The recipients of renal transplants are susceptible to a number of complications. The incidence of each is variable and partially subject to specific surgical transplantation techniques and management patterns.
Pathology
Renal transplant complications
These can be broadly categorized as perirenal, renal parenchymal, renal collecting system, and/or renal vascular complications 1,2:
perioperative acute tubular necrosis
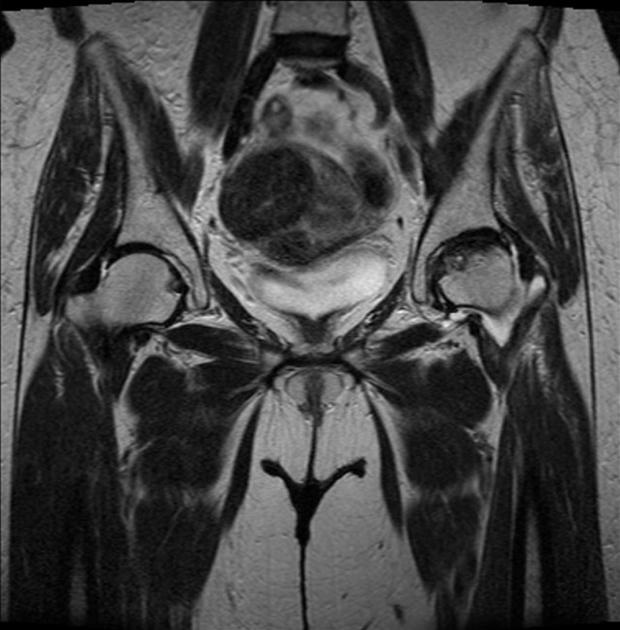
renal allograft torsion (rare) 7
-
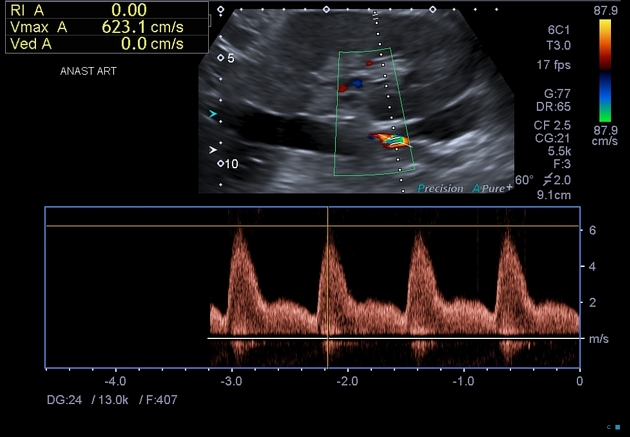
renal arterial stenosis in the transplant renal artery 3:
peak systolic velocity (PSV) >200 cm/s
2:1 PSV ratio between stenotic and prestenotic artery
spectral broadening distally (i.e. turbulent flow)
+/- renal parenchymal tardus-parvus waveform
acute perioperative renal artery thrombosis
-
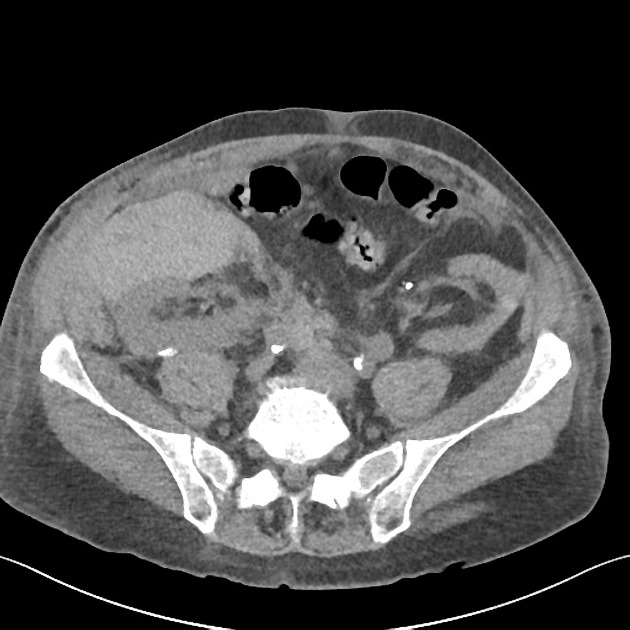
perinephric fluid collection: occurring roughly in the order below post-surgery
-
urinary obstruction 3
although usually presents within the first 6 months following the transplant, may occur years later
clinically presents with rising creatinine and absence of renal colic (renal allograft is denervated)
site of obstruction is typically near transplant ureter / native bladder anastomosis
-
causes of obstruction 3
transplant ureter stenosis (most commonly due to scarring, kinking, or secondary to anastomotic technique)
less commonly pelvic fibrosis, calculi, papillary necrosis, external compression
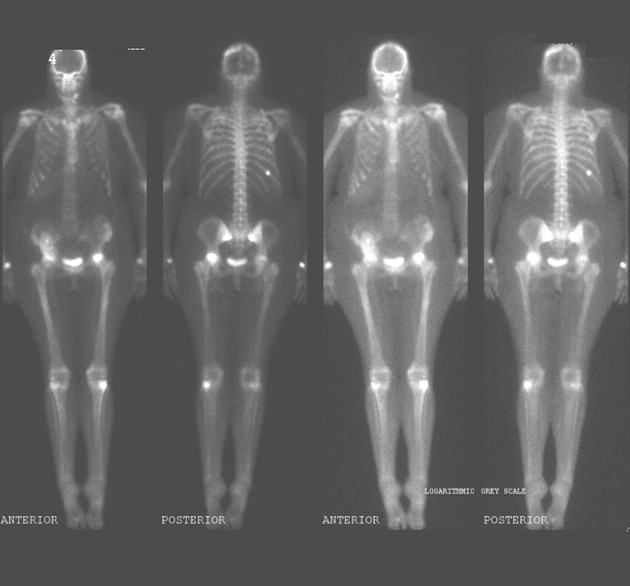
graft pyelonephritis 4
-
infections 6:
-
nosocomial and procedure-related
occurring <1 month after transplantation
donor related infections: HSV, rabies, West Nile virus
recipient acquired infections: Aspergillus spp., Pseudomonas spp.
-
latent, prior and opportunistic
occurring 1-6 months after transplantation
depending if the patient is on pneumocystis pneumonia and antiviral prophylaxis
with: BK virus, HCV, adenovirus, influenza, Cryptococcus neoformans, Mycobacterium tuberculosis
without: Pneumocystis jirovecii, Herpes family, HBV, Listeria, Nocardia, Toxoplasma spp.
-
community-acquired
occurring >6 months after transplantation
urinary tract infection, late viral infections and others (e.g. Nocardia, Aspergillus)
-
donor-related malignancy
Extra-renal transplant complications
increased incidence of malignancy: e.g. lymphoma
Treatment and prognosis
The 1-year survival rate of deceased renal allografts were over 93% in 2014 5.






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.