Splenic artery embolization is an endovascular technique for treatment of splenic and splenic artery pathology as an alternative to splenic artery ligation or splenectomy. It often results in successfully treating the underlying pathology, while maintaining at least partial splenic function.
On this page:
Indications
traumatic splenic injury, particularly AAST grade III-V injuries in haemodynamically stable patients
Procedure
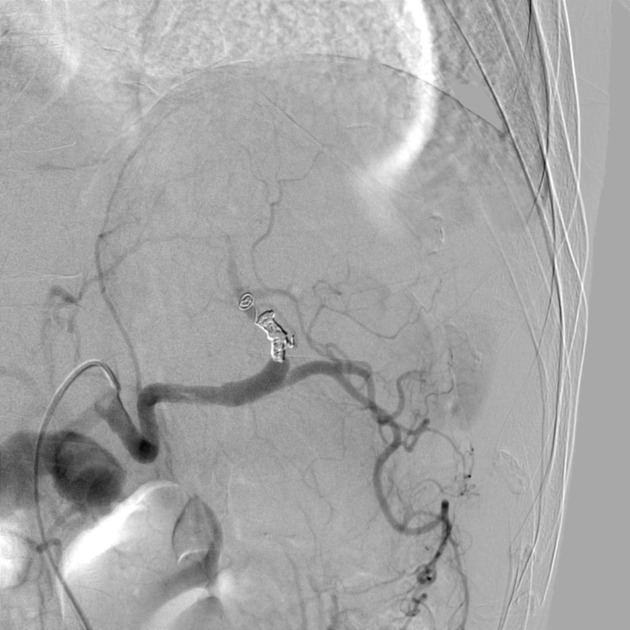
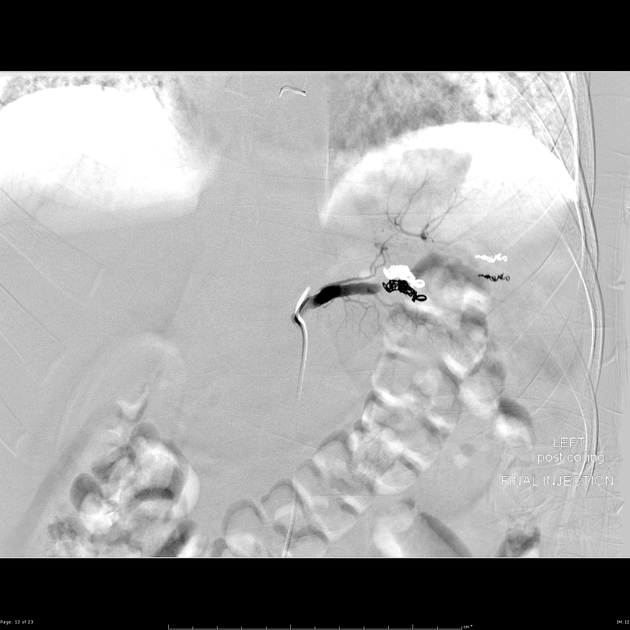
Technique
There are a multitude of techniques including:
partial or complete embolization
proximal or distal embolization
coil, particle or glue embolization
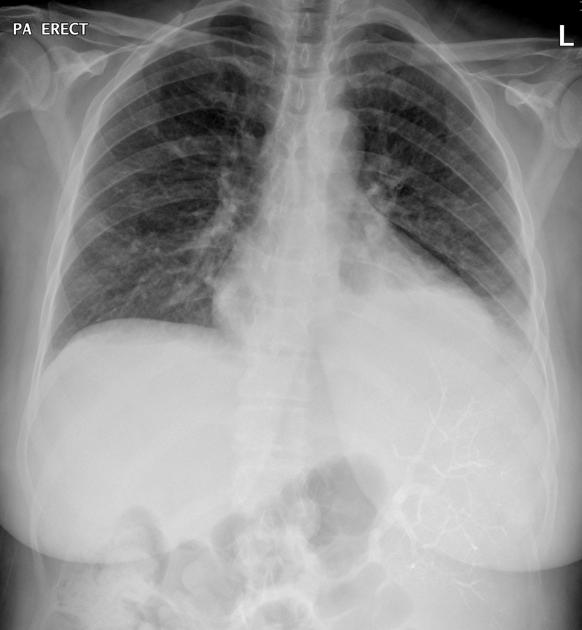
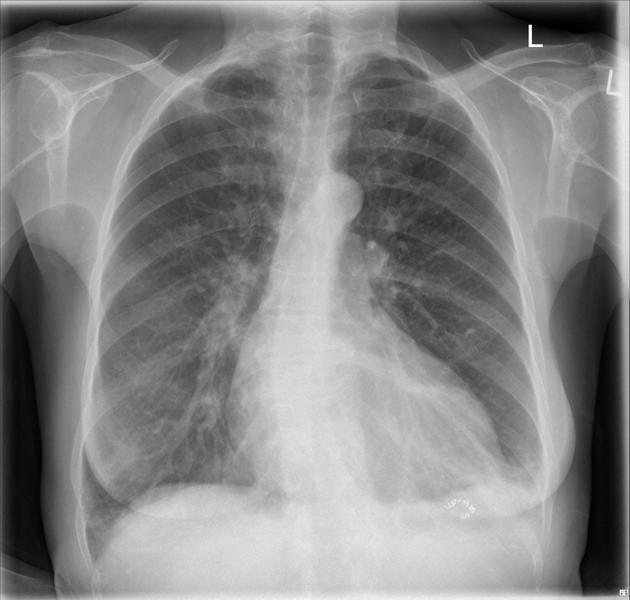
Complications
left pleural effusion and atelectasis (20-50%) 3,4
splenic infarct (~3%) 2
-
splenic abscess (~2%) 2,3
NB gas post splenic embolization may be a normal/incidental finding, although can represent infection in a minority 7
Outcomes
In contrast to patients who undergo splenectomy, patients who undergo splenic artery embolization are demonstrated to have preserved immune function at long term follow up. This evidence is supported by research that reports the lack of circulating Howell-Jolly bodies on follow up (nuclear remnants in RBCs that occur in asplenic patients).




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.