Tamoxifen-associated endometrial changes
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created The Radswiki had no recorded disclosures.
View The Radswiki's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosures- Endometrial changes associated with tamoxifen
- Endometrial changes associated with tamoxifen use
- Tamoxifen-induced endometrial changes
The oncological agent tamoxifen has pro-oestrogenic changes on the endometrium resulting in abnormal growth with an increased prevalence of:
- endometrial polyps: occurs in ~8-36% of women in treated 8
- endometrial hyperplasia: occurs in ~1-20% of women treated ref
- cystic endometrial atrophy
- endometrial carcinoma
On this page:
Epidemiology
Up to one-half of breast cancer patients who are treated with tamoxifen may develop an endometrial lesion within 6-36 months. Therefore, any patient who develops bleeding while taking tamoxifen requires evaluation.
Pathology
Tamoxifen is a non-steroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM), which acts as an "anti-estrogen". It binds to the estrogen receptor and is used primarily for adjuvant therapy in breast cancer. However, it can also act as a pro-estrogen agonist in a low estradiol environment. The agonist properties can affect the endometrium, and does, in half of treated patients.
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
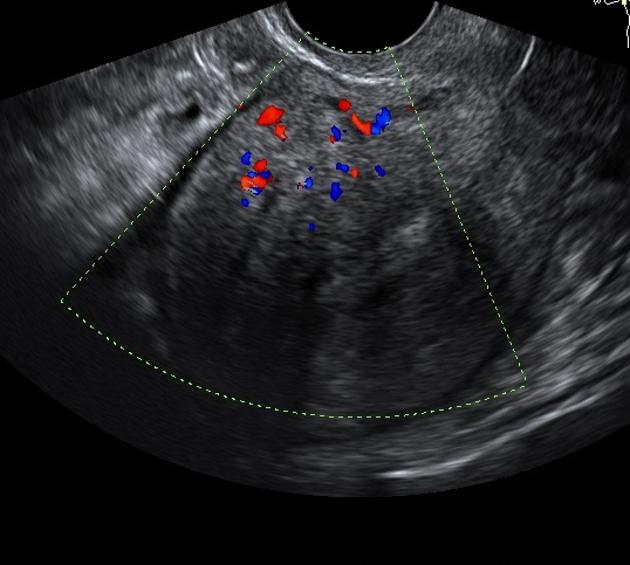
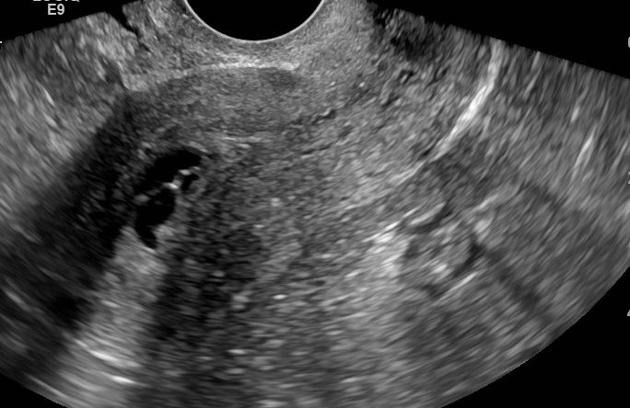
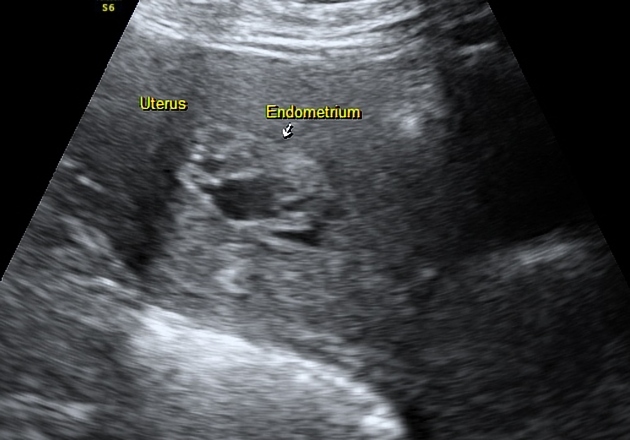
Tamoxifen may cause the endometrium to appear thickened, irregular, and cystic. Most patients tend to display a multiplicity of findings.
-
normal endometrial thickness despite tamoxifen use, i.e. <5 mm (although ~50% of those receiving tamoxifen have been reported to have a thickness of >8 mm) 2
- it has also been reported that the degree of endometrial thickening corresponds to the duration of tamoxifen therapy
- subendometrial cysts
-
endometrial polyps
- usually larger than in untreated women
- sonohysterography may be useful for their identification
MRI
Endometrial thickening and subendometrial cysts, similar to pelvic ultrasound.
Treatment and prognosis
Ultrasound screening of asymptomatic patients taking tamoxifen has been shown to be problematic due to a high number of false positives. Thus, routine ultrasound is not typically recommended for screening if a patient on tamoxifen is not experiencing bleeding 11,12.
It has been proposed that patients taking tamoxifen who present with vaginal bleeding should go directly to hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy 7.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Nalaboff KM, Pellerito JS, Ben-levi E. Imaging the endometrium: disease and normal variants. Radiographics. 21 (6): 1409-24. Radiographics (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Hann LE, Giess CS, Bach AM et-al. Endometrial thickness in tamoxifen-treated patients: correlation with clinical and pathologic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997;168 (3): 657-61. AJR Am J Roentgenol (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 3. Buijs C, Willemse PH, De vries EG et-al. Effect of tamoxifen on the endometrium and the menstrual cycle of premenopausal breast cancer patients. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer. 2009;19 (4): 677-81. doi:10.1111/IGC.0b013e3181a47cbe - Pubmed citation
- 4. Dallenbach-hellweg G, Schmidt D, Hellberg P et-al. The endometrium in breast cancer patients on tamoxifen. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2000;263 (4): 170-7. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. (link) - Pubmed citation
- 5. Hann LE, Gretz EM, Bach AM et-al. Sonohysterography for evaluation of the endometrium in women treated with tamoxifen. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177 (2): 337-42. AJR Am J Roentgenol (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 6. Williams PL, Laifer-narin SL, Ragavendra N. US of abnormal uterine bleeding. Radiographics. 23 (3): 703-18. doi:10.1148/rg.233025150 - Pubmed citation
- 7. Dreisler E, Poulsen LG, Antonsen SL et-al. EMAS clinical guide: assessment of the endometrium in peri and postmenopausal women. Maturitas. 2013;75 (2): 181-90. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2013.03.011 - Pubmed citation
- 8. Ascher SM, Imaoka I, Lage JM. Tamoxifen-induced uterine abnormalities: the role of imaging. Radiology. 2000;214 (1): 29-38. doi:10.1148/radiology.214.1.r00ja4429 - Pubmed citation
- 9. Gupta A, Desai A, Bhatt S. Imaging of the Endometrium: Physiologic Changes and Diseases: Women's Imaging. (2017) Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 37 (7): 2206-2207
- 10. Polin SA, Ascher SM. The effect of tamoxifen on the genital tract. (2008) Cancer imaging : the official publication of the International Cancer Imaging Society. 8: 135-45. doi:10.1102/1470-7330.2008.0020 - Pubmed
- 11. Love CD, Muir BB, Scrimgeour JB, Leonard RC, Dillon P, Dixon JM. Investigation of endometrial abnormalities in asymptomatic women treated with tamoxifen and an evaluation of the role of endometrial screening. (1999) Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 17 (7): 2050-4. doi:10.1200/JCO.1999.17.7.2050 - Pubmed
- 12. Fung MF, Reid A, Faught W, Le T, Chenier C, Verma S, Brydon E, Fung KF. Prospective longitudinal study of ultrasound screening for endometrial abnormalities in women with breast cancer receiving tamoxifen. (2003) Gynecologic oncology. 91 (1): 154-9. doi:10.1016/s0090-8258(03)00441-4 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta previa
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumors
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumors of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumors
- mixed germ cell tumor
- yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumor
- sex cord / stromal tumors of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumor of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumors (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumors
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.