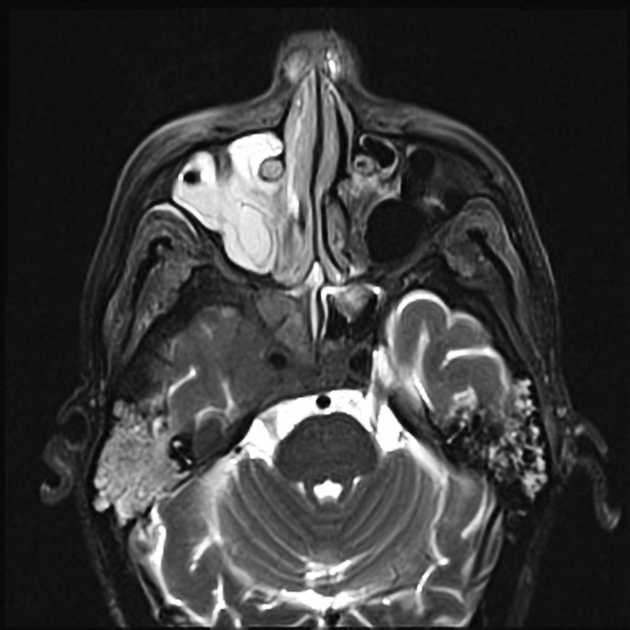
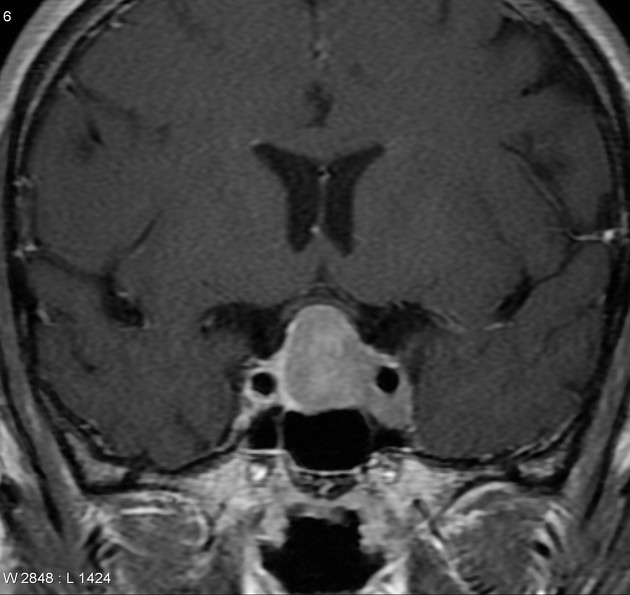
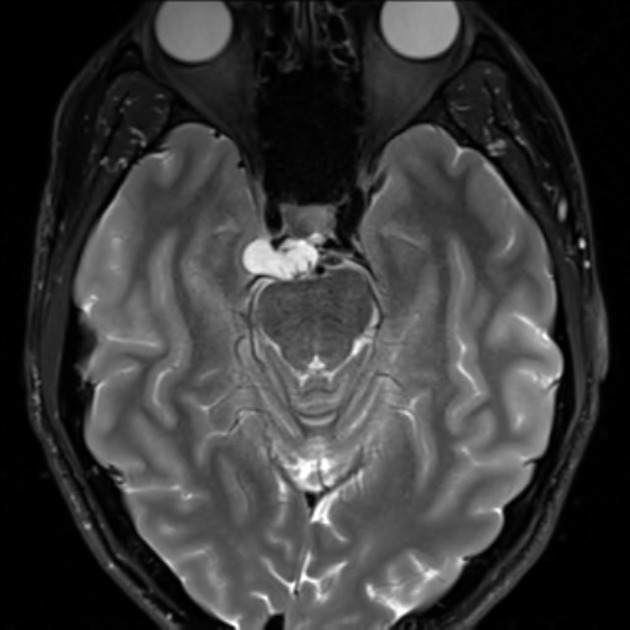
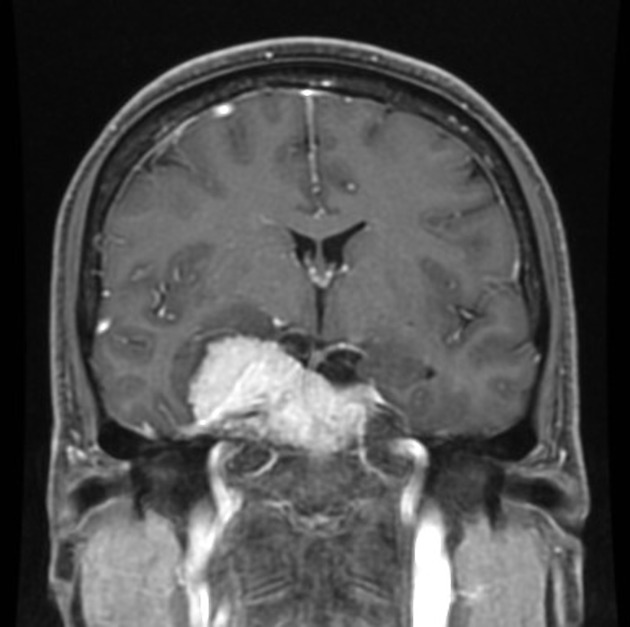
Cavernous sinus syndromes refer to constellations of clinical signs and symptoms referable to pathology within or adjacent to the cavernous sinus.
On this page:
Clinical presentation
Patients present with multiple unilateral cranial neuropathies involving any combination of the following:
- ophthalmoplegia (cranial nerves III, IV, or VI), most commonly presenting as diplopia
- facial sensory loss (cranial nerves V1 and V2)
- Horner syndrome (oculosympathetic fibers)
Pain can occur, especially with inflammatory processes.
Additional symptoms may be vascular in origin:
- chemosis
- proptosis
Pathology
Causes are diverse 1-4 and may be organized by surgical sieve:
- neoplastic
- secondary (direct invasion, perineural spread, or hematogenous spread)
- head and neck tumors, e.g. nasopharyngeal carcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, juvenile angiofibroma
- pituitary tumors, e.g. pituitary adenoma, craniopharyngioma
- skull base tumors, e.g. chordoma, chondrosarcoma
- distant metastases, e.g. lung cancer, breast cancer
- hematolymphoid tumors, e.g. lymphoma, plasmacytoma, leukemia
- histiocytoses, e.g. Langerhans cell histiocytosis, Rosai-Dorfman disease
- primary
- secondary (direct invasion, perineural spread, or hematogenous spread)
- autoinflammatory
- infection
- bacterial
- meningitis
- cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis (septic cavernous sinusitis)
- actinomycosis
- fungal
- viral
- bacterial
- vascular
- congenital/developmental
- traumatic






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.