Physical principles of ultrasound
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Mirjan M. Nadrljanski had no recorded disclosures.
View Mirjan M. Nadrljanski's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no recorded disclosures.
View Andrew Murphy's current disclosures- Physical principles of ultrasound
- Ultrasound physics
Medical ultrasound is based on the use of high-frequency sound to aid in the diagnosis and treatment of patients. Ultrasound frequencies range from 2 to approximately 15 MHz, although even higher frequencies may be used in some situations.
The ultrasound beam originates from mechanical oscillations of numerous crystals in a transducer, which is excited by electrical pulses (piezoelectric effect). The transducer converts one type of energy into another (electrical <--> mechanical/sound).
The ultrasound waves (pulses of sound) are sent from the transducer, propagate through different tissues, and then return to the transducer as reflected echoes. The returned echoes are converted back into electrical impulses by the transducer crystals and are further processed to form the ultrasound image presented on the screen.
Ultrasound transducers contain a range of ultrasound frequencies, termed bandwidth. For example, 2.5-3.5 MHz for general abdominal imaging and 5.0-7.5 MHz for superficial imaging.
Ultrasound waves are reflected at the surfaces between the tissues of different density, the reflection being proportional to the difference in impedance. If the difference in density is increased, the proportion of reflected sound is increased, and the proportion of transmitted sound is proportionately decreased.
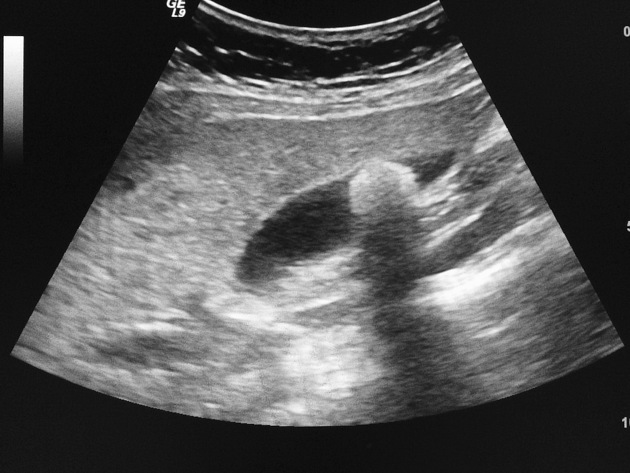
If the difference in tissue density is very different, then the sound is completely reflected, resulting in total acoustic shadowing. Acoustic shadowing is present behind bones, calculi (stones in kidneys, gallbladder, etc.) and air (intestinal gas) (See Fig. 1 with acoustic shadowing).
Echoes are not produced if there is no difference in a tissue or between tissues. Homogenous fluids like blood, bile, urine, contents of simple cysts, ascites and pleural effusion are seen as echo-free structures.
References
- 1. Sprawls P. Physical principles of medical imaging. Aspen Pub. ISBN:083420309X. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Bushberg JT, Seibert JA, Jr. EML et-al. The Essential Physics of Medical Imaging. LWW. ISBN:0781780578. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
Related articles: Imaging technology
- imaging technology
- imaging physics[+][+]
- imaging in practice
-
x-rays[+][+]
- x-ray physics
- x-ray in practice
- x-ray production
- x-ray tube
- filters
- automatic exposure control (AEC)
- beam collimators
- grids
- air gap technique
- cassette
- intensifying screen
- x-ray film
- image intensifier
- digital radiography
- digital image
- mammography
- x-ray artifacts
- radiation units
- radiation safety
- radiation detectors
- fluoroscopy[+][+]
-
computed tomography (CT)[+][+]
- CT physics
- CT in practice
- CT technology
- CT image reconstruction
- CT image quality
- CT dose
-
CT contrast media
-
iodinated contrast media
- agents
- water soluble
- water insoluble
- vicarious contrast material excretion
- iodinated contrast media adverse reactions
- agents
- non-iodinated contrast media
-
iodinated contrast media
-
CT artifacts
- patient-based artifacts
- physics-based artifacts
- hardware-based artifacts
- ring artifact
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifacts
- CT safety
- history of CT
-
MRI [+][+]
- MRI physics
- MRI in practice
- MRI hardware
- signal processing
-
MRI pulse sequences (basics | abbreviations | parameters)
- T1 weighted image
- T2 weighted image
- proton density weighted image
- chemical exchange saturation transfer
- CSF flow studies
- diffusion weighted imaging (DWI)
- echo-planar pulse sequences
- fat-suppressed imaging sequences
- gradient echo sequences
- inversion recovery sequences
- metal artifact reduction sequence (MARS)
-
perfusion-weighted imaging
- techniques
- derived values
- saturation recovery sequences
- spin echo sequences
- spiral pulse sequences
- susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI)
- T1 rho
- MR angiography (and venography)
-
MR spectroscopy (MRS)
- 2-hydroxyglutarate peak: resonates at 2.25 ppm
- alanine peak: resonates at 1.48 ppm
- choline peak: resonates at 3.2 ppm
- citrate peak: resonates at 2.6 ppm
- creatine peak: resonates at 3.0 ppm
- functional MRI (fMRI)
- gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) peak: resonates at 2.2-2.4 ppm
- glutamine-glutamate peak: resonates at 2.2-2.4 ppm
- Hunter's angle
- lactate peak: resonates at 1.3 ppm
- lipids peak: resonates at 1.3 ppm
- myoinositol peak: resonates at 3.5 ppm
- MR fingerprinting
- N-acetylaspartate (NAA) peak: resonates at 2.0 ppm
- propylene glycol peak: resonates at 1.13 ppm
-
MRI artifacts
- MRI hardware and room shielding
- MRI software
- patient and physiologic motion
- tissue heterogeneity and foreign bodies
- Fourier transform and Nyquist sampling theorem
- MRI contrast agents
- MRI safety
-
ultrasound
- ultrasound physics
-
transducers[+][+]
- linear array
- convex array
- phased array
- frame averaging (frame persistence)
- ultrasound image resolution
- imaging modes and display[+][+]
- pulse-echo imaging
- real-time imaging
-
Doppler imaging
- Doppler effect
- color Doppler
- power Doppler
- B flow
- color box
- Doppler angle
- pulse repetition frequency and scale
- wall filter
- color write priority
- packet size (dwell time)
- peak systolic velocity
- end-diastolic velocity
- resistive index
- pulsatility index
- Reynolds number
- panoramic imaging
- compound imaging
- harmonic imaging
- elastography
- scanning modes
- 2D ultrasound
- 3D ultrasound
- 4D ultrasound
- M-mode
-
ultrasound artifacts
- acoustic shadowing
- acoustic enhancement
- beam width artifact
- reverberation artifact
- ring down artifact
- mirror image artifact
- side lobe artifact
- speckle artifact
- speed displacement artifact
- refraction artifact
- multipath artifact
- anisotropy
- electrical interference artifact
- hardware-related artifacts
- Doppler artifacts
- aliasing
- tissue vibration
- spectral broadening
- blooming
- motion (flash) artifact
- twinkling artifact
- acoustic streaming
- biological effects of ultrasound
- history of ultrasound
-
nuclear medicine [+][+]
- nuclear medicine physics
- detectors
- tissue to background ratio
-
radiopharmaceuticals
- fundamentals of radiopharmaceuticals
- radiopharmaceutical labeling
- radiopharmaceutical production
- nuclear reactor produced radionuclides
- cyclotron produced radionuclides
- radiation detection
- dosimetry
- specific agents
- carbon-11
- chromium-51
- fluorine agents
- gallium agents
- Ga-67 citrate
- Ga-68
- iodine agents
-
I-123
- I-123 iodide
- I-123 ioflupane (DaTSCAN)
- I-123 ortho-iodohippurate
- I-131
-
MIBG scans
- I-123 MIBG
- I-131 MIBG
-
I-123
- indium agents
- In-111 Octreoscan
- In-111 OncoScint
- In-111 Prostascint
- In-111 oxine labeled WBC
- krypton-81m
- nitrogen-13
- oxygen-15
- phosphorus-32
- selenium-75
-
technetium agents
- Tc-99m DMSA
- Tc-99m DTPA
- Tc-99m DTPA aerosol
- Tc-99m HMPAO
- Tc-99m HMPAO labeled WBC
- Tc-99m MAA
- Tc-99m MAG3
- Tc-99m MDP
- Tc-99m mercaptoacetyltriglycine
- Tc-99m pertechnetate
- Tc-99m labeled RBC
- Tc-99m sestamibi
- Tc-99m sulfur colloid
- Tc-99m sulfur colloid (oral)
- thallium-201 chloride
- xenon agents
- in vivo therapeutic agents
- pharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine
-
emerging methods in medical imaging[+][+]
- radiography
- phase-contrast imaging
- CT
- deep-learning reconstruction
- photon counting CT
- virtual non-contrast imaging
- ultrasound
- magnetomotive ultrasound (MMUS)
- superb microvascular imaging
- ultrafast Doppler imaging
- ultrasound localization microscopy
- MRI
- nuclear medicine
- total body PET system
- immuno-PET
- miscellaneous
- radiography
Related articles: Imaging physics
- imaging physics
- imaging in practice
- imaging technology
-
x-ray physics[+][+]
- ionizing radiation
- interaction with matter
- x-ray spectrum
- radiation units
- effective dose
- entrance skin dose
- radiation safety
- radiation damage (biomolecular)
- radiation damage (skin injury)
- stochastic effect
- CT physics
-
MRI physics[+][+]
- B0
- chemical shift
- dependence of magnetization (proton density, field strength and temperature)
- echo time
- eddy currents
- electromagnetic induction
- Ernst angle
- flip angle
- Larmor frequency
- magnetic dipole
- magnetic field gradient
- magnetic susceptibility
- magnetism
- molecular tumbling rate effects on T1 and T2
- net magnetization vector (NMV)
- relaxation
- repetition time
- resonance and radiofrequency (RF)
- units of magnetism
- ultrasound physics
- nuclear medicine physics




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.