Thyroid cartilage
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Tom Spencer had no recorded disclosures.
View Tom Spencer's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
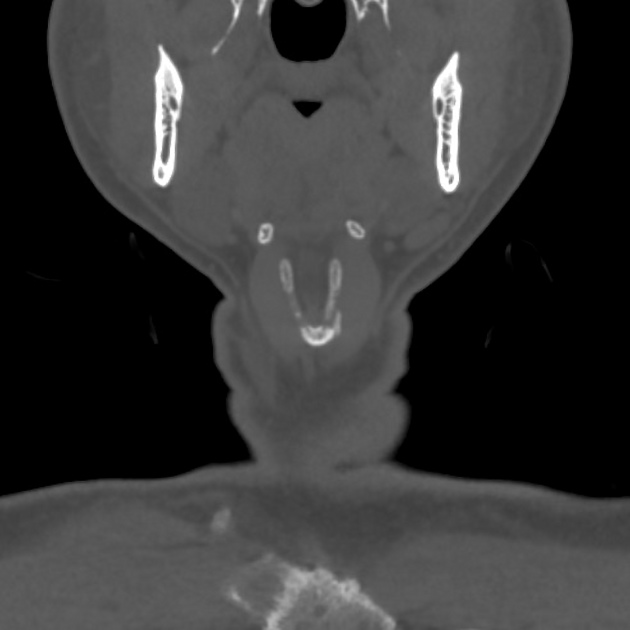
View Craig Hacking's current disclosuresThe thyroid cartilage is the largest of the cartilages of the larynx, with its superior border sitting at the level of the C4 vertebra.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
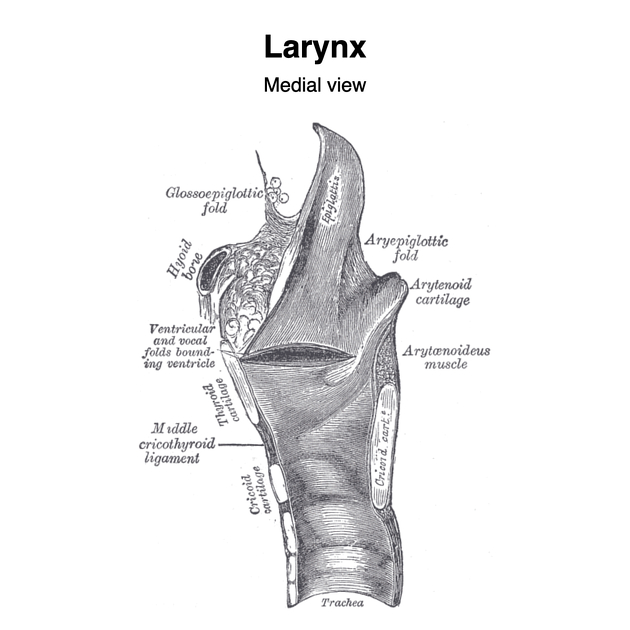
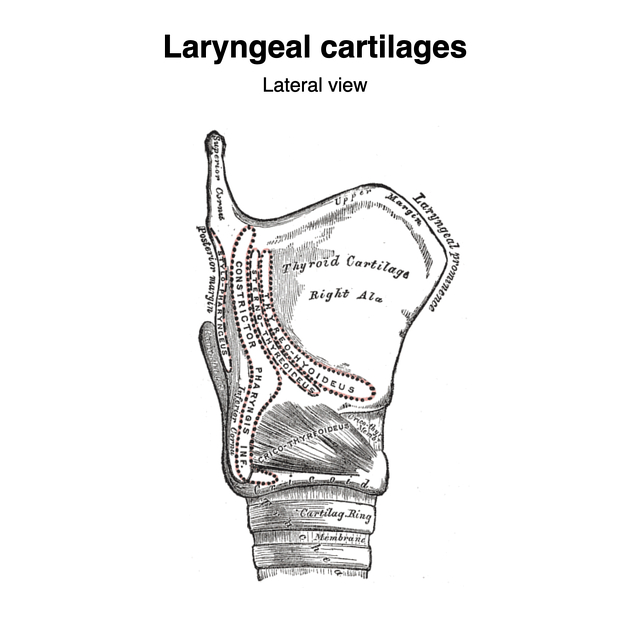
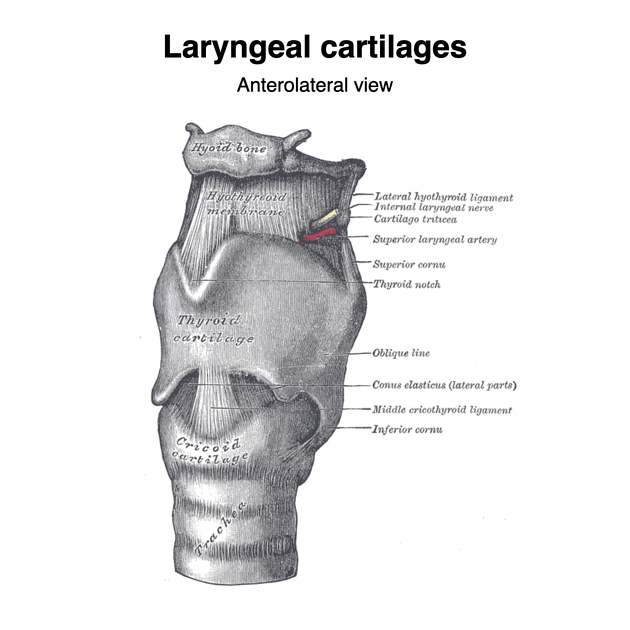
The thyroid cartilage consists of bilateral flattened laminae that are fused in the anterior midline to form the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). Each lamina possesses an oblique ridge laterally, with a tubercle superiorly and inferiorly. The posterior border of the laminae are free and project upwards and downwards as the superior and inferior horns (cornua) respectively. The superior horns attach to the hyoid bone via the thyrohyoid membrane and lateral thyrohyoid ligaments. The inferior horns directly articulate with the cricoid cartilage at the cricothyroid joint.
Musculoligamentous attachments
-
superior border
thyrohyoid membrane
median thyrohyoid ligament
lateral thyrohyoid ligaments
-
inferior border
cricothyroid membrane
median cricothyroid ligament
-
oblique ridge
-
internal surface
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Anatomical variants
thyroid cartilage calcification 4
cyst-like change in the thyroid cartilage 5
agenesis of the thyroid horns 6
ectopic superior thyroid horns 6
lateral thyrohyoid ossification 6
terminal segmentation of the thyroid horns 6
buckled thyroid cartilage 7
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Clinically oriented anatomy. LWW. ISBN:1451119453. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Mcminn. Last's Anatomy. Elsevier Australia. (2003) ISBN:0729537528. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Butler P, Mitchell A, Healy JC. Applied Radiological Anatomy. Cambridge University Press. (2012) ISBN:0521766664. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Wenaas A, Wenaas TB, Wenaas OJ, Wenaas. The progression of thyroid cartilage calcification as it relates to the utilization of laryngeal ultrasound. (2016) The Laryngoscope. doi:10.1002/lary.25582 - Pubmed
- 5. Chetcuti K, Avula S. Cyst-like change in the thyroid cartilage: A developmental variant in children. (2016) Ultrasound (Leeds, England). 24 (4): 237-240. doi:10.1177/1742271X16671040 - Pubmed
- 6. Pinheiro J, Pinheiro CJ, Pinheiro LdAB, Pinheiro OJ, Pinheiro RCM, Pinheiro. Laryngeal anatomical variants and their impact on the diagnosis of mechanical asphyxias by neck pressure. (2018) Forensic science international. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2018.06.019 - Pubmed
- 7. Chang B, Chang LK, Chang NE, Chang MM, Chang. Buckled Thyroid Cartilage: An Anatomic Variant. (2018) Journal of voice : official journal of the Voice Foundation. doi:10.1016/j.jvoice.2017.07.020 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Vertebral levels (anatomical landmarks)
- Ligaments of the larynx
- Intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- External carotid artery
- Cricoid cartilage
- Levator glandulae thyroideae muscle
- Inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle
- Paraglottic space
- Internal carotid artery
- Laryngeal cartilages
- Muscles of mastication
- Cartilage
- Guttman test (larynx)
- Common carotid artery
- Thyroid gland
- Branchial apparatus
- Stylopharyngeus muscle
- Laryngeal paraganglia
- Killian dehiscence
- True vocal cords
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck












 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.