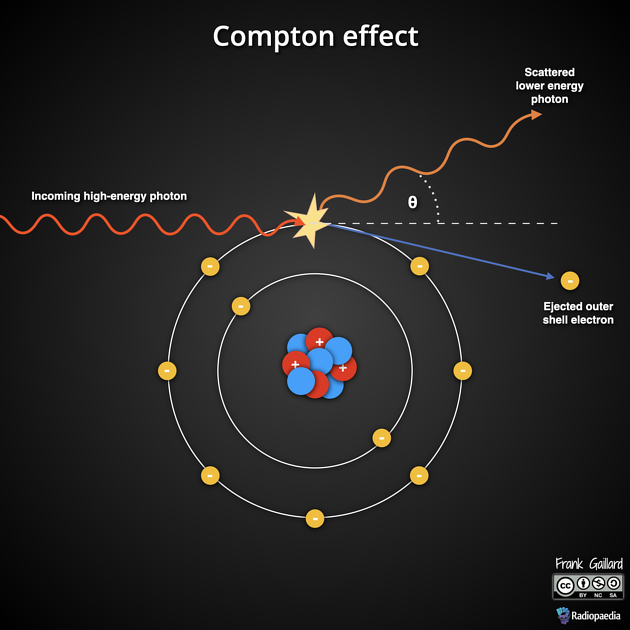
Compton effect or Compton scatter is one of principle forms of photon interaction. It is the main cause of scattered radiation in a material. It occurs due to the interaction of the photon (x-ray or gamma) with free electrons (unattached to atoms) or loosely bound valence shell (outer shell) electrons. The resultant incident photon is scattered (changes direction) and imparts energy to the electron (recoil electron). The scattered photon will have a different wavelength (observed phenomenon) and thus a different energy (E=hc/λ). Energy and momentum are conserved in this process.
On this page:
The energy of the scattered photon
The Compton effect is a partial absorption process and as the original photon has lost energy, known as Compton shift (i.e. a shift of wavelength/frequency). The wavelength change of the scattered photon can be determined by 0.024 (1- cos θ), where θ is scattered photon angle. Thus, the energy of the scattered photon decreases with increasing scattered photon angle 5. The higher incident photon energy will cause a greater percentage loss of their energy during Compton scatter while lower energy photons will lose a smaller percentage of their energy 6.
Probability of Compton effect
-
directly proportional to
number of outer shell electrons, i.e. the electron density
physical density of the material
-
very weakly dependent on
photon energy; relatively constant over the range 10-600keV 1
-
does not depend on
atomic number (unlike photoelectric effect and pair production)
In other words, the probability of the Compton effect is dependent on the number of electrons per gram in the absorbing material, which for most elements is approximately the same (approx. 3 x 1023). An exception though is the element hydrogen, which has no neutrons in its nucleus and therefore has an electron density which is twice that of all other elements (approx. 6 x 1023 ), thus the Compton effect is independent of the atomic number (Z) of the absorber.
Compton effect becomes the dominant process when human tissues are irradiated in the 30 keV to 30 MeV energy range which is the diagnostic and therapeutic radiation range 5.
History and etymology
Named after Professor Arthur Holly Compton (1892-1962), US physicist, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1927 for his discovery of Compton effect 2. The results obtained by A. H. Compton were then confirmed by Charles Thomson Rees Wilson, using the cloud chamber (invented by him in 1911) 7,8.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.