Adenocarcinoma (urinary bladder)
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Ammar Ashraf had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Ammar Ashraf's current disclosures- Bladder adenocarcinoma
- Urachal carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma of bladder
- Adenocarcinoma of the bladder
- Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder
Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder is rare and accounts for only ~1% of all bladder cancers (90% are transitional cell carcinomas).
On this page:
Pathology
Metaplasia of urinary bladder induced by chronic irritation or infection can lead to adenocarcinoma. Pathological types of adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder are:
- mucinous adenocarcinoma
- signet-ring type
- papillary adenocarcinoma
- not otherwise specified (NOS)
Bladder adenocarcinoma may be subclassified as primary (two-thirds are non-urachal and one-third are urachal 2) or secondary (metastases).
Aetiology
- persistent urachal remnant (most common)
- cystitis glandularis (itself secondary to bladder outlet obstruction, chronic infection and/or bladder calculi)
- schistosomiasis (bilharziasis), especially where endemic
- associated with bladder exstrophy
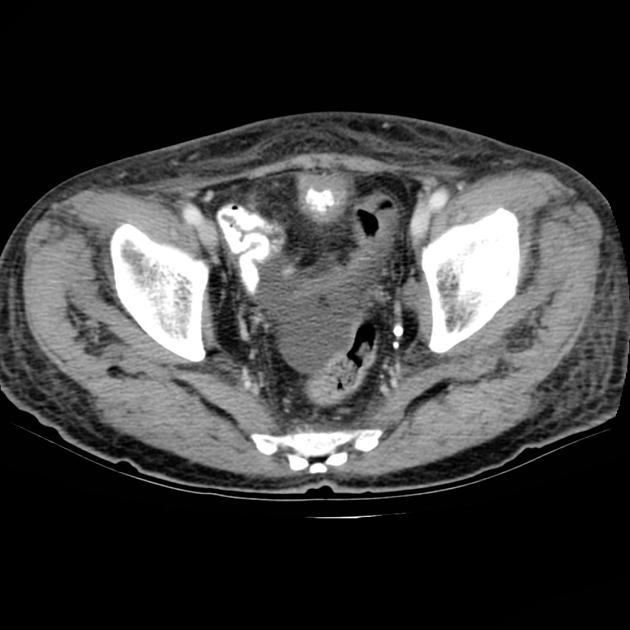
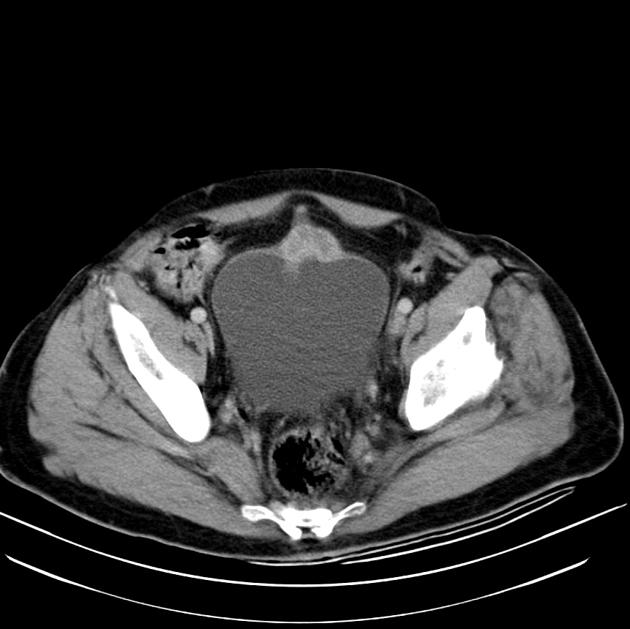
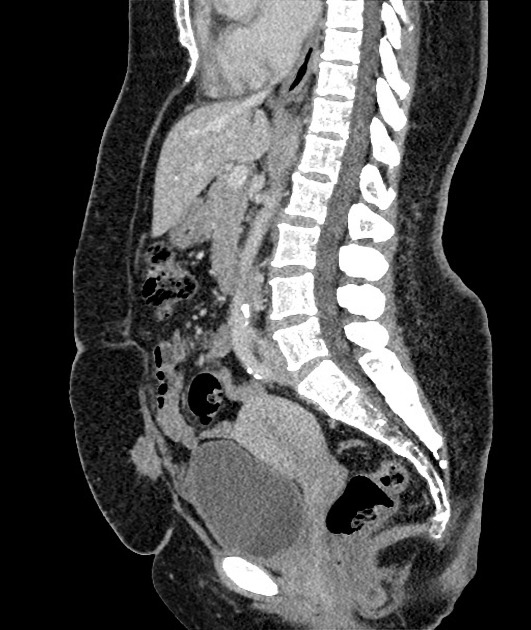
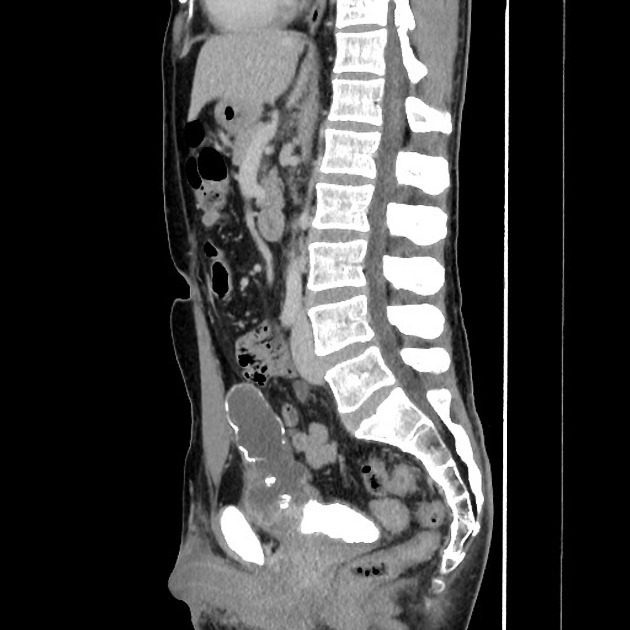
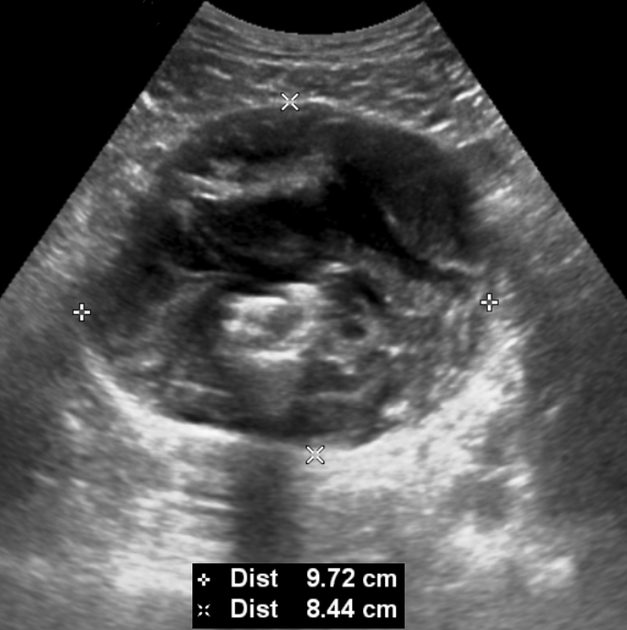
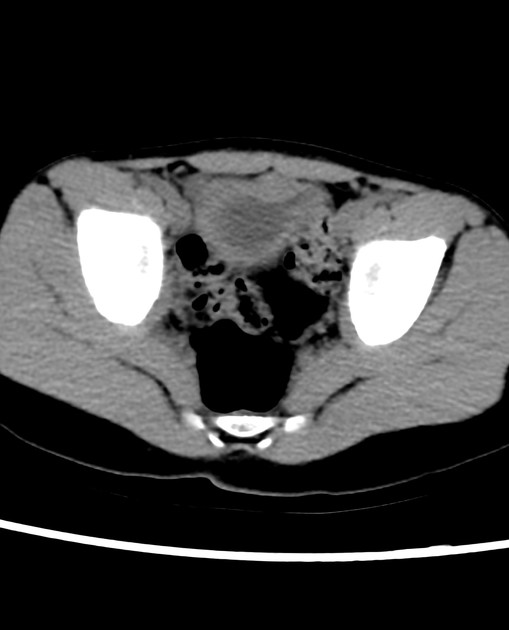
Radiographic features
CT
Non-urachal adenocarcinoma
- diffuse bladder wall thickening
- stranding of perivesical fat
- regional lymphadenopathy
- invasion of rectus muscles
Urachal adenocarcinoma
- characteristically in the midline at the dome of the bladder, or along the course of urachus (from the bladder to umbilicus)
- a midline, infraumbilical soft tissue mass with peripheral calcification is characteristically urachal adenocarcinoma unless proven otherwise (calcification in 70% of cases)
- usually large tumours (5-6 cm) with prominent extravesical component
- mixed solid-cystic appearance in most cases
MRI
Solid components of the tumour are isointense, while cystic mucinous component appears hyperintense on T2W images. Localising a urachal carcinoma may be easier on the sagittal images.
Treatment and prognosis
Due to their extravesical location, urachal carcinomas present very late and thus carry a poor prognosis. Radical cystectomy is considered the treatment of choice. However, en bloc resection of the extravesical component, adjacent peritoneum and the abdominal wall is also needed.
References
- 1. Wong-you-cheong JJ, Woodward PJ, Manning MA et-al. From the Archives of the AFIP: neoplasms of the urinary bladder: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 26 (2): 553-80. doi:10.1148/rg.262055172 - Pubmed citation
- 2. Kapur P, Lotan Y, King E et-al. Primary adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder: value of cell cycle biomarkers. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011;135 (6): 822-30. doi:10.1309/AJCP76KUVOTBKQRY - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Hematospermia
- Cutaneous and subcutaneous metastases
- Bladder cancer
- Cystitis cystica
- Urachus
- Urachal cyst
- Urinary bladder wall or lumen calcification (differential)
- Leptomeningeal metastases
- Transitional cell carcinoma (urinary bladder)
- Tumours of the seminal vesicles
- Vesicourachal diverticulum
- Urogenital curriculum
- Urinary bladder wall thickening
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta praevia
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynaecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumours
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumours of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumours
- mixed germ cell tumour
- yolk sac tumour (endodermal sinus tumour)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumour
- sex cord / stromal tumours of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumour of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumours (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumours
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.