Superparamagnetism
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Ballinger J, Jones J, Bell D, et al. Superparamagnetism. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 27 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-22455
rID:
22455
Article created:
1 Apr 2013,
J. Ray Ballinger
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created J. Ray Ballinger had no recorded disclosures.
View J. Ray Ballinger's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosures
Revisions:
9 times, by
7 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Sections:
Tags:
Superparamagnetic materials consist of individual domains of elements that have ferromagnetic properties in bulk. Their magnetic susceptibility is between that of ferromagnetic and paramagnetic materials.
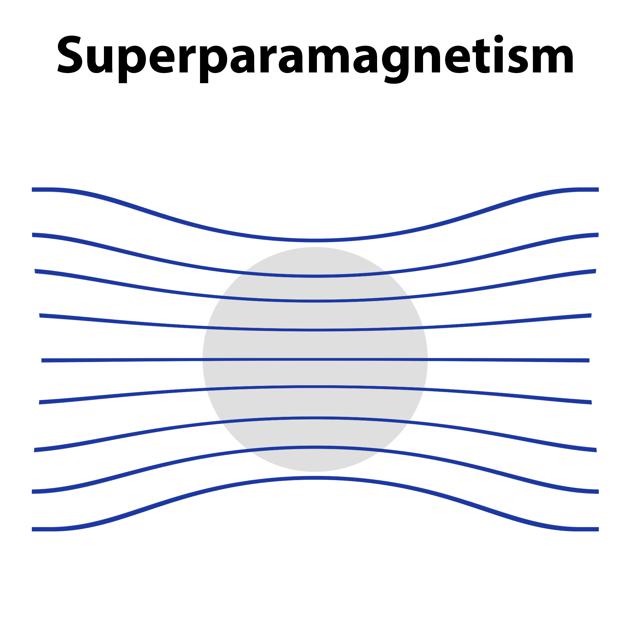
The figure illustrates the effect of a superparamagnetic material (grey circle) on the magnetic field flux lines (blue). Examples of superparamagnetic materials include iron-containing contrast agents for bowel, liver, and lymph node imaging.
References
- 1. Alfred L. Horowitz. MRI Physics for Physicians. (2012) ISBN: 9781468403336
- 2. M A Flower. Webb's Physics of Medical Imaging, Second Edition. (2016) ISBN: 9781466568952
Incoming Links
Related articles: Imaging physics
- imaging physics
- imaging in practice
- imaging technology
-
x-ray physics
- ionizing radiation
- interaction with matter
- x-ray spectrum
- radiation units
- effective dose
- entrance skin dose
- radiation safety
- radiation damage (biomolecular)
- radiation damage (skin injury)
- stochastic effect
- CT physics
-
MRI physics
- B0
- chemical shift
- dependence of magnetization (proton density, field strength and temperature)
- echo time
- eddy currents
- electromagnetic induction
- Ernst angle
- flip angle
- Larmor frequency
- magnetic dipole
- magnetic field gradient
- magnetic susceptibility
- magnetism
- molecular tumbling rate effects on T1 and T2
- net magnetization vector (NMV)
- relaxation
- repetition time
- resonance and radiofrequency (RF)
- units of magnetism
- ultrasound physics
- nuclear medicine physics




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.