The knee menisci are fibrocartilaginous structures that sit within the knee joint, deepening the tibiofemoral articulation. Their main role is shock absorption, improve stability of the knee joint, and load transmission. They also play an important role in synovial fluid dynamic circulation and also considered by some to be involved in proprioception.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
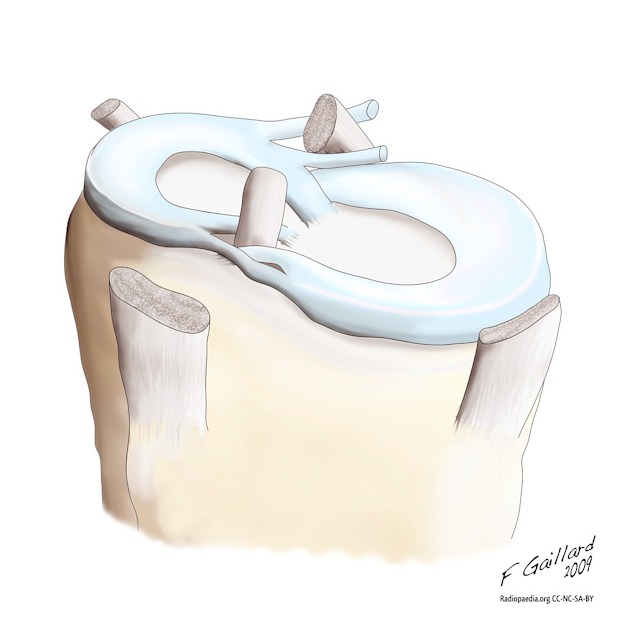
There are two fibrocartilaginous menisci in the knee joint: a medial meniscus within the medial tibiofemoral compartment and a lateral meniscus within the lateral tibiofemoral compartment. Each meniscus is C-shaped in the transverse plane and consists of the following parts (from anterior to posterior):
anterior root attachment
anterior horn
body (located centrally)
posterior horn
posterior root attachment
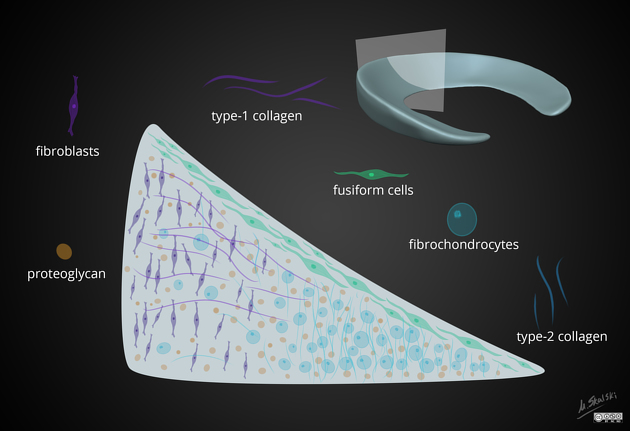
In cross-section, they have a triangular shape, being thicker peripherally and thinning to a free-edge centrally.
Medial versus lateral meniscus
The medial and lateral menisci differ in size and shape as follows:
-
medial meniscus
C-shape - open and wide, almost semi-circular
larger than lateral meniscus
posterior horn substantially larger than anterior horn
-
lateral meniscus
C-shape - tight and closed off more like an incomplete circle, i.e. anterior and posterior tibial roots are very close to each other
smaller than medial meniscus
anterior and posterior horns same size
Surfaces
The meniscal surfaces are named according to a simple nomenclature which is particularly helpful when describing meniscal tears.
superior articular surface - also known as femoral surface
inferior articular surface - also known as tibial surface
inner free edge
periphery
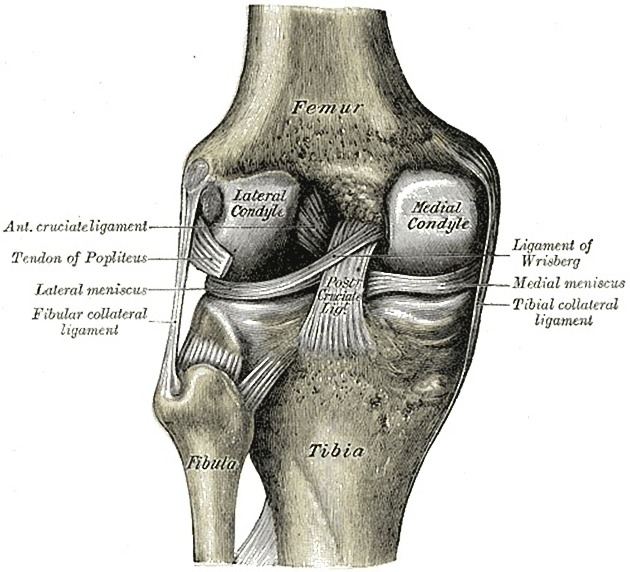
Attachments
-
medial meniscus
the anterior horn of the medial meniscus attaches immediately anterior to the tibial attachment of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in the intercondylar area
medial aspect attached to the deep (third) layer of the medial collateral ligament
posterior horn is attached to the posterior intercondylar area of the tibial plateau, between PCL insertion posteriorly and posterior root attachment of lateral meniscus, anteriorly
-
lateral meniscus
the anterior horn of the lateral meniscus attaches immediately lateral to the tibial attachment of the ACL on the intercondylar area
no attachment to the lateral collateral ligament
attached to joint capsule except anterior horn and posterior most portion of posterior horn; this is due to the passage of the intra-articular portion of the popliteus tendon
posterior horn of the lateral meniscus attaches to the posterior intercondylar area of the tibial plateau anterior to the medial meniscus and posterior to ACL
-
other attachments
-
meniscofemoral ligament: posterior horn of the lateral meniscus to the lateral aspect of the medial femoral condyle
transverse meniscal (or genual) ligament (of Winslow) attaches the anterior horns to each other
joint capsule peripherally except the lateral meniscus at the site of the popliteus tendon hiatus
-
small ligaments/retinaculia from LM to the capsule:
inferior meniscopopliteal ligament at the body: the floor of popliteal hiatus
superior and inferior meniscopopliteal ligaments at body-posterior horn junction
superior meniscopopliteal ligament at posterior horn: the roof of popliteal hiatus
-
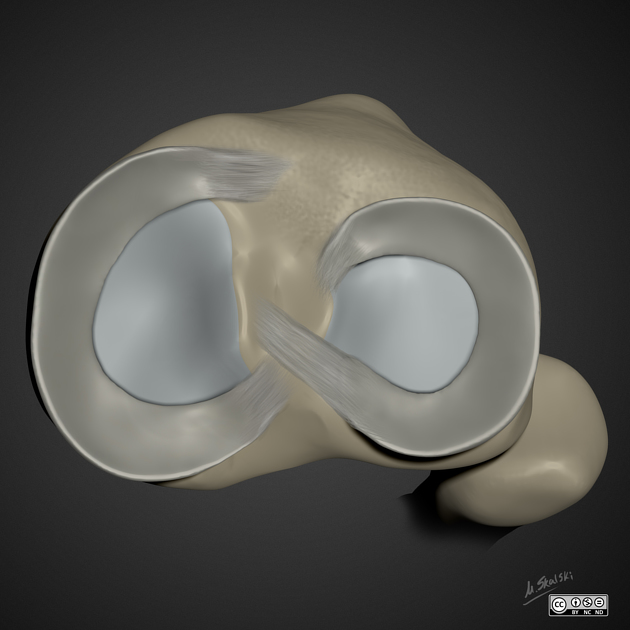
Blood supply
The menisci are vascularized only via the periphery and the root attachments and therefore the inner portions are avascular. This has important implications on the healing and surgical management of meniscal tears.
-
red zone: outer one-third
supply from the peripheral meniscal plexus, in turn formed from the medial, lateral and middle genicular arteries 6,8
-
white zone: inner two-thirds
no vascular supply; diffusion dependent 6
-
red-white zone: transition between outer third and inner two-thirds
reflecting the reality that the loss of perfusion is gradual and also variable from site to site, patient to patient
Innervation
posterior articular branch of the tibial nerve and terminal obturator and femoral nerve branches 8
Variant anatomy
discoid meniscus 4,5
congenital hypoplasia or absence 4
-
anomalous insertion of the medial meniscus (AIMM) (2%)
anterior root onto the ACL or intercondylar notch 4
anterior root onto anterior margin of the tibia in the midline 5
no attachment of anterior root: stabilized by the transverse meniscal ligament 5
meniscal ossicle (rare; incidence <0.2%) 5





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.