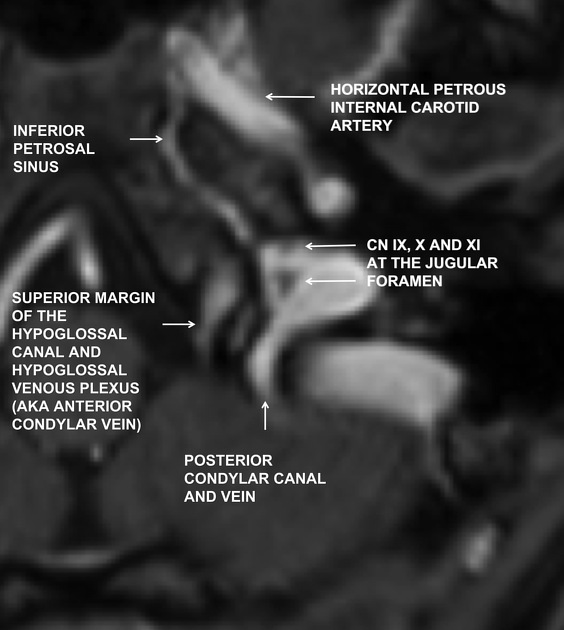
Jugular foramen
Updates to Article Attributes
The jugular foramen is the cranial foramen between the petrous temporal bone and occipital bone where the sigmoid sinus and inferior petrosal sinus drain into the internal jugular vein and where cranial nerves IX–XI (glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory) exit.
Gross anatomy
Divisions: 2-part classification
The jugular foramen is commoncommonly described in two parts, separated by a fibrous septum or a bony septum called thejugular spine (intrajugular processes on the opposing surfaces of the temporal and occipital bones):
- pars nervosa: anteromedial and smaller
- pars vascularis: posterolateral and larger
This nomenclature is misleading because both compartments contain vascular and neural structures.
Pars nervosa
The pars nervosa is the anteromedial portion of the jugular foramen and is smaller than the larger, posterolateral pars vascularis. It contains:
The inferior petrosal sinus drains the cavernous sinus and courses in the petro-occipital fissure adjacent to the clivus prior to its exit through the pars nervosa and subsequent drainage into the internal jugular vein beneath the foramen.
The glossopharyngeal nerve yields a tympanic branch (Jacobson nerve) which reaches and supplies the middle ear along with the inferior tympanic artery via the inferior tympanic canaliculus which is occasionally seen at CT in cross-section at the level of the caroticojugular spine.
Pars vascularis
The pars vascularis is the posterolateral portion of the jugular foramen and is larger than the smaller anteromedial portion termed the pars nervosa. It contains:
- jugular bulb: a venous expansion sitting in the jugular fossa, between the endocranial sigmoid sinus and the exocranial jugular vein
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
The vagus nerve yields an auricular branch (Arnold nerve) via the mastoid canaliculus on the lateral wall of the foramen adjacent to the mastoid segment of the facial nerve.
Divisions: 3-part classification
In this system, the foramen is divided into 3 parts, 2 venous and 1 neural 3,4:
- petrosal part: anteromedial, passes the inferior petrosal sinus
- intrajugular part: between the venous compartments and around the intrajugular processes, passes the glossopharyngeal nerve (anterolateral) and vagus and accessory nerve complex (posteromedial)
- sigmoid part: posterolateral, passes the sigmoid sinus
Radiographic features
The size of the normal jugular foramen is remarkably variable and asymmetrical. However, the normal foramen will always be well-corticated. Therefore, the bony margin (and not the size) of the foramen should guide diagnostic evaluation.
CT
CT appearance of the foramen depends upon the level and angulation of the scan. The foramen has been described as having the shape of a sitting duck on the highest axial cuts.





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.