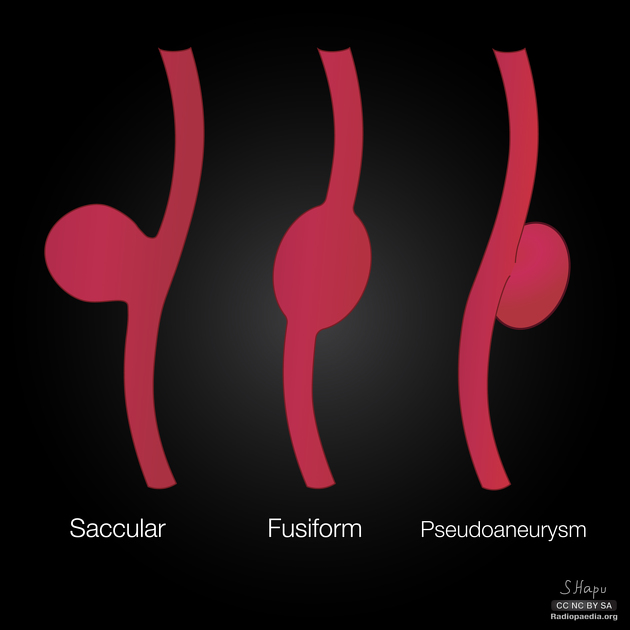
False aneurysms, also known as pseudoaneurysms, are abnormal outpouchings or dilatation of arteries which are bounded only by the tunica adventitia, the outermost layer of the arterial wall. These are distinguished from true aneurysms, which are bounded by all three layers of the arterial wall. Pseudoaneurysms typically occur when there is a breach in the vessel wall such that blood leaks through the inner wall but is contained by the adventitia or surrounding perivascular soft tissue.
On this page:
Images:
Pathology
Etiology
trauma (dissection or laceration)
-
iatrogenic (dissection, laceration or puncture)
arterial catheterization - accounts for most iatrogenic pseudoaneurysms 4
biopsy, surgery
spontaneous dissection
fibromuscular dysplasia (dissection)
mycotic aneurysm (inflammatory digestion of the vessel wall)
-
regional inflammatory process
vessel injury/erosion due to a tumor: relatively uncommon
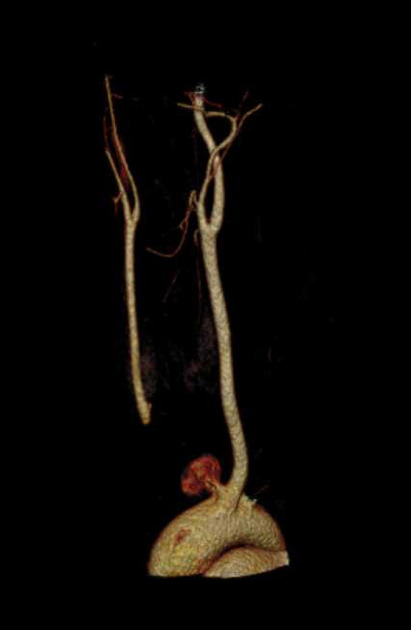
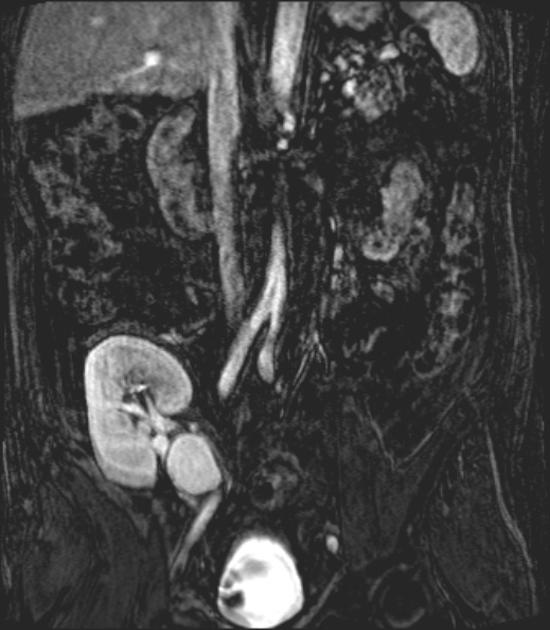
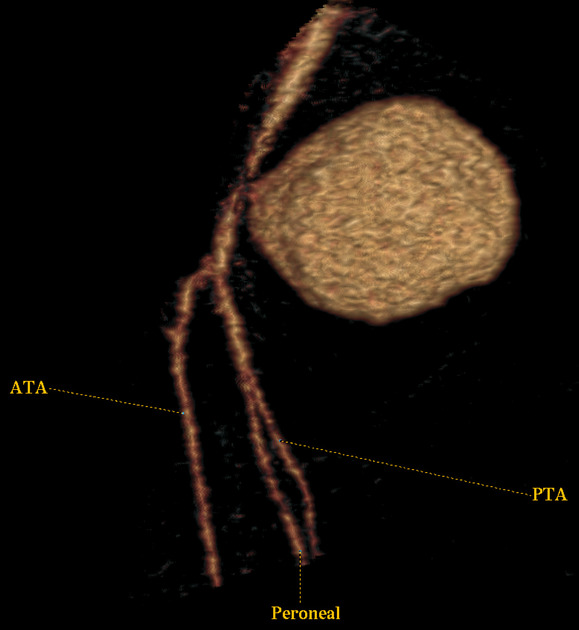
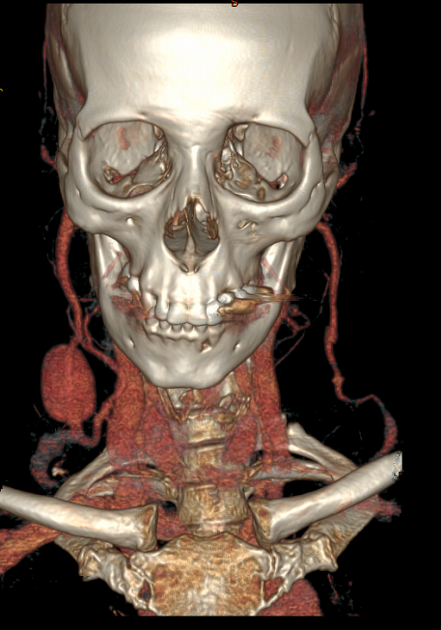
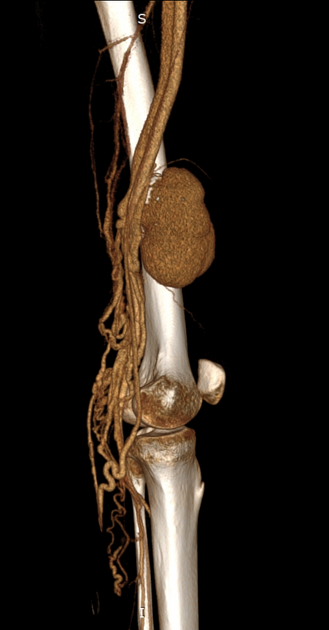
Location
They can involve any arterial segment or even a cardiac chamber. Examples include
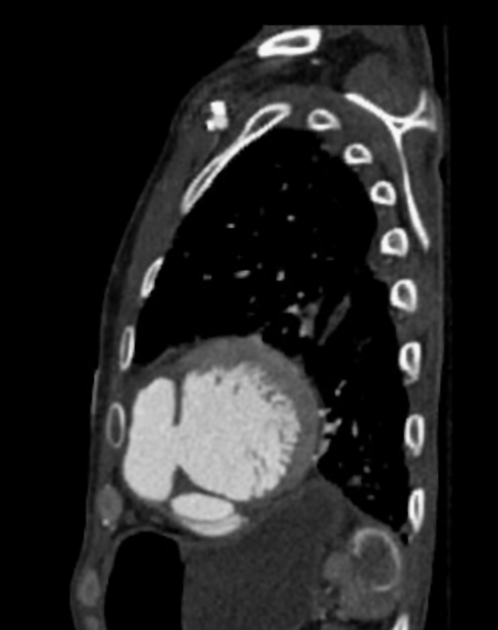
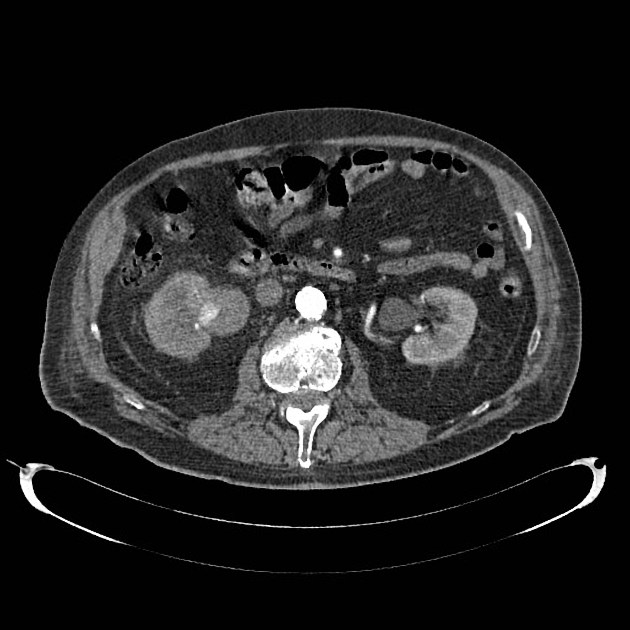
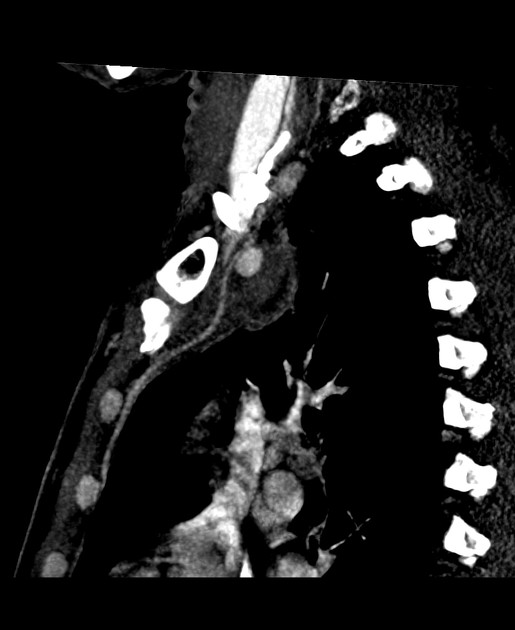
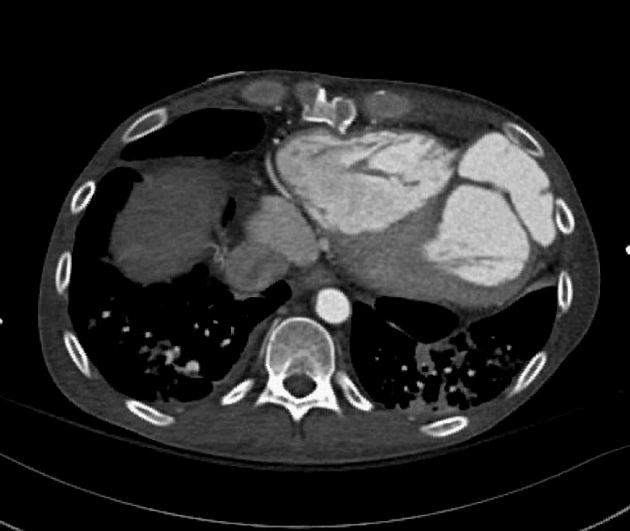
aortic pseudoaneurysm: traumatic aortic pseudoaneurysm
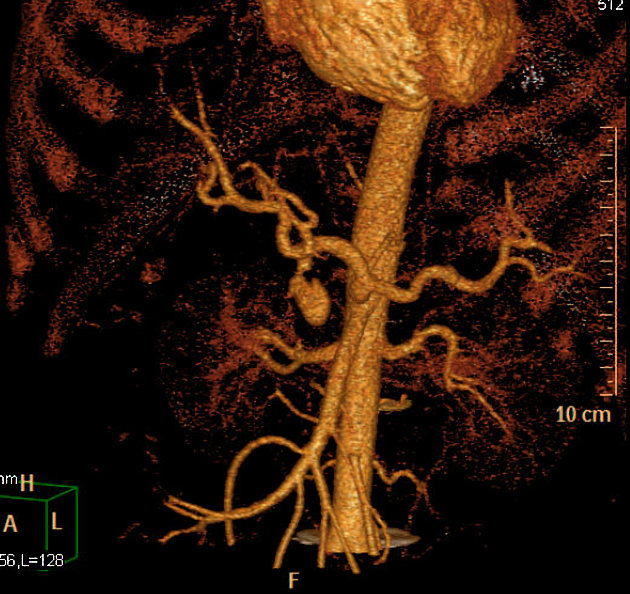
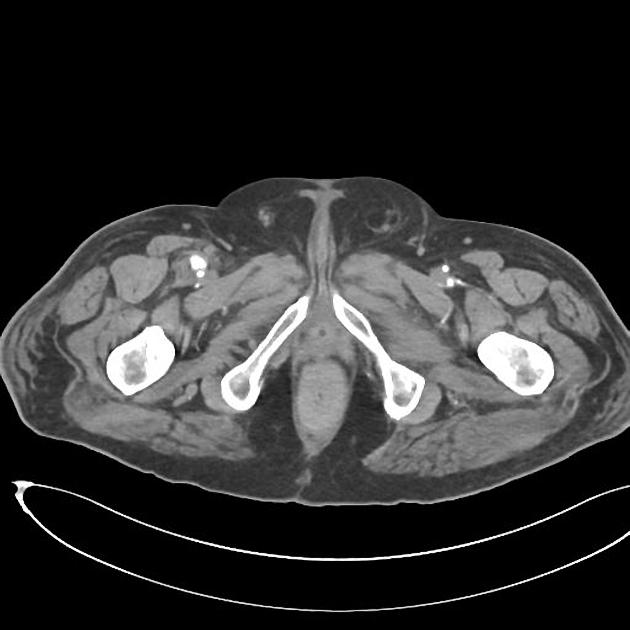
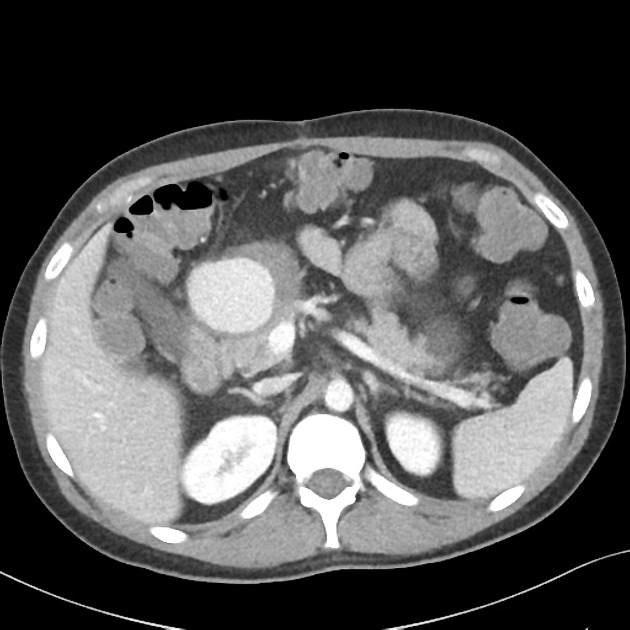
femoral artery pseudoaneurysm: relatively common site due to femoral punctures
Rare locations
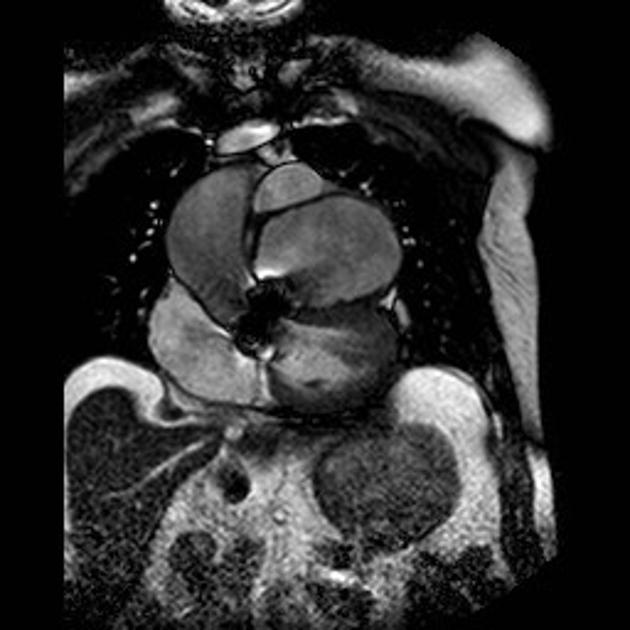
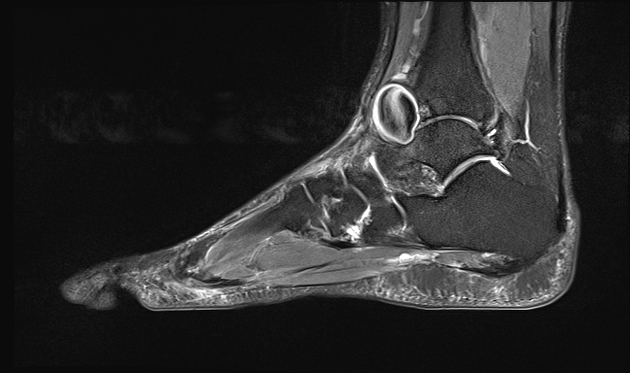
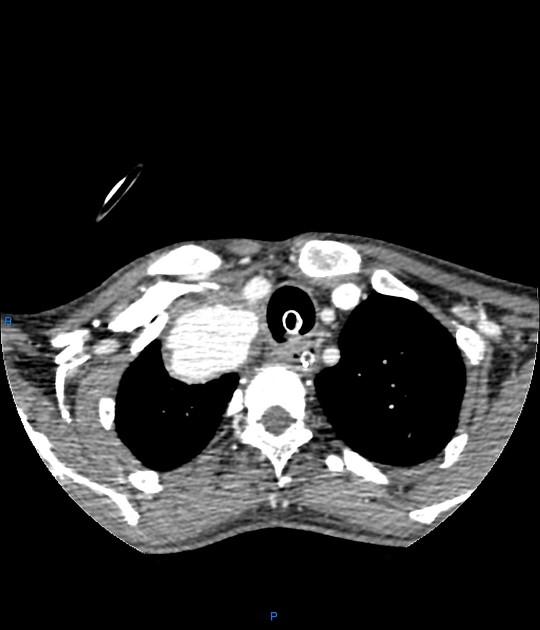
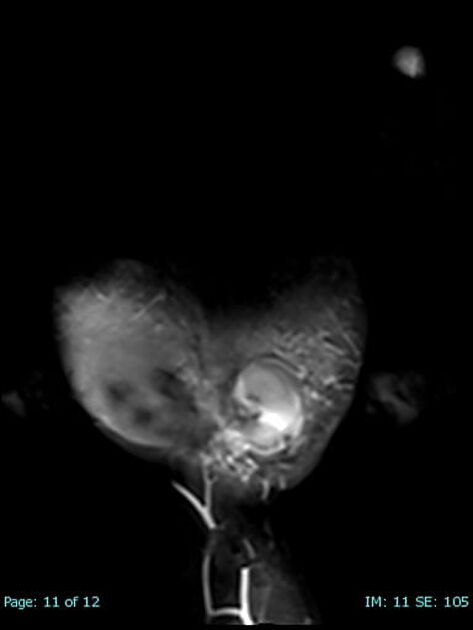
Radiographic features
Some of the imaging features may be dependent on location.
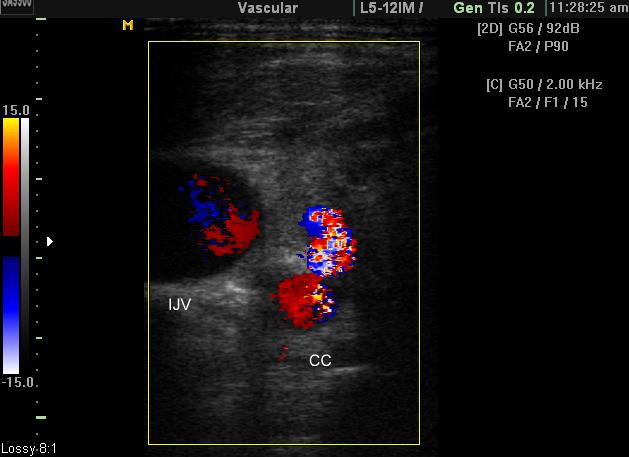
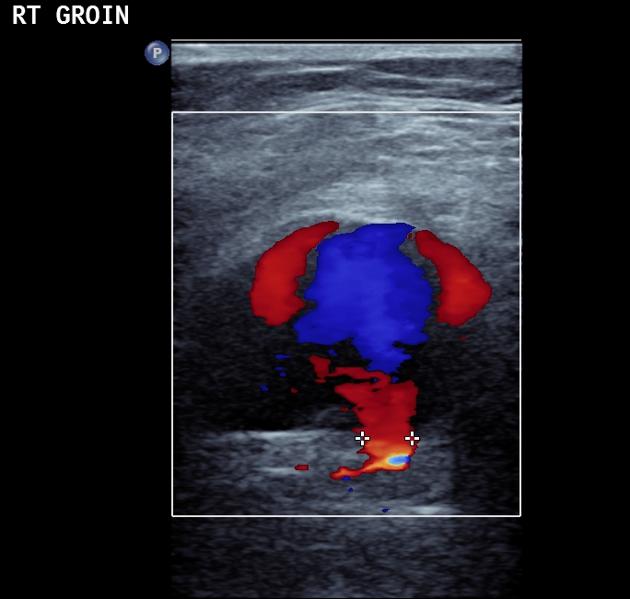
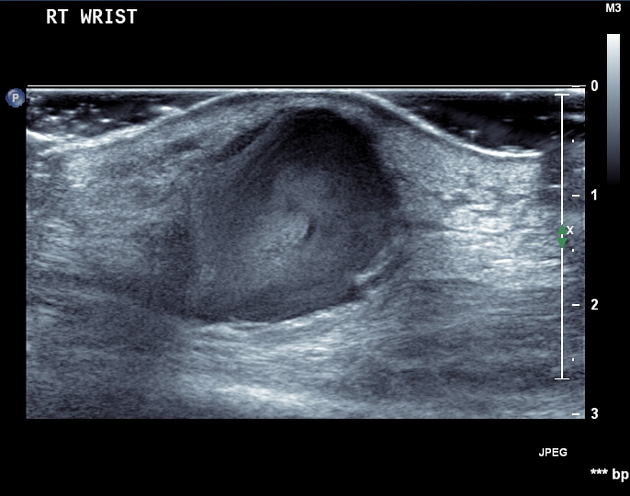
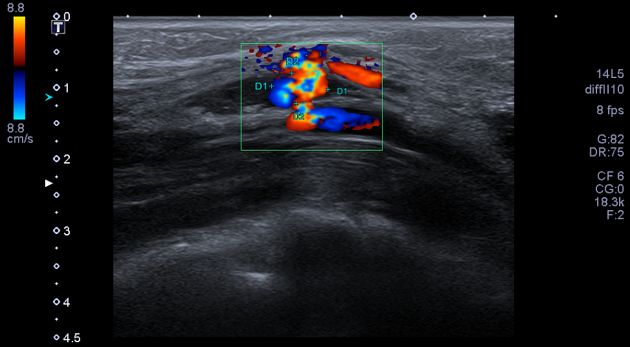
Ultrasound
Due to the turbulent forward and backward flow, a characteristic yin-yang sign may be seen on color flow while a "to and fro" pattern may be seen with pulsed Doppler.
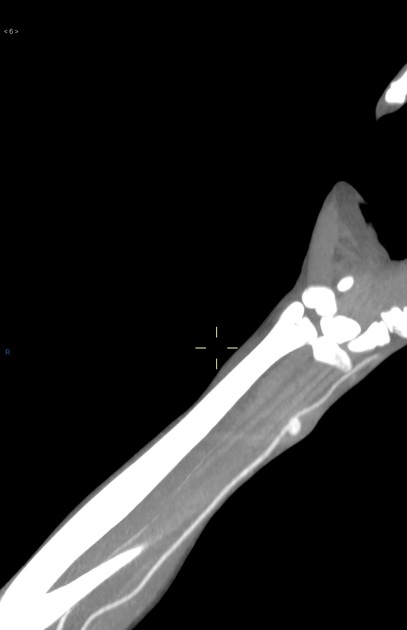
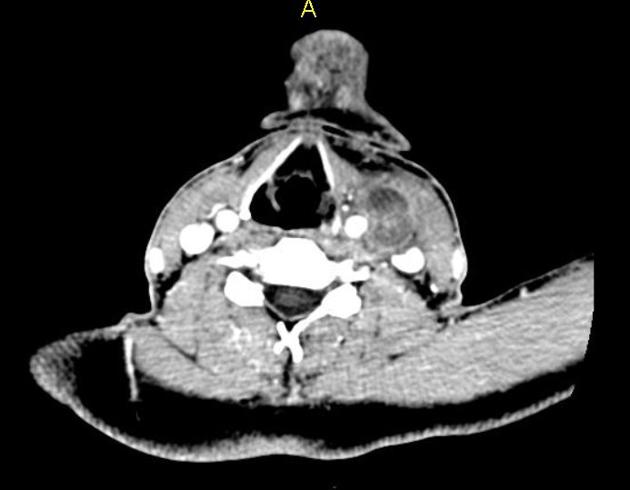
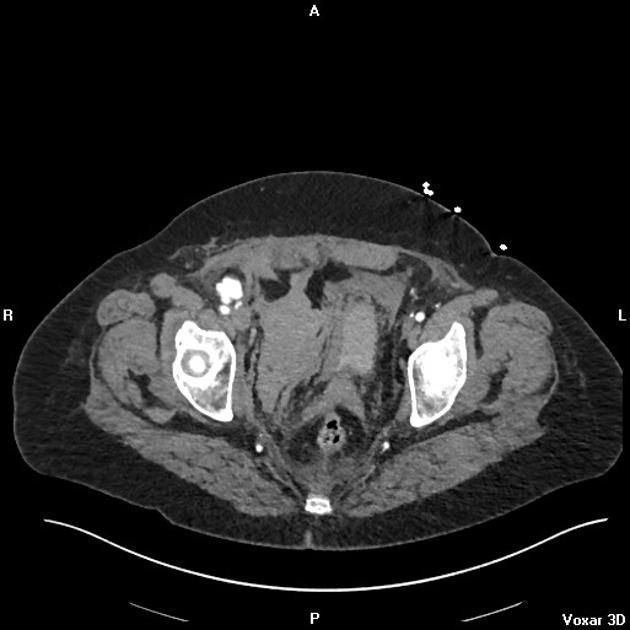
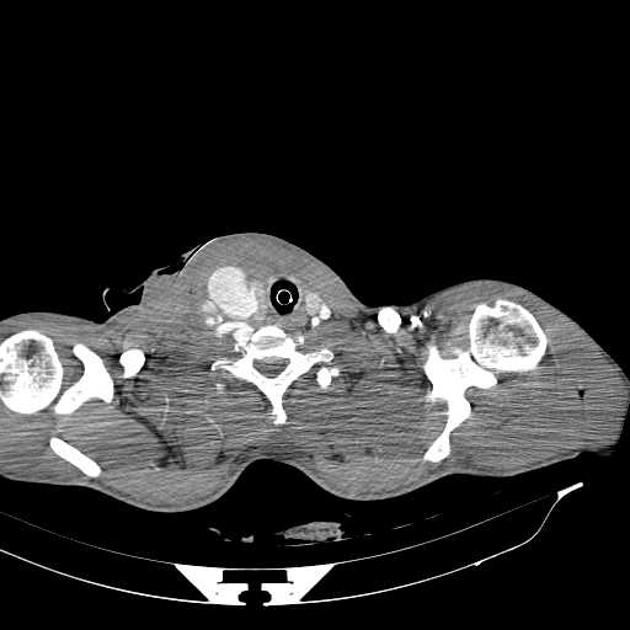
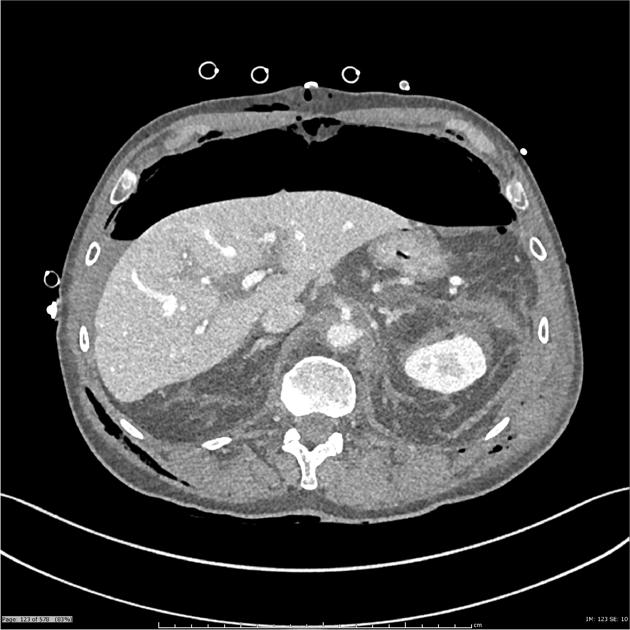
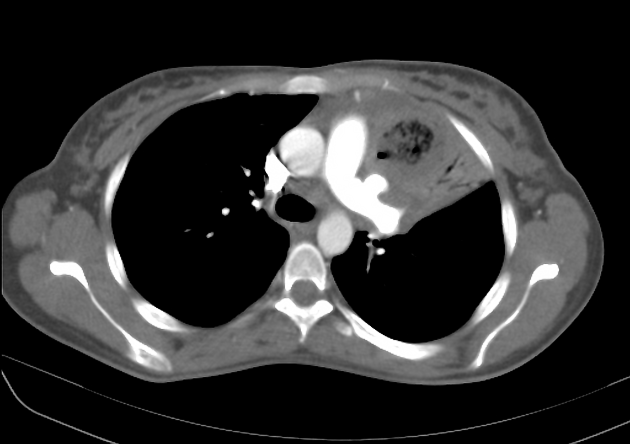
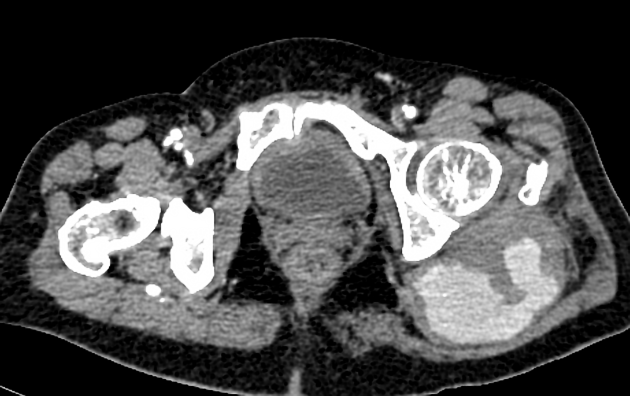
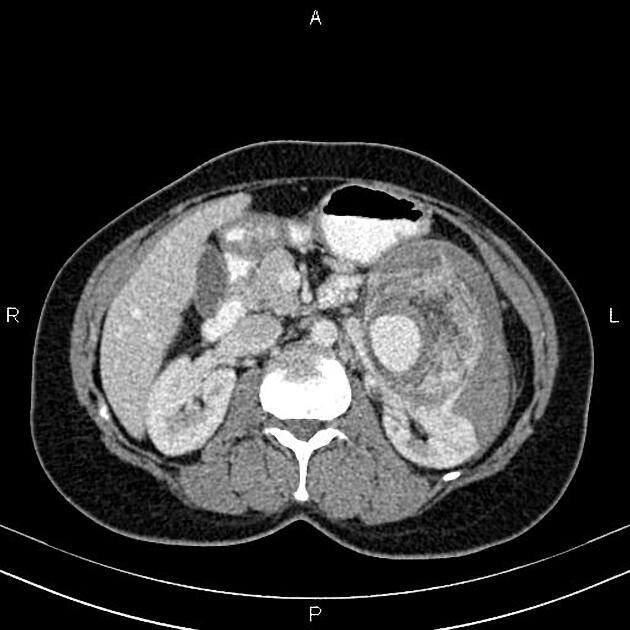
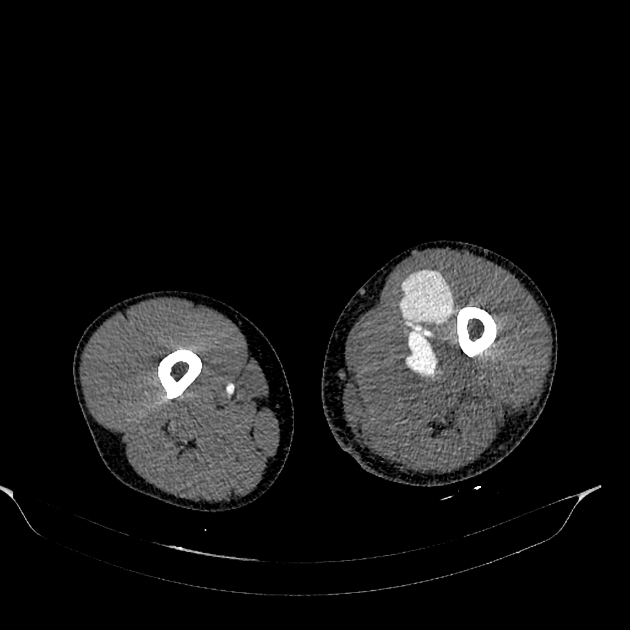
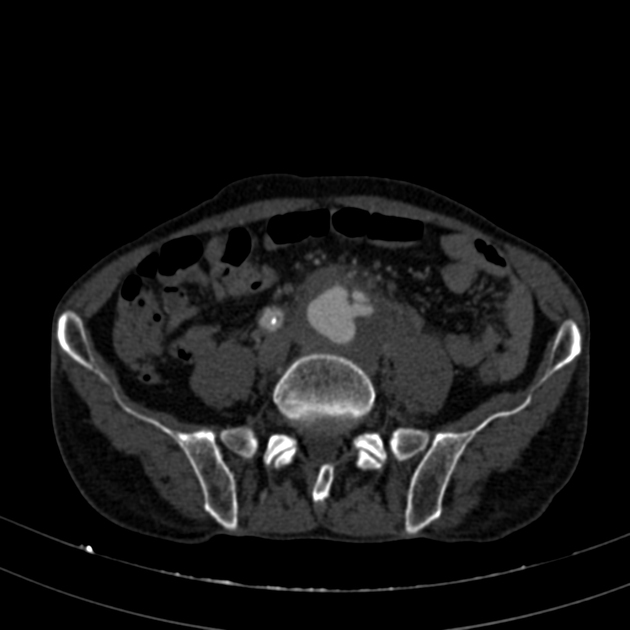
CT
hypoattenuating (non-contrast) or hyperattenuating (contrast-enhanced) smooth-walled sac adjacent to an artery, usually with a communication 6
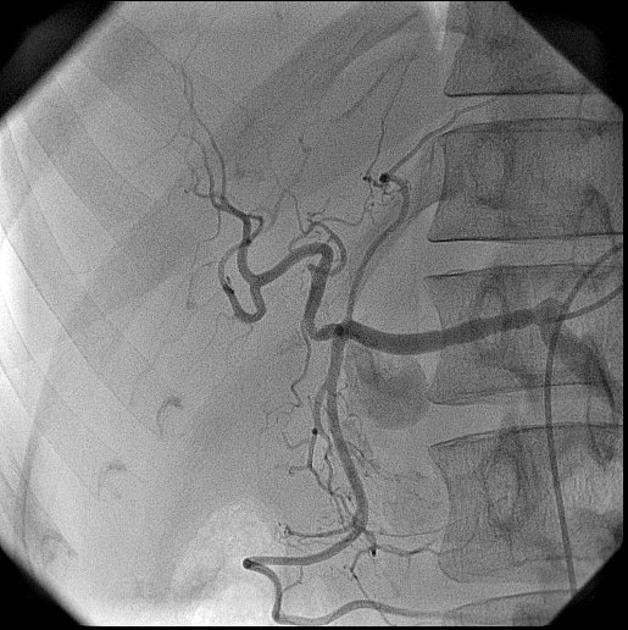
Treatment and prognosis
The risk of rupture is higher than that of a true aneurysm of comparable size due to poor support of the aneurysm wall and thus false aneurysms generally require treatment.





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.