Intracranial arterial fenestration
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Travis Fahrenhorst-Jones had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Travis Fahrenhorst-Jones's current disclosures- Intracranial artery fenestration
- Fenestration of intracranial arteries
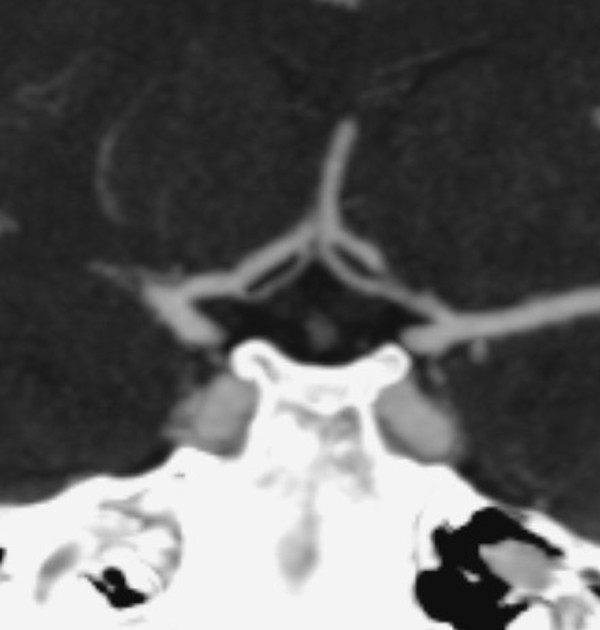
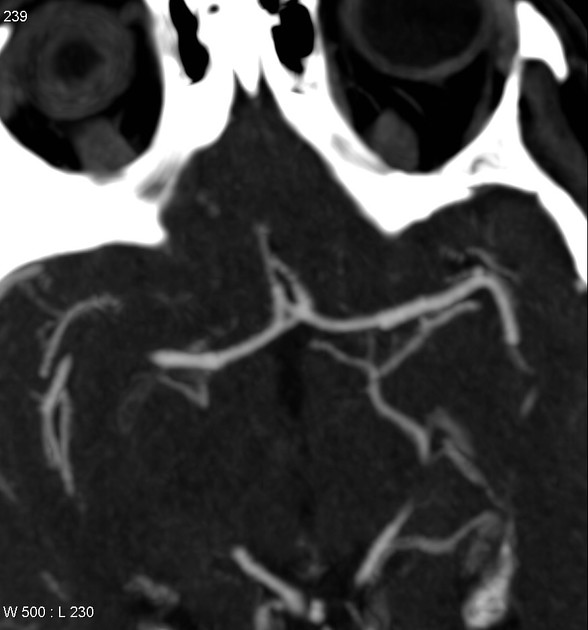
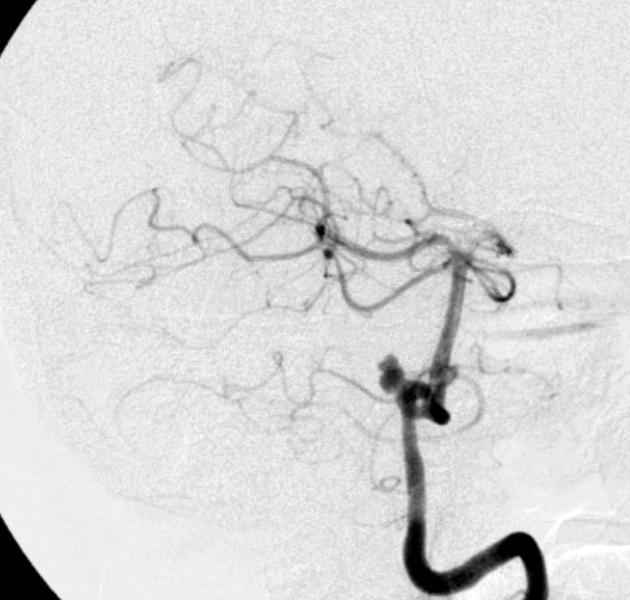
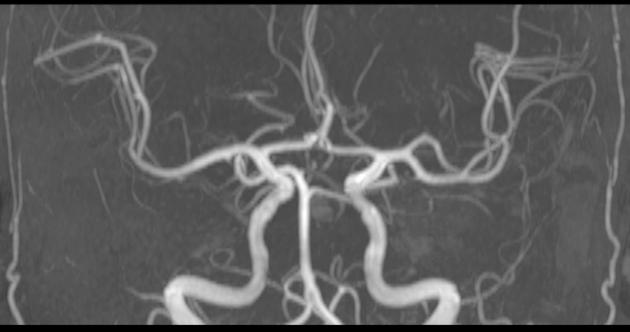
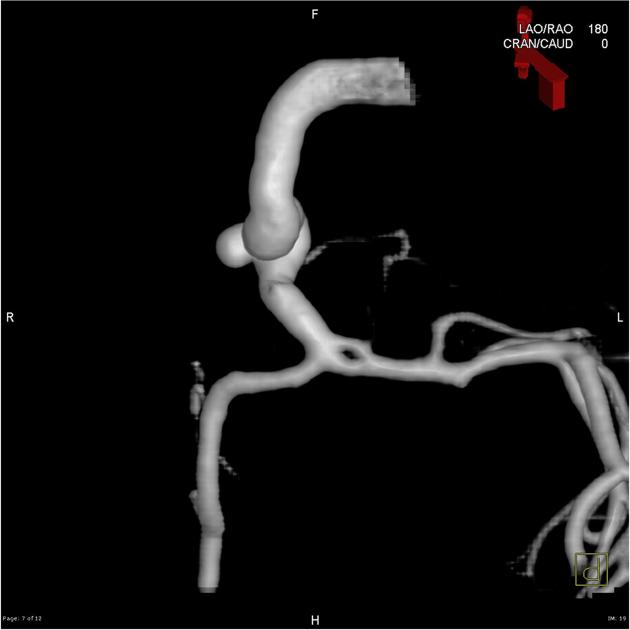
Intracranial arterial fenestration refers to segmental duplication of the intracranial arteries. They may be contrasted to arterial duplication, which consists of two distinct vessels with separate origins and no downstream convergence. They are rare anomalies, felt to result from incomplete fusion of primitive embryologic vessels.
Fenestration is the luminal division of the vessel into two separate and parallel channels which rejoin distally 1. Each channel has distinct endothelial and muscularis layers, may be differently sized, and may share adventitial layer depending on degree of embryological fusion 3. Although a fenestration is usually of considered to be of minimal significance, there is an association with aneurysm formation near proximal part of fenestration 2. This is hypothesized to be secondary to focal defects in media layer near sites of channel divergence/convergence 4,5.
Fenestration is more common in the posterior circulation. The rate of fenestrations based on published angiographic series has been much lower than that at cadaveric series. Reported incidence of intracranial fenestration on imaging series is 3:
intracranial internal cartoid artery: rare
-
A1 segment: ~2%
A2 segment: ~2% (autopsy series)
basilar artery fenestration: ~0.6%
vertebral artery: ~1%
References
- 1. Gailloud P, Albayram S, Fasel JH et-al. Angiographic and embryologic considerations in five cases of middle cerebral artery fenestration. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002;23 (4): 585-7. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Uchino A, Takase Y, Nomiyama K, Egashira R, Kudo S. Fenestration of the Middle Cerebral Artery Detected by MR Angiography. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2006;5(1):51-5. doi:10.2463/mrms.5.51 - Pubmed
- 3. Dimmick SJ, Faulder KC. Normal variants of the cerebral circulation at multidetector CT angiography. Radiographics. 2009;29 (4): 1027-43. Radiographics (full text) - doi:10.1148/rg.294085730 - Pubmed citation
- 4. Cooke DL, Stout CE, Kim WT, Kansagra AP, Yu JP, Gu A, Jewell NP, Hetts SW, Higashida RT, Dowd CF, Halbach VV. Cerebral arterial fenestrations. (2014) Interventional neuroradiology : journal of peritherapeutic neuroradiology, surgical procedures and related neurosciences. 20 (3): 261-74. doi:10.15274/INR-2014-10027 - Pubmed
- 5. Sanders W, Sorek P, Mehta B. Fenestration of Intracranial Arteries with Special Attention to Associated Aneurysms and Other Anomalies. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1993;14(3):675-80. PMC8333398 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Arterial fenestration
- ACOM and right M1 fenestrations
- Basilar artery fenestration
- Posterior cerebral artery fenestration
- Vertebral artery fenestration
- Lateral medullary syndrome
- Qudrigeminal cistern lipoma and multiple anatomic variations of intracranial arteries
- Vein of Trolard thrombosis with venous infarction (CT perfusion)
- Fenestration of vertebral artery
- Anterior comminucating artery fenestration complex with saccular aneurysm
- Anterior communicating artery fenestration
- Anterior cerberal artery fenestration
- Anterior cerebral arterial variations
- Ruptured posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm at fenestrated vertebral artery
- Acom artery fenestration - complex
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.