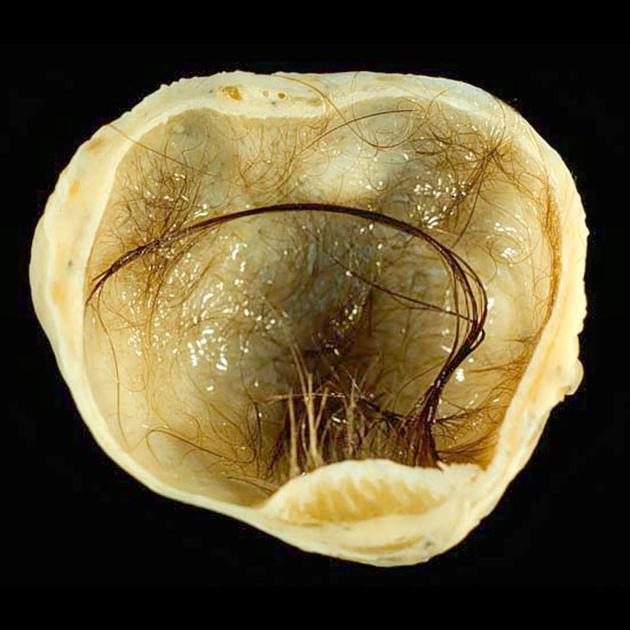
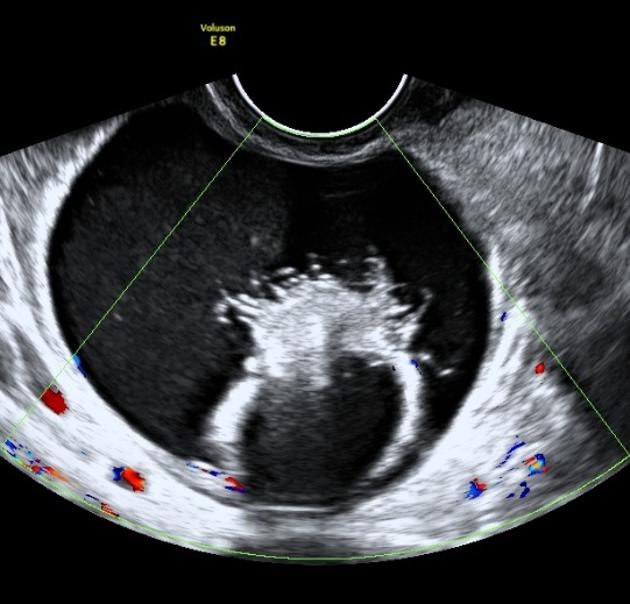
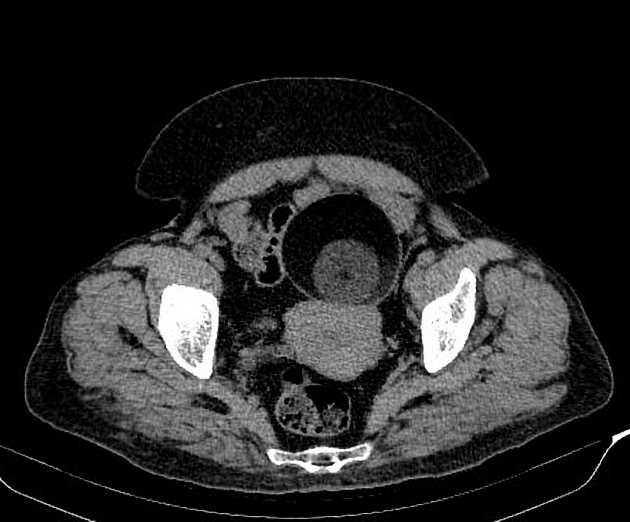
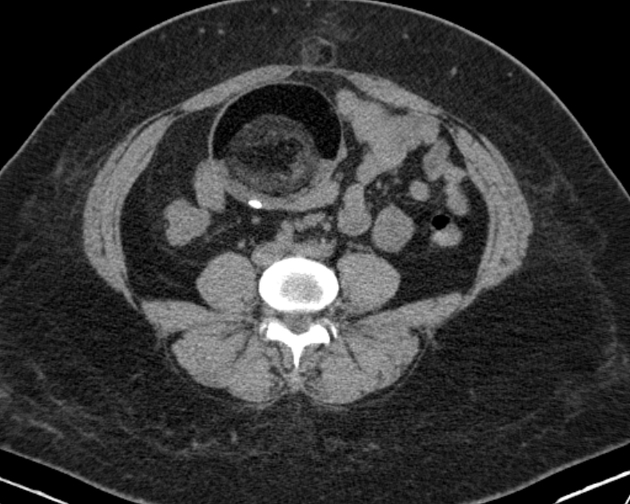
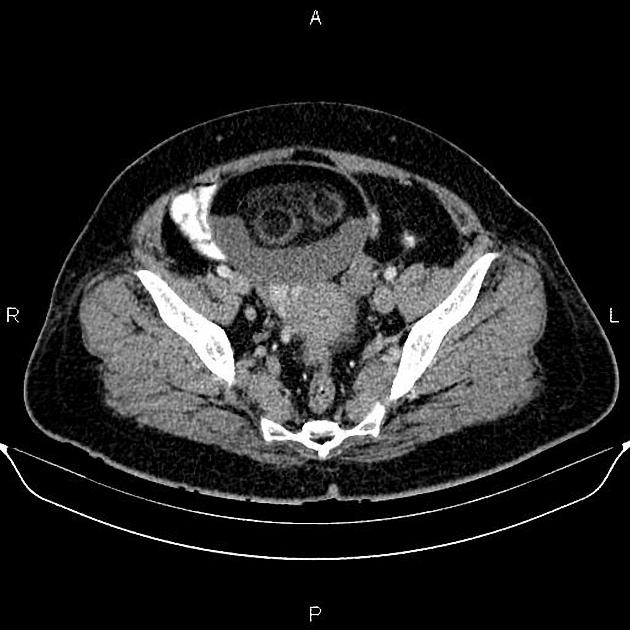
A Rokitansky nodule or dermoid plug refers to a solid protuberance projecting from an ovarian cyst in the context of mature cystic teratoma. It often contains calcific, dental, adipose, hair, and/or sebaceous components 1. This region has the highest propensity to undergo malignant transformation.
Radiographic features
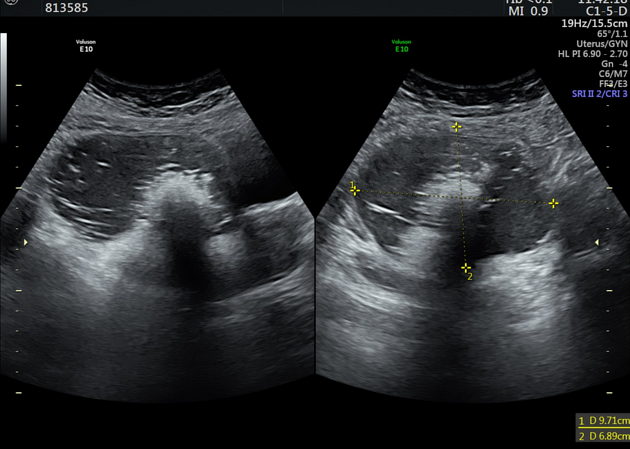
Ultrasound
A Rokitansky nodule is seen as a densely echogenic nodule, with posterior acoustic shadowing, projecting into the lumen of the mature cystic teratoma.
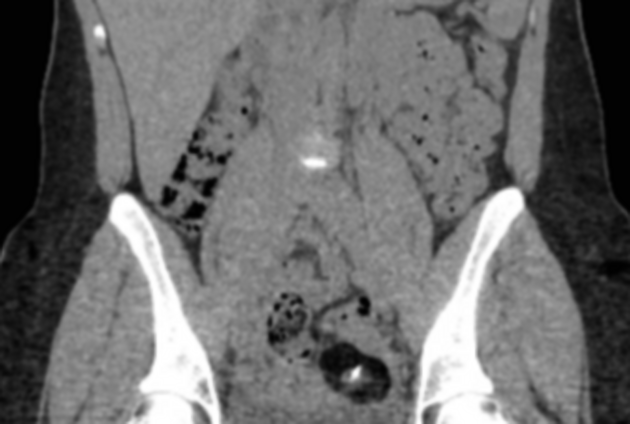
CT
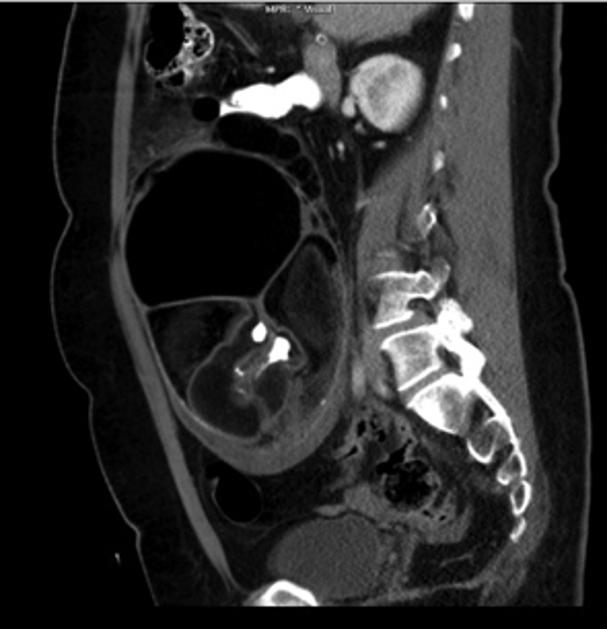
A Rokitansky nodule might be seen as a focal mural thickening, round structure protruding into the cystic lumen, a bridging tissue across the cyst, a cystic structure or sometimes only tooth. Features like contrast enhancement, an obtuse angle between the soft tissue and the wall of the cyst, extracapsular tumor growth with extension into the adjacent structures, should all raise the possibility of a malignant transformation.
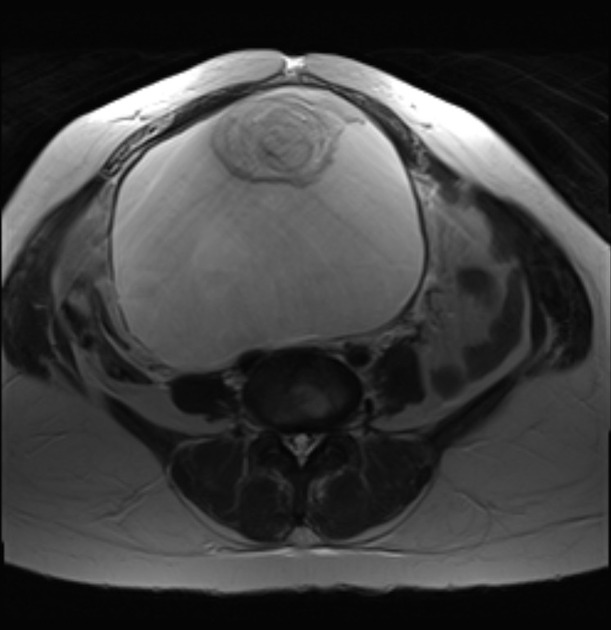
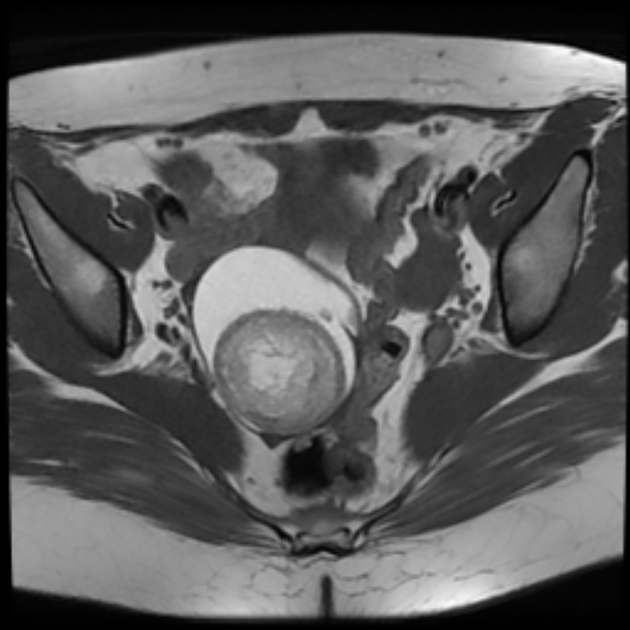
MRI
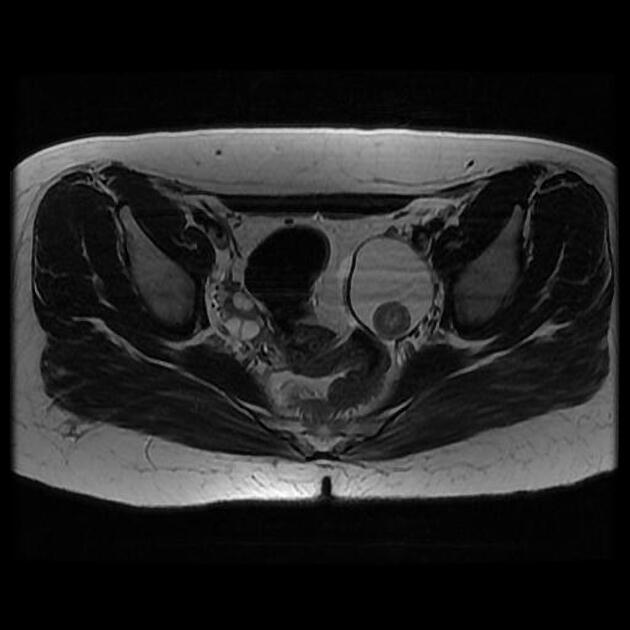
Rokitansky nodules are best evaluated with MRI, where the exact number, size, relationship with the cyst wall, shape and content is more evident.
History and etymology
It is named after Carl von Rokitansky (1804-1878), a Viennese pathologist 4.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.