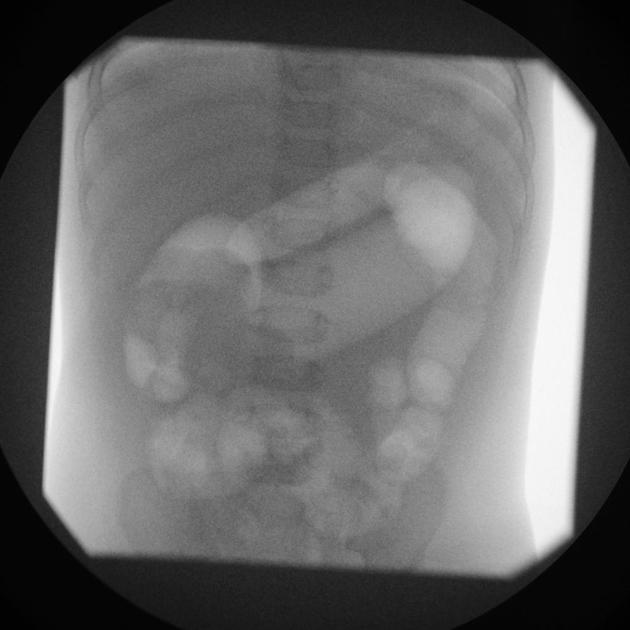
Intussusception reduction is a procedure performed in pediatric patients who have an ileocolic intussusception.
There are several ways that reduction can be achieved radiologically:
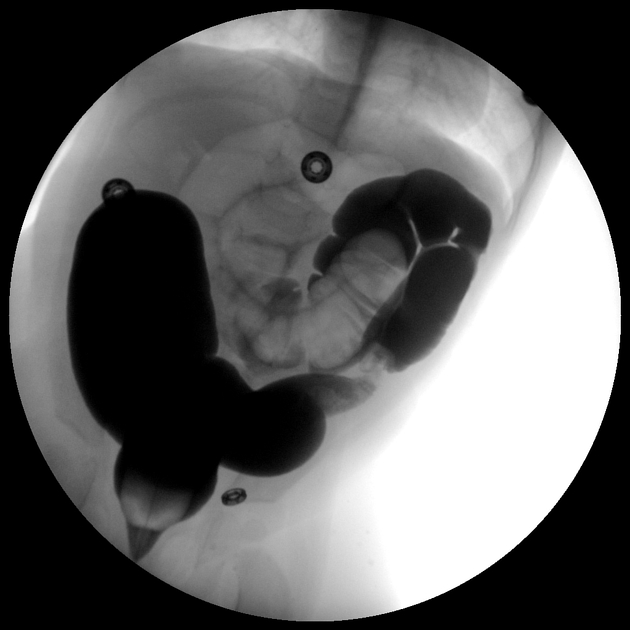
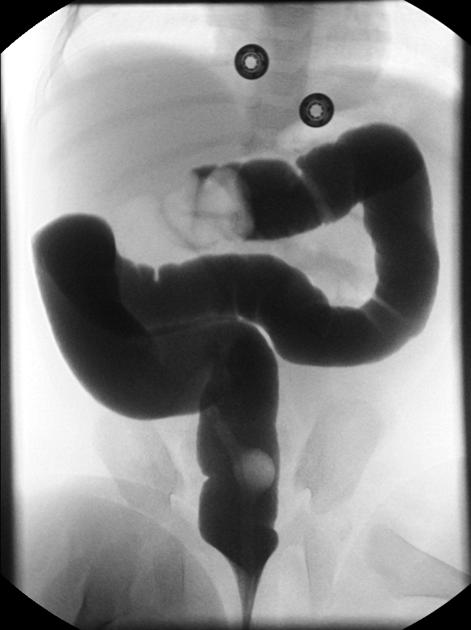
air-reduction under fluoroscopic guidance
hydrostatic-reduction under fluoroscopic guidance
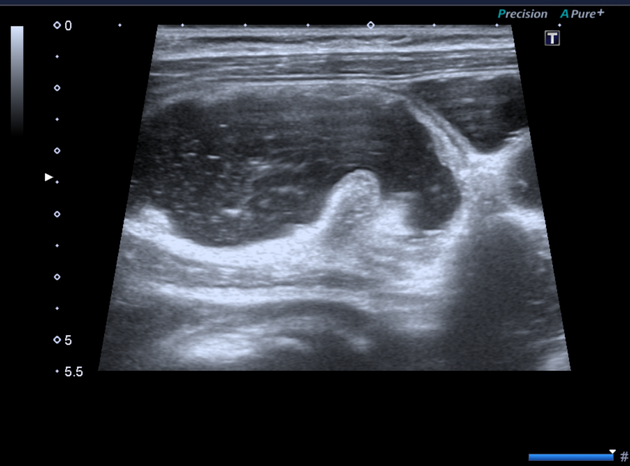
physical reduction under US guidance
hydrostatic-reduction under US guidance
In air-reduction and water-reduction methods, a catheter is inserted into the rectum of the child, and under fluoroscopic guidance, air or water is instilled into the large bowel.
Assessment with ultrasound prior to the reduction allows stratified risk assessment. Intussusception with reduced vascularity or interloop fluid is usually more challenging to reduce. Most facilities that perform this procedure require IV access, staff, and equipment for fluid resuscitation with the backup of a pediatric surgeon.
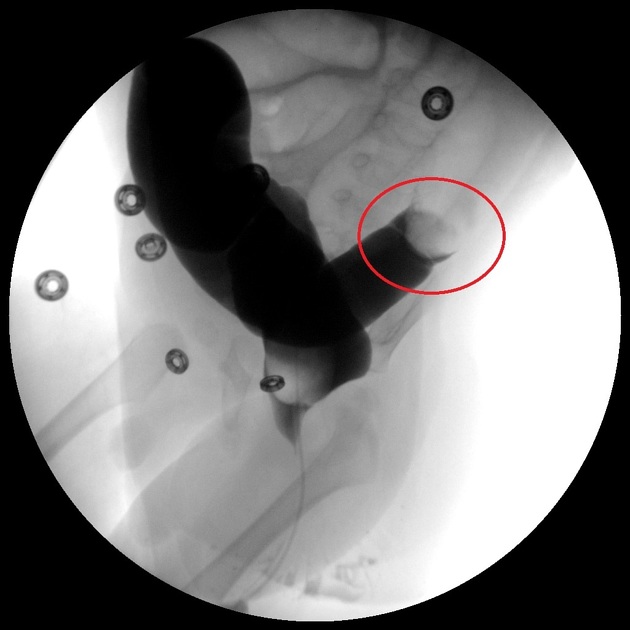
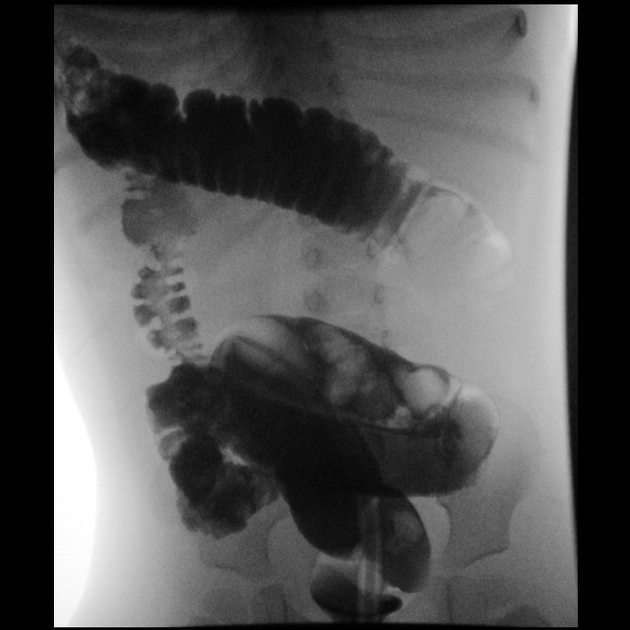
With air-reduction, pressures in the region of 60-100 mmHg are used which may reduce the intussusception back to the ileocecal valve. There are a variety of protocols that have been suggested with some advocating 3 attempts lasting 3 minutes. Success is achieved when there is reduction of the 'mass' and air or contrast refluxes into the terminal ileum.
Reduction is less likely to be successful if:
there is associated small bowel obstruction
over 24 hours of symptoms
lethargy
Complications
-
it is the main risk of reduction, but since without radiological reduction, an operation is required, this risk is worth taking
rectum is the most likely portion of the bowel to perforate, so it is important to monitor the diameter of the rectum during the procedure rather than just concentrating on the position of the intussusception
-
recurrence:
may occur in up to 10%, often within 3 days
repeat imaging-guided reduction is advised but should not be attempted more than 3 times
Contraindications
signs of peritonitis
perforation





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.