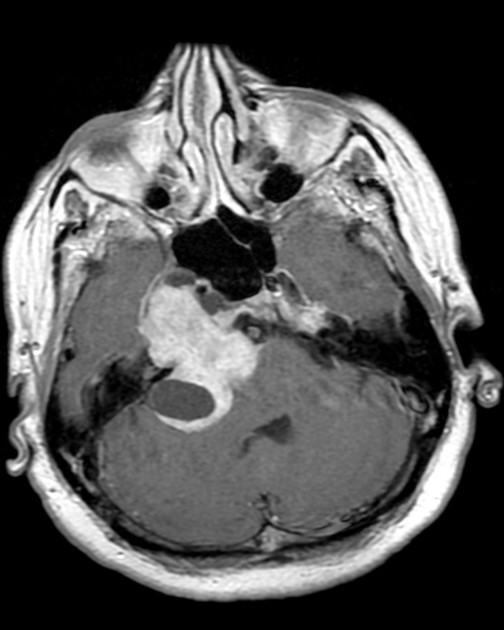
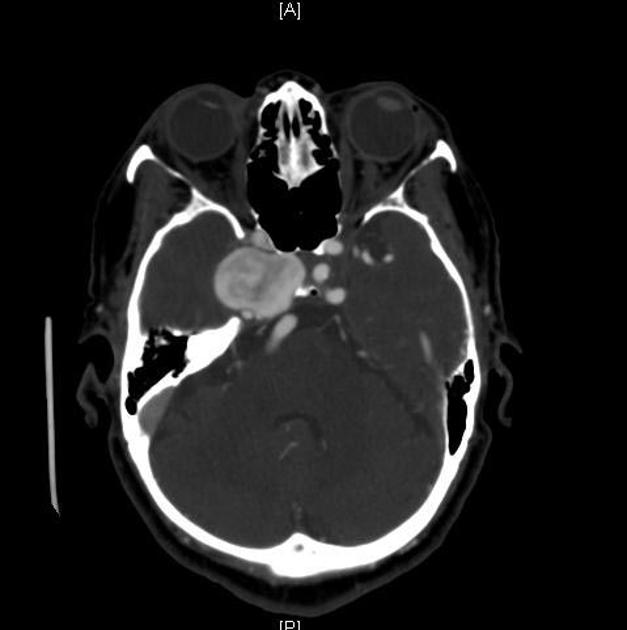
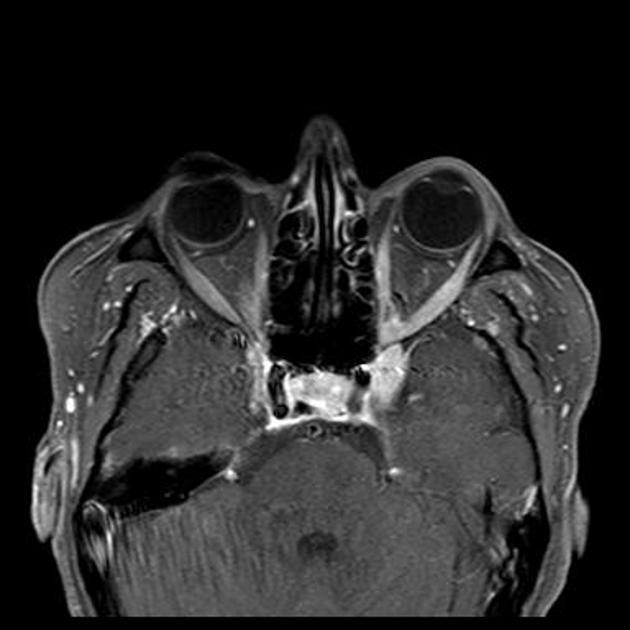
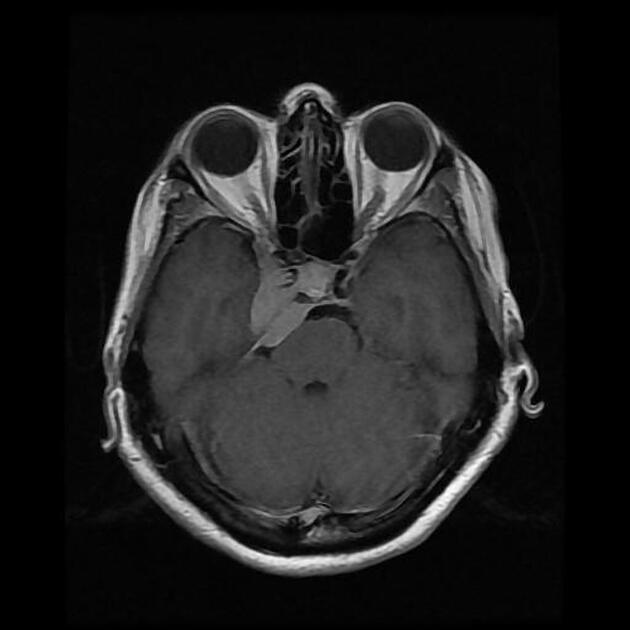
A cavernous sinus mass has a wide differential, including:
- meningioma
- orbital apical inflammation with cavernous sinus involvement (Tolosa-Hunt syndrome)
- infection
-
schwannoma
- any of the cranial nerves traversing the cavernous sinus: III, IV, V (V1 and V2) and VI
- trigeminal schwannoma is the most common
- cavernous hemangioma
- lymphoma/ neurolymphomatosis
- metastatic disease (i.e. perineural spread of tumor through neural foramina)
- aneurysm
- hemangiopericytoma
- neurosarcoidosis: rarely involves the cavernous sinus
- pituitary macroadenoma
-
base of skull tumor
- chondrosarcoma
- osteosarcoma
- chordoma (usually midline)
- juvenile angiofibroma
- nasopharyngeal carcinoma with intracranial extension (especially in Southeast Asia)








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.