Inguinal canal lipoma
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Ciléin Kearns had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Ciléin Kearns's current disclosures- Lipoma of inguinal canal
- Spermatic cord lipoma
- Inguinal canal lipomas
- Round ligament lipoma
- Lipoma of the spermatic cord
- Cord lipoma
Inguinal canal lipomas (also known as spermatic cord lipomas, peritesticular lipomas, and round ligament lipomas), are a relatively common but often under-recognised finding on imaging.
On this page:
Terminology
'Spermatic cord lipoma' is variably used to mean a true lipoma of the spermatic cord (originating from adipose cells and with no communication with the inguinal canal), an inguinal canal lipoma (extraperitoneal fat extension through the inguinal canal), or a hernia of intraperitoneal fat through the inguinal canal, with or without a hernial sac 5.
Clinical presentation
Lipomas are usually asymptomatic but can sometimes cause pain and discomfort. They can present as a non-tender soft scrotal mass 4.
Pathology
They have no communication with the peritoneal fat. They are not considered true tumours of fat but extrusions of extraperitoneal fat extending into the inguinal canal.
Radiographic features
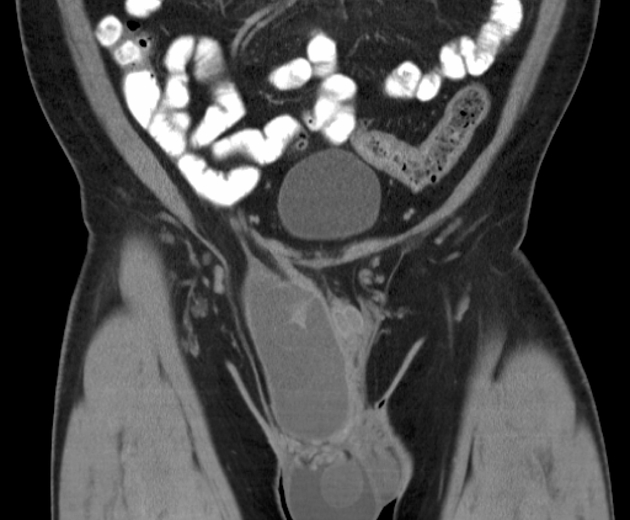
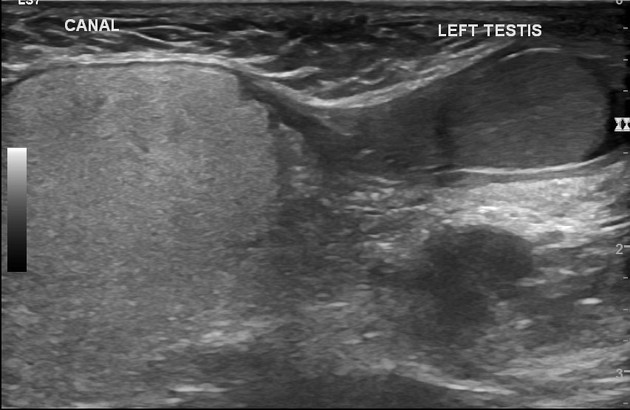
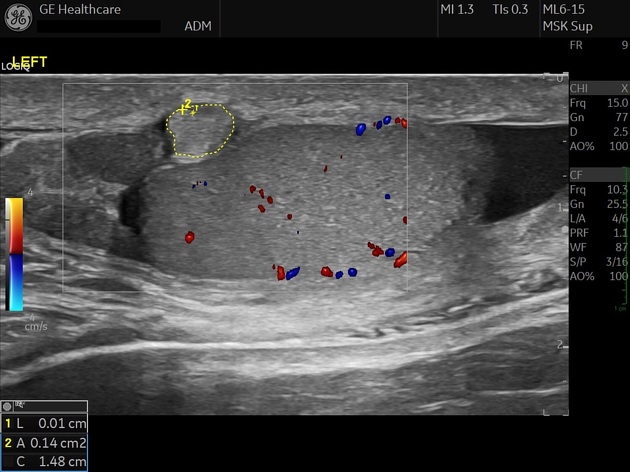
Ultrasound
It is seen as a well defined, solid hyperechoic mass, expanding the inguinal canal, which gently effaces the spermatic cord.
CT
The lesion shows attenuation corresponding to fat (-20 to -70 HU). No associated soft tissue component or enhancement.
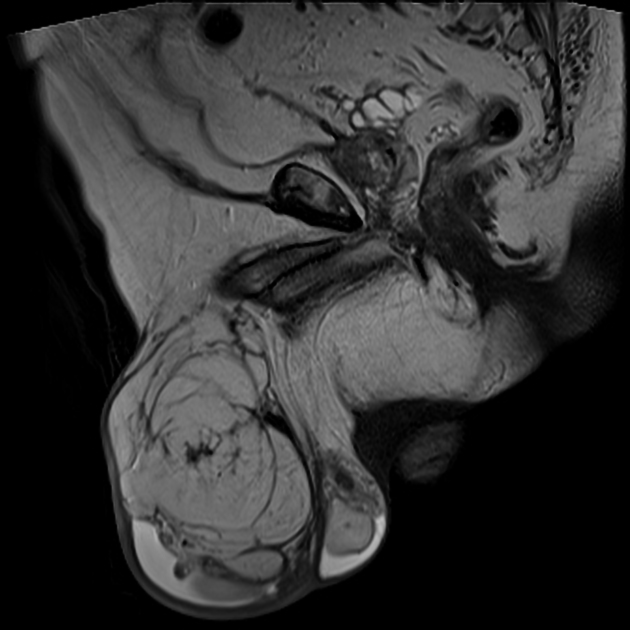
MRI
Oval shaped mass with typical fat signal characteristics:
T1: high signal
T2: high signal
fat-suppressed sequences: shows fat suppression
Treatment and prognosis
They are a benign entity and no treatment is usually required in incidental asymptomatic cases. Resection can be offered to patients who are clinically symptomatic.
Differential diagnosis
On imaging, possible differential considerations include:
inguinal hernias containing fat
-
other inguinal canal / spermatic cord masses 3
subcutaneous lipoma overlying the spermatic cord
See also
References
- 1. Fataar S. CT of inguinal canal lipomas and fat-containing inguinal hernias. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2011;55 (5): 485-92. doi:10.1111/j.1754-9485.2011.02288.x - Pubmed citation
- 2. Bhosale PR, Patnana M, Viswanathan C et-al. The inguinal canal: anatomy and imaging features of common and uncommon masses. Radiographics. 2008;28 (3): 819-35. Radiographics (full text) - doi:10.1148/rg.283075110 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Akbar SA, Sayyed TA, Jafri SZ, Hasteh F, Neill JS. Multimodality imaging of paratesticular neoplasms and their rare mimics. (2003) Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 23 (6): 1461-76. doi:10.1148/rg.236025174 - Pubmed
- 4. Gabriel H, Hammond N, Marquez R et al. Gamut of Extratesticular Scrotal Masses: Anatomic Approach to Sonographic Differential Diagnosis. Radiographics. 2023;43(4):e220113. doi:10.1148/rg.220113 - Pubmed
- 5. Köckerling F & Schug-Pass C. Spermatic Cord Lipoma—A Review of the Literature. Front Surg. 2020;7:39. doi:10.3389/fsurg.2020.00039 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta praevia
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynaecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumours
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumours of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumours
- mixed germ cell tumour
- yolk sac tumour (endodermal sinus tumour)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumour
- sex cord / stromal tumours of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumour of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumours (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumours
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.