The point-of-care ultrasound (PoCUS) curriculum is one of our curriculum articles and aims to be a collection of articles that represent the core applications of ultrasonography in a point-of-care setting.
Point-of-care ultrasound refers to ultrasonography which may be simultaneously performed, interpreted and utilised by a health care provider at the time of consultation, in proximity to the patient. The goals and scope are fundamentally different from the traditional sonographer-performed ultrasound, limited to specific clinical questions that narrow a clinician's differentials, guide clinical therapy, and direct consultations and disposition.
While more detailed and complex ultrasonography applications may provide information that is more detailed than PoCUS, have greater anatomic specificity, or identify alternative diagnoses, PoCUS is non-invasive, rapidly deployed and does not entail removal of the patient from their clinical area, e.g. resuscitation suite.
PoCUS consensus statements emphasise engaging consultants early on in work-up, ultimately improving initial diagnostic accuracy, initiation of proper management, and allowing PoCUS to play a complementary role to traditional imaging modalities.
While grouping applications of PoCUS is largely arbitrary, the indications for PoCUS tend to revolve around either the function of an anatomical structure or a syndrome eliciting interrogation of systems pertaining to the differential diagnosis.
On this page:
Anatomy
Thorax
-
key findings
-
lung
-
pleura
mirror sign
-
Cardiac
-
anatomy
-
pulmonic valve
-
key findings
Abdomen
-
tubular gastrointestinal organs
-
gastric antrum
-
solid gastrointestinal organs
-
biliary tree
-
fundus
body
neck
-
head
neck
body
tail
-
spleen
-
genitourinary
-
key findings
peristalsis
bladder volume
Aorta
-
thoracic aorta
-
abdominal aorta branches
-
key findings
sinuses of valsalva
sinotubular junction
Upper and lower Limb
-
upper limb
-
musculoskeletal
-
vessels
-
nerves
median nerve
radial nerve
ulnar nerve
-
-
key findings
Ear, Nose and Throat
-
anatomy
-
key findings
Ocular
-
anatomy
anterior chamber
posterior chamber
-
key findings
Gynaecological
-
key findings
Nervous system
-
central nervous system
transcranial doppler
-
peripheral nervous system
brachial plexus
key findings
Radiological examinations
-
cardiac
-
lung
-
abdomen and thorax
focused assessment with sonography in HIV/TB (FASH)
pericardiocentesis (ultrasound)
thoracentesis (ultrasound)
paracentesis (ultrasound)
-
neurovascular
-
nerves
supraclavicular brachial plexus block
axillary nerve block
radial nerve block
ulnar nerve block
median nerve block
-
vasculature
central venous access (ultrasound)
peripheral venous access (ultrasound)
-
Pathology
Thorax
-
lungs and airways
-
trachea
-
lungs
-
alveolar-interstitial pathology
-
dynamic
static
-
interstitium
-
-
pleural pathology
-
-
vessels
-
thoracic aorta
-
-
cardiac
-
structure
-
function
-
systolic dysfunction
-
wall motion abnormalities
-
regional
-
global
-
-
-
left atrial pressure
elevated vs normal
-
grade I
formerly "impaired filling"
-
grade II
formerly "pseudonormal"
-
grade III
formerly "restrictive filling"
-
-
-
-
valvular dysfunction
-
atrioventricular valves
-
tricuspid valve
-
mitral valve
-
-
semilunar valves
-
pulmonic valve
-
aortic valve
-
-
-
Abdomen
-
gastrointestinal tract
-
peritoneal recesses
-
right upper quadrant
-
liver
-
biliary tree
-
gallbladder
-
pancreas
-
complications
-
-
spleen
-
renal
-
Ocular
Male reproductive system
-
scrotum
-
testicular adnexa
Female reproductive system
-
uterus
-
gravid
-
puerperium
-
non-gravid
-
adnexa
-
ectopic pregnancy
-
interstitial ectopic pregnancy
-
pelvic inflammatory disease
-
-
ovaries
-
fallopian tubes
-
Upper and Lower extremities
-
venous
-
axillary
-
-
musculoskeletal
-
upper extremity
-
shoulder
-
proximal upper extremity
-
-
Soft tissue
-
infectious






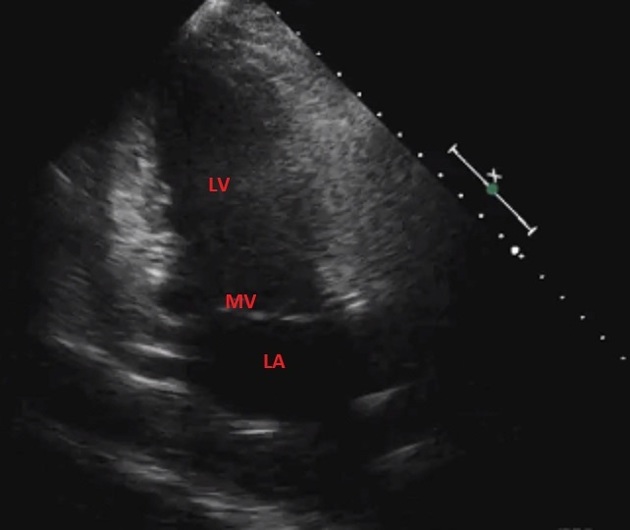










 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.