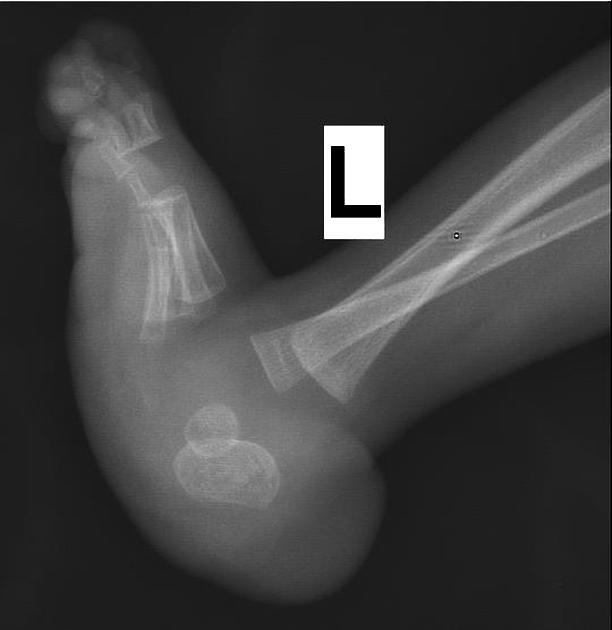
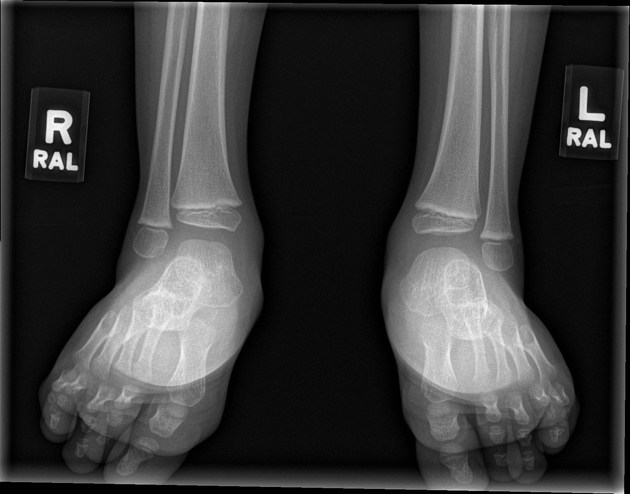
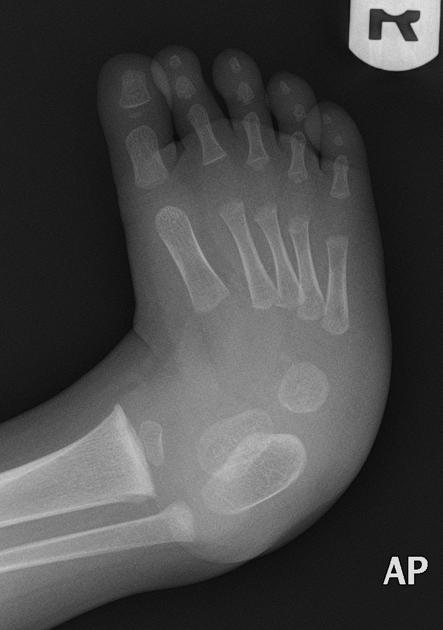
A rocker bottom foot (also known as a congenital vertical talus) is a congenital anomaly of the foot. It is characterized by a prominent calcaneus/heel and a convexly rounded sole.
On this page:
Pathology
It results from a dorsal and lateral dislocation of the talonavicular joint.
Associations
- aneuploidic syndromic
- non-aneuploidic non-syndromic
Radiographic features
For assessment of the foot alignment abnormalities, it is important to perform weight-bearing images or an equivalent in neonates:
- fixed equinus: plantarflexion of the calcaneus
- vertical talus: plantarflexion of the talus (increased talocalcaneal angle)
- irreducible dorsal subluxation or dislocation of the navicular
- forefoot valgus: divergence of bases of the metatarsal heads on AP and superimposition of the metatarsal bones on the lateral view
- long axis of the talus passes plantar to the metatarsal axis on lateral view and medial to the first metatarsal on AP view
The presence of a rocker bottom foot in an antenatal ultrasound scan is sometimes classified as a soft sign for aneuploidic anomalies 3.
Differential diagnosis
In the antenatal/neonatal period consider clubfoot.
In the adult period consider acquired rocker bottom deformity occurring secondary to:
- underlying neuromuscular disorder(s)
- diabetic foot (Charcot joint) 2








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.