-glass opacification
- Thoracic HRCT terminology
- Pulmonary haemophilus influenzae infection
- Centrilobular lung nodules
- Part solid lung nodule
- Lung adenocarcinoma presenting as pure ground-glass nodule
- Non-invasive thymoma
- Pulmonary haemorrhage due to bronchiectasis
- COVID-19 induced mesenteric venous infarction with small bowel obstruction
- Spontaneous pneumomediastinum with extensive subcutaneous emphysema complicating a COVID-19 pneumonia
- COVID-19 pneumonia - paediatric
- COVID-19 pneumonia
- COVID-19 pneumonia
- COVID-19 pneumonia
- COVID-19 pneumonia
- COVID-19 pneumonia
- COVID-19 pneumonia
- COVID-19 pneumonia
- Lung abscesses
- Pulmonary tuberculosis with COPD
- Invasive lung adenocarcinoma
- Fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.